 W
WAirpower or air power consists of the application of military aviation, military strategy and strategic theory to the realm of aerial warfare and close air support. Airpower began in the advent of powered flight early in the 20th century. Airpower represents a "complex operating environment that has been subjected to considerable debate". British doctrine defines airpower as "the ability to project power from the air and space to influence the behaviour of people or the course of events." The Australian Experience of Air Power defines Airpower as being composed of Control of the Air, Strike, Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance, and Air Mobility roles.
 W
WAn armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the Latin arma, meaning "arms" and -stitium, meaning "a stopping".
 W
WOperation Bagration was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Belorussian Strategic Offensive Operation a military campaign fought between 23 June and 19 August 1944 in Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front of World War II. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of 34 divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. It was the biggest defeat in German military history and the fifth deadliest campaign in Europe, killing around 450,000 soldiers, while 300,000 others were cut off in Courland Pocket.
 W
WThe Baltic Project was a plan promoted by the Admiral Lord Fisher to procure a speedy victory during the First World War over Germany. It involved landing a substantial force, either British or Russian soldiers, on the flat beaches of Pomerania on the North German coast, less than 100 mi (160 km) from Berlin.
 W
WFrom the late 16th century into the 18th century battalia, was a description used both for the positioning of units in an army on a battle field and the formation in which individual units deployed for battle. Sometimes it was used to describe the main body of an army deploy for battle but excluding the wings and other units such as those deployed in front of the main line in skirmishing formation etc. Battalia differs from battalion which is generally the smallest military unit capable of independent operations and would have formed up in its battalia when going into battle.
 W
WThe Latin phrase bellum se ipsum alet or bellum se ipsum alit, and its German rendering Der Krieg ernährt den Krieg describe the military strategy of feeding and funding armies primarily with the resources of occupied territories. It is closely associated with mass starvation in the population of these territories. The phrase, coined by Ancient Roman statesman Cato the Elder, is primarily associated with the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648).
 W
WBlitzkrieg is a method of warfare where the attacker spearheads an offence using a rapid overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armoured and motorised or mechanised infantry formations with close air support, with the intent to break through the opponent's line of defence by short, fast, and powerful attacks and then dislocates the defenders, using speed and surprise to encircle them with the help of air superiority. Through the employment of combined arms in manoeuvre warfare, blitzkrieg attempts to unbalance the enemy by making it difficult for it to respond to the continuously changing front, then defeat it in a decisive Vernichtungsschlacht.
 W
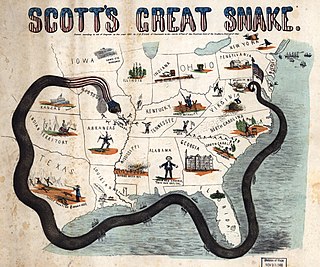
WA blockade is an effort to cut off supplies, war material or communications from a particular area by force, either in part or totally. A blockade is not an embargo or sanctions, which are legal barriers to trade. It is also distinct from a siege in that a blockade is usually directed at an entire country or region, rather than a fortress or city. While most blockades historically took place at sea, blockade is still used on land to prevent someone entering a place.
 W
WA border outpost, border out post, border observation post or BOP is an outpost maintained by a sovereign state on its border, usually one of a series placed at regular intervals, to watch over and safeguard its border with a neighboring state with which it may or may not have friendly relations. Such posts are manned by border guards and are at all times connected by radio communication with ongoing border patrols in their region and the force headquarters in the interior of the country for their day-to-day functioning, passing on intelligence and for requesting supplies and any needed reinforcements in emergencies.
 W
WA breakout is a military operation to end a situation of investment by offensive operations that achieve a breakthrough. It is used in contexts such as this: "The British breakout attempt from Normandy". It is one of four possible outcomes of investment, the others being relief, surrender, or reduction.
 W
WA ceasefire, also spelled cease fire, is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Historically, the concept existed at least by the time of the Middle Ages, when it was known as a 'truce of God'. Ceasefires can be declared as a humanitarian gesture, be preliminary, i.e., prior to a political agreement, or definitive, i.e., with the intention of resolving a conflict. Ceasefires may be declared as part of a formal treaty, but they have also been called as part of an informal understanding between opposing forces.
