 W
WIn mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponentiation of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x2 − 4x + 7. An example in three variables is x3 + 2xyz2 − yz + 1.
 W
WIn mathematics, a constant function is a function whose (output) value is the same for every input value. For example, the function y(x) = 4 is a constant function because the value of y(x) is 4 regardless of the input value x.
 W
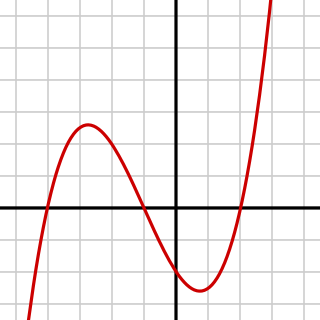
WIn mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form
 W
WIn calculus and related areas of mathematics, a linear function from the real numbers to the real numbers is a function whose graph is a line in the plane. The characteristic property of linear functions is that when the input variable is changed, the change in the output is proportional to the change in the input.
 W
WIn algebra, a quadratic function, a quadratic polynomial, a polynomial of degree 2, or simply a quadratic, is a polynomial function with one or more variables in which the highest-degree term is of the second degree.
 W
WIn algebra, a quartic function is a function of the form
 W
WIn algebra, a quintic function is a function of the form
 W
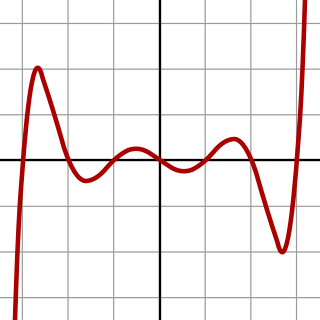
WIn algebra, a septic equation is an equation of the form
 W
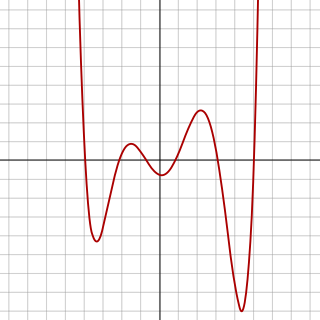
WIn algebra, a sextic polynomial is a polynomial of degree six. A sextic equation is a polynomial equation of degree six—that is, an equation whose left hand side is a sextic polynomial and whose right hand side is zero. More precisely, it has the form: