 W
WInternet security is a branch of computer security. It encompasses the Internet, browser security, web site security, and network security as it applies to other applications or operating systems as a whole. Its objective is to establish rules and measures to use against attacks over the Internet. The Internet is an inherently insecure channel for information exchange, with high risk of intrusion or fraud, such as phishing, online viruses, trojans, ransomware and worms.
 W
WClickjacking is a malicious technique of tricking a user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives, thus potentially revealing confidential information or allowing others to take control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous objects, including web pages.
 W
WCross-site cooking is a type of browser exploit which allows a site attacker to set a cookie for a browser into the cookie domain of another site server.
 W
WCross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the same-origin policy. Cross-site scripting carried out on websites accounted for roughly 84% of all security vulnerabilities documented by Symantec up until 2007. XSS effects vary in range from petty nuisance to significant security risk, depending on the sensitivity of the data handled by the vulnerable site and the nature of any security mitigation implemented by the site's owner network.
 W
WAn evil twin is a fraudulent Wi-Fi access point that appears to be legitimate but is set up to eavesdrop on wireless communications. The evil twin is the wireless LAN equivalent of the phishing scam.
 W
WTrojan:Win32/FakeSysdef, originally dispersed as an application called "HDD Defragmenter" hence the name "FakeSysdef" or "Fake System Defragmenter", is a Trojan targeting the Microsoft Windows operating system that was first documented in late 2010.
 W
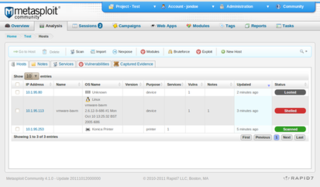
WThe Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company Rapid7.
 W
WNikto is a free software command-line vulnerability scanner that scans webservers for dangerous files/CGIs, outdated server software and other problems. It performs generic and server type specific checks. It also captures and prints any cookies received. The Nikto code itself is free software, but the data files it uses to drive the program are not. Version 1.00 was released December 27, 2001.
 W
WReflected DOM Injection (RDI) is an evasive XSS technique which uses a third party website to construct and execute an attack. This technique can be implemented on websites that use a user-provided URL as part of their service
 W
WIn computing, a Trojan horse is any malware that misleads users of its true intent. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek story of the deceptive Trojan Horse that led to the fall of the city of Troy.
 W
WIn computer security, a vulnerability is a weakness which can be exploited by a threat actor, such as an attacker, to cross privilege boundaries within a computer system. To exploit a vulnerability, an attacker must have at least one applicable tool or technique that can connect to a system weakness. In this frame, vulnerabilities are also known as the attack surface.
 W
WA web shell is a shell-like interface that enables a web server to be remotely accessed, often for the purposes of cyberattacks. A web shell is unique in that a web browser is used to interact with it.