 W
WA citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city" and thus means "little city", so called because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core. Ancient Sparta had a citadel, as did many other Greek cities and towns.
 W
WA counter-offensive is a large-scale military strategic offensive operation, usually by forces that had successfully halted the enemy's offensive, while occupying defensive positions.
 W
WThe cult of the offensive refers to a strategic military dilemma in which leaders believe that offensive advantages are so great that a defending force would have no hope of repelling the attack and therefore choose to attack. It is most often used to explain the causes of World War I and the subsequent heavy losses that occurred year after year, on all sides, during the fighting on the Western Front.
 W
WDefensively equipped merchant ship (DEMS) was an Admiralty Trade Division programme established in June 1939, to arm 5,500 British merchant ships with an adequate defence against enemy submarines and aircraft. The acronym DEMS was used to describe the ships carrying the guns, the guns aboard the ships, the military personnel manning the guns, and the shore establishment supporting the system.
 W
WDeterrence theory is the idea that an inferior force, by virtue of the destructive power of the force's weapons, could deter a more powerful adversary, provided that this force could be protected against destruction by a surprise attack. This doctrine gained increased prominence as a military strategy during the Cold War with regard to the use of nuclear weapons and is related to, but distinct from, the concept of Mutual assured destruction, which models the preventative nature of full-scale nuclear attack that would devastate both parties in a nuclear war. Deterrence is a strategy intended to dissuade an adversary from taking an action not yet started by means of threat of reprisal, or to prevent them from doing something that another state desires. The strategy is based on the psychological concept of the same name. A credible nuclear deterrent, Bernard Brodie wrote in 1959, must be always at the ready, yet never used.
 W
WThe Empty Fort Strategy is the 32nd of the Chinese Thirty-Six Stratagems. The strategy involves using reverse psychology to deceive the enemy into thinking that an empty location is full of traps and ambushes, and therefore induce the enemy to retreat. Some examples are listed in the following sections.
 W
WEncirclement is a military term for the situation when a force or target is isolated and surrounded by enemy forces.
 W
WFirepower is the military capability to direct force at an enemy. Firepower involves the whole range of potential weapons. The concept is generally taught as one of the three key principles of modern warfare wherein the enemy forces are destroyed or have their will to fight negated by sufficient and preferably overwhelming use of force as a result of combat operations.
 W
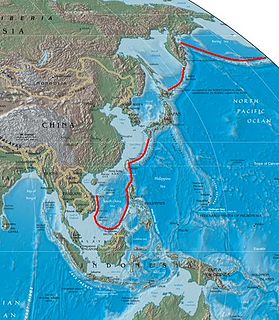
WThe first island chain refers to the first chain of major archipelagos out from the East Asian continental mainland coast. Principally composed of the Kuril Islands, Japanese Archipelago, Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan (Formosa), the northern Philippines, and Borneo; from the Kamchatka Peninsula to the Malay Peninsula. Some definitions of the first island chain anchor the northern end on the Russian Far East coast north of Sakhalin Island, with Sakhalin Island being the first link in the chain. However, others consider the Aleutians as the farthest north-eastern first link in the chain. The first island chain forms one of three island chain doctrines within the Island Chain Strategy.
 W
WIn military tactics, a flanking maneuver, or flanking manoeuvre is a movement of an armed force around an enemy force's side/flank to achieve an advantageous position over it. Flanking is useful because a force's fighting strength is typically concentrated in its front, therefore to circumvent an opposing force's front and attack its flank is to concentrate one's own offense in the area where the enemy is least able to concentrate defense.
 W
WThe flexible defense is a military theory about the design of modern fortifications. The examples of "flexible" defense-lines are not based on dense lines of heavily armed, large and expensive concrete fortifications as the systems such as the Maginot Line were. Their protective capacity hinges on multiple lines of obstacles and small shelters fitting into the environment. They are "flexible" because soldiers are not locked in pillboxes, but fight instead in easily replaceable open earth-wood maden positions, while bunkers serve only as shelters during bombardments. As a result, they are able to adapt to the opponent's movements, and there are no easily targeted large buildings in these lines.
 W
WA fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere.
 W
WInvestment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced.
 W
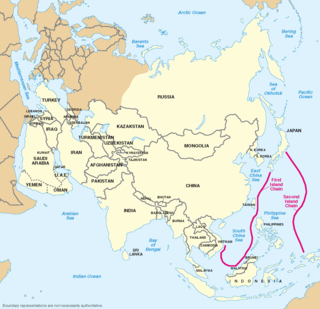
WThe Island Chain Strategy is a strategy first mentioned by American foreign policy commentator John Foster Dulles in 1951 during the Korean War. It suggests surrounding the Soviet Union and China by sea. The island chain concept did not become a major theme in American policy, but it has become a major fixation of both American and Chinese analysts to this day. For the U.S. the island chain strategy is a big part of the military of the United States's force projection in the Eastern part of Asia. For Chinese, the concept is used as part of their fears of encirclement by American forces. For both sides, the island chain strategy emphasizes the geographical and strategic importance of Taiwan.
 W
WLeapfrogging, also known as island hopping, was a military strategy employed by the Allies in the Pacific War against the Empire of Japan and the Axis powers during World War II.
 W
WA line of communication is the route that connects an operating military unit with its supply base. Supplies and reinforcements are transported along the line of communication. Therefore, a secure and open line of communication is vital for any military force to continue to operate effectively. Prior to the advent of the use of telegraph and radio in warfare, lines of communication were also the routes used by despatch riders on horseback and runners to convey and deliver orders and battle updates to and from unit commanders and headquarters. Thus, a unit whose lines of communication were compromised was vulnerable to becoming isolated and defeated, as the means for requesting reinforcements and resupply is lost. The standard military abbreviation is LOC, or SLOC for Sea line of communication or ALOC for air line of communication.
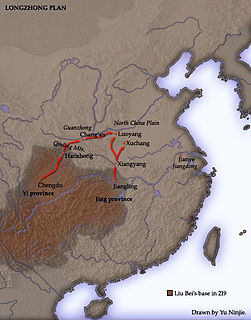 W
WThe Longzhong Plan is the name given to a strategic plan by Zhuge Liang, a statesman and regent of the Shu Han state in the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of China. Zhuge Liang presented the plan to Liu Bei, a warlord who became the founding emperor of the Shu Han state, sometime in 207 towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty when Liu Bei visited him at his residence in Longzhong (隆中), an area in the west of present-day Xiangyang, Hubei.
 W
WA main supply route (MSR) is the route or routes designated within an area of operations upon which the bulk of traffic flows in support of military operations and humanitarian operations. MSR is a term that is also used in insurgency and irregular war scenarios.
 W
WThe Manstein Plan is one of the names used to describe the war plan of the German Army during the Battle of France in 1940. The original invasion plan was an awkward compromise devised by General Franz Halder, the chief of Oberkommando des Heeres staff that satisfied no one. Documents with details of the plan fell into Belgian hands during the Mechelen incident of 10 January 1940 and the plan was revised several times, each giving more emphasis to an attack by Army Group A through the Ardennes, which progressively reduced the offensive by Army Group B through the Low Countries to a diversion.
 W
WMilitarism is the belief or the desire of a government or a people that a state should maintain a strong military capability and to use it aggressively to expand national interests and/or values. It may also imply the glorification of the military and of the ideals of a professional military class and the "predominance of the armed forces in the administration or policy of the state".
 W
WNATO Joint Military Symbology is the NATO standard for military map marking symbols. Originally published in 1986 as Allied Procedural Publication 6 (APP-6), NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems, the standard has evolved over the years and is currently in its fifth version (APP-6D). The symbols are designed to enhance NATO's joint interoperability by providing a standard set of common symbols. APP-6 constituted a single system of joint military symbology for land, air, space and sea-based formations and units, which can be displayed for either automated map display systems or for manual map marking. It covers all of the joint services and can be used by them.
 W
WThe concept of networked swarming warfare was first proposed by HUO Dajun in 2003. The key feature of the information age is the networking of organizational structure. The rising networked organization will overcome the limitation of traditional geography and link the operational resources distributed widely to form a military action network which combine strike range, speed and lethality, three elements of originally different developing, fundamentally transforming our idea of battle space. With the trend of decentralization of forces, we need to develop more small units with independent combat functions; meanwhile we can join these small units into a whole network as the technology's development. The warfare based on this network is called networked swarming warfare.
 W
WAn observation post, temporary or fixed, is a position from which soldiers can watch enemy movements, to warn of approaching soldiers, or to direct artillery fire. In strict military terminology, an observation post is any preselected position from which observations are to be made - this may include very temporary installations such as a vehicle parked as a roadside checkpoint, or even an airborne aircraft.
 W
WAn offset is some means of asymmetrically compensating for a disadvantage, particularly in a military competition. Rather than match an opponent in an unfavorable competition, changing the competition to more favorable footing enables the application of strengths to a problem that is otherwise either unwinnable or winnable only at unacceptable cost. An offset strategy consequently seeks to deliberately change an unattractive competition to one more advantageous for the implementer. In this way, an offset strategy is a type of competitive strategy that seeks to maintain advantage over potential adversaries over long periods of time while preserving peace where possible.
 W
WIn the field of military theory, the operational level of war represents the level of command that connects the details of tactics with the goals of strategy.
 W
WA military outpost is detachment of troops stationed at a distance from the main force or formation, usually at a station in a remote or sparsely populated location, positioned to stand guard against unauthorized intrusions and surprise attacks; and the station occupied by such troops, usually a small military base or settlement in an outlying frontier, limit, political boundary or in another country. Outposts can also be called miniature military bases based on size and number of troops it houses.
 W
WA primary measure of a nation's power projection is its over-the-beach capability. This consists of the number of soldiers, tanks, vehicles, and helicopters that a nation can stage over an adversary's defended coast in a time of war. Generally, these elements only count if they can be projected across hundreds of kilometers of open ocean. Over-the-beach capability determines a nation's power projection together with forward airpower, alliances, and nuclear options.
 W
WThe pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanks (sides) of an enemy formation.
 W
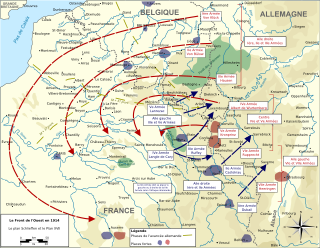
WPlan XVII was the name of a "scheme of mobilization and concentration" that was adopted by the French Conseil Supérieur de la Guerre (the peacetime title of the French Grand Quartier Général from 1912 to 1914, to be put into effect by the French Army in the event of war between France and Germany. Though it was not "a prescribed narrative for the campaign" or battle plan, the deployment made possible a prompt invasion of Germany and/or Belgium before Germany could mobilise its reserves, simultaneous to a Russian invasion of East Prussia.
 W
WPower projection is a term used in military and political science to refer to the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory.
 W
WIn nuclear strategy, a first strike is a preemptive surprise attack employing overwhelming force. First strike capability is a country's ability to defeat another nuclear power by destroying its arsenal to the point where the attacking country can survive the weakened retaliation while the opposing side is left unable to continue war. The preferred methodology is to attack the opponent's strategic nuclear weapon facilities, command and control sites, and storage depots first. The strategy is called counterforce.
 W
WA Pyrrhic victory is a victory that inflicts such a devastating toll on the victor that it is tantamount to defeat. Winning a Pyrrhic victory takes a heavy toll that negates any true sense of achievement or damages long-term progress.
 W
WA rout is a panicked, disorderly and undisciplined retreat of troops from a battlefield, following a collapse in a given unit's command authority, unit cohesion and combat morale.
 W
WThe Schlieffen Plan was a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on 4 August 1914. Schlieffen was Chief of the General Staff of the German Army from 1891 to 1906. In 1905 and 1906, Schlieffen devised an army deployment plan for a war-winning offensive against the French Third Republic. German forces were to invade France through the Netherlands and Belgium rather than across the common border. After losing the First World War, German official historians of the Reichsarchiv and other writers described the plan as a blueprint for victory. Generaloberst (Colonel-General) Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, succeeded Schlieffen as Chief of the German General Staff in 1906 and was dismissed after the First Battle of the Marne. German historians claimed that Moltke had ruined the plan by meddling with it out of timidity.
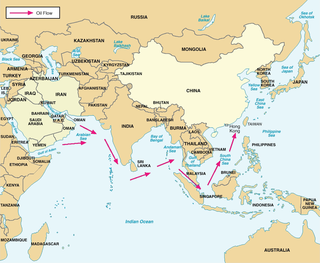 W
WSea lines of communication is a term describing the primary maritime routes between ports, used for trade, logistics and naval forces. It is generally used in reference to naval operations to ensure that SLOCs are open, or in times of war, to close them.
 W
WSealift is a term used predominantly in military logistics and refers to the use of cargo ships for the deployment of military assets, such as weaponry, vehicles, military personnel, and supplies. It complements other means of transport, such as strategic airlifters, in order to enhance a state's ability to project power.
 W
WSi vis pacem, para bellum is a Latin adage translated as "If you want peace, prepare for war".
 W
WA siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from Latin: sedere, lit. 'to sit'. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is not uncommon, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics.
 W
WThe Singapore strategy was a naval defence policy of the British Empire that evolved in a series of war plans from 1919 to 1941. It aimed to deter aggression by the Empire of Japan by providing for a base for a fleet of the Royal Navy in the Far East, able to intercept and defeat a Japanese force heading south towards India or Australia. To be effective it required a well-equipped base; Singapore, at the eastern end of the Strait of Malacca, was chosen in 1919 as the location of this base; work continued on this naval base and its defences over the next two decades.
 W
WStrategic bombing is a military strategy used in total war with the goal of defeating the enemy by destroying its morale, its economic ability to produce and transport materiel to the theatres of military operations, or both. It is a systematically organized and executed attack from the air which can utilize strategic bombers, long- or medium-range missiles, or nuclear-armed fighter-bomber aircraft to attack targets deemed vital to the enemy's war-making capability.
 W
WA strategic railway is a railway proposed or constructed primarily for military strategic purposes, as opposed to the usual purpose of a railway, which is the transport of civilian passengers or freight. Although the archetypal strategic railway would be one constructed solely as part of a military strategy, such a railway has only ever existed in theory. Thus, a strategic railway is, in practice, one for which any intended or contemplated civilian purpose is subordinate to the military strategic purpose.
 W
WSurrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully, without fighting, or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sovereign state may surrender following defeat in a war, usually by signing a peace treaty or capitulation agreement. A battlefield surrender, either by individuals or when ordered by officers, normally results in those surrendering becoming prisoners of war.
 W
WOne tercio was a military unit of the Spanish Army during the time of the House of Austria. The Tercios were famous for their resistance on the battlefield, forming the elite of the military units available to the kings of the Hispanic Monarchy of the time. The thirds were the essential piece of the terrestrial hegemony, and sometimes also maritime of the Spanish Empire. The Tercio is considered the rebirth of the infantry on the battlefield, comparable to the Roman legions or the Macedonian phalanxes.
 W
WTrench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied fighting lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front starting in September 1914.
 W
WAccording to military terminology, a two-front war occurs, when opposing forces encounter on two geographically separate fronts. The forces of two or more allied parties usually simultaneously engage an opponent in order to increase their chances of success. The opponent consequently encounters severe logistic difficulties as he is forced to divide and disperse his troops, defend an extended front line and is at least partly cut off from access to trade and exterior resources. However, by virtue of the central position he might possess the advantages of the interior lines.
 W
WUnrestricted submarine warfare is a type of naval warfare in which submarines sink vessels such as freighters and tankers without warning, as opposed to attacks per prize rules. Prize rules call for submarines to surface and search merchantmen and place crews in "a place of safety" before sinking them, unless the ship showed "persistent refusal to stop ... or active resistance to visit or search".
 W
WAn unsinkable aircraft carrier is a term sometimes used to refer to a geographical or political island that is used to extend the power projection of a military force. Because such an entity is capable of acting as an airbase and is a physical landmass not easily destroyed, it is, in effect, an immobile aircraft carrier that cannot be sunk.
 W
WVictory disease occurs in military history when complacency or arrogance, brought on by a victory or a series of victories, makes an engagement end disastrously for a commander and his forces.
 W
WA tactical withdrawal or retreating defensive action is a type of military operation, generally meaning that retreating forces draw back while maintaining contact with the enemy. A withdrawal may be undertaken as part of a general retreat, to consolidate forces, to occupy ground that is more easily defended, force the enemy to overextend to secure a decisive victory, or to lead the enemy into an ambush. It is considered a relatively risky operation, requiring discipline to keep from turning into a disorganized rout or at the very least doing severe damage to the military's morale.