 W
WThe Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service of the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax law. It is part of the Department of the Treasury and led by the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, who is appointed to a five-year term by the President of the United States. The duties of the IRS include providing tax assistance to taxpayers; pursuing and resolving instances of erroneous or fraudulent tax filings; and overseeing various benefits programs, including the Affordable Care Act.
 W
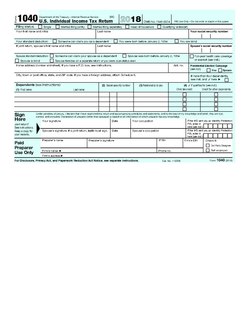
WForm 1040 is an IRS tax form used for personal federal income tax returns filed by United States residents. The form calculates the total taxable income of the taxpayer and determines how much is to be paid or refunded by the government.
 W
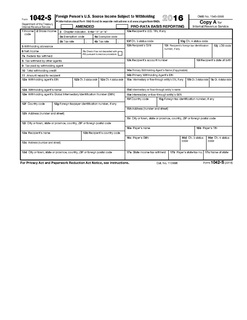
WForms 1042, 1042-S and 1042-T are United States Internal Revenue Service tax forms dealing with payments to foreign persons, including non-resident aliens, foreign partnerships, foreign corporations, foreign estates, and foreign trusts.
 W
WForm 1098-T, Tuition Statement, is an American IRS tax form filed by eligible education institutions to report payments received and payments due from the paying student. The institution has to report a form for every student that is currently enrolled and paying qualifying tuition and related expenses.
 W
WIn the United States, Form 1099-K "Payment Card and Third Party Network Transactions" is a variant of Form 1099 used to report payments received through reportable payment card transactions and/or settlement of third-party payment network transactions. Form 1099-K is sent out to payees by a payment settlement entity if there are more than 200 such transactions and the gross payments exceed $20,000. This threshold will be reduced in 2022 to $600 with no minimum number of transactions. Reportable payment card transactions do not include ATM withdrawals or checks issued in connection with a payment card.
 W
WIn the United States, Form 1099-R is a variant of Form 1099 used for reporting on distributions from pensions, annuities, retirement or profit sharing plans, IRAs, charitable gift annuities and Insurance Contracts. Form 1099-R is filed for each person who has received a distribution of $10 or more from any of the above.
 W
WThe Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a United States federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 amendment, it represents the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the enactment of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965.
 W
WThe 2010 Austin suicide attack occurred on Thursday, February 18, 2010, when Andrew Joseph Stack III deliberately crashed his single-engine Piper Dakota light aircraft into Building I of the Echelon office complex in Austin, Texas, United States, killing himself and Internal Revenue Service (IRS) manager Vernon Hunter. Thirteen others were injured, two severely. The four-story office building housed an IRS field office occupying the top three floors, along with a couple of private businesses on the first floor. Prior to the crash, Stack had posted a suicide note to his website, expressing his disillusionment with corporations and government agencies such as the IRS. Stack is also suspected of having set fire that morning to his two-story North Austin house, which was mostly destroyed.
 W
WThe Internal Revenue Service Building is a federal building which serves as the headquarters of the Internal Revenue Service. It is located at 1111 Constitution Avenue, Northwest, Washington, D.C., in the Federal Triangle.
 W
WConfessions of a Tax Collector is a non-fiction memoir by author and former Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax collector Richard Yancey. Published in 2004 by HarperCollins, the book is a memoir of the author's twelve years employed by the IRS. It received a positive review from Publishers Weekly, and The Wall Street Journal called it "one of the top five books ever written about taxes."
 W
WInternal Revenue Service, Criminal Investigation (IRS-CI) is the United States federal law enforcement agency responsible for investigating potential criminal violations of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code and related financial crimes, such as money laundering, currency violations, tax-related identity theft fraud, and terrorist financing that adversely affect tax administration. While other federal agencies also have investigative jurisdiction for money laundering and some Bank Secrecy Act violations, IRS-CI is the only federal agency that can investigate potential criminal violations of the Internal Revenue Code, in a manner intended to foster confidence in the tax system and deter violations of tax law. Criminal Investigation is a division of the Internal Revenue Service, which in turn is a bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury.
 W
WThe Independent Office of Appeals ("Appeals") is an independent organization within the U.S. Internal Revenue Service that helps taxpayers resolve their tax disputes through an informal, administrative process. Its mission is to resolve tax controversies fairly and impartially, without litigation.
 W
WThe Internal Revenue Service Restructuring and Reform Act of 1998, also known as Taxpayer Bill of Rights III,, resulted from hearings held by the United States Congress in 1996 and 1997. The Act included numerous amendments to the Internal Revenue Code of 1986.
 W
WIR$ is a Franco-Belgian comics series written by Stephen Desberg, illustrated by Bernard Vrancken and published by Le Lombard in French and Cinebook in English.
 W
WIn 2013, the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) revealed that it had selected political groups applying for tax-exempt status for intensive scrutiny based on their names or political themes. This led to wide condemnation of the agency and triggered several investigations, including a Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) criminal probe ordered by United States Attorney General Eric Holder. Conservatives claimed that they were specifically targeted by the IRS, but an exhaustive report released by the Treasury Department's Inspector General in 2017 found that from 2004 to 2013, the IRS used both conservative and liberal keywords to choose targets for further scrutiny.
 W
WThis is a partial list of allegations of misuse of the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS), which traces its roots to the creation of the Commissioner of Internal Revenue in 1862. Examples of political profiling controversies include cases in which IRS employees or government officials have allegedly used IRS resources to target individuals and groups for espousing or expressing particular political beliefs.
 W
WThe Office of Professional Responsibility (OPR) at the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is responsible for all matters related to "tax practitioner" misconduct, discipline and practice before the IRS under 31 CFR Subtitle A, Part 10. A tax practitioner, sometimes referred to as a tax professional, is generally an attorney, CPA or enrolled agent.
 W
WThe Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service of the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax law. It is part of the Department of the Treasury and led by the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, who is appointed to a five-year term by the President of the United States. The duties of the IRS include providing tax assistance to taxpayers; pursuing and resolving instances of erroneous or fraudulent tax filings; and overseeing various benefits programs, including the Affordable Care Act.
 W
WThe Office of the Taxpayer Advocate, also called the Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS), is an office within the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) of the U.S. Department of the Treasury, reporting directly to the Commissioner of Internal Revenue. The office is under the supervision and direction of the National Taxpayer Advocate who is appointed by the Secretary of Treasury. The office was created under the Taxpayer Bill of Rights 2, an act of the United States Congress which became law on July 30, 1996. The office replaced the previous Office of the Ombudsman within the IRS.
 W
WThe Taxpayer First Act is a law that makes significant reforms to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
 W
WThe Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration (TIGTA) is an office in the United States Federal government. It was established in January 1999 in accordance with the Internal Revenue Service Restructuring and Reform Act of 1998 to provide independent oversight of Internal Revenue Service (IRS) activities. As mandated by RRA 98, TIGTA assumed most of the responsibilities of the IRS' former Inspection Service.
 W
WForm W-2 is an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax form used in the United States to report wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from them. Employers must complete a Form W-2 for each employee to whom they pay a salary, wage, or other compensation as part of the employment relationship. An employer must mail out the Form W-2 to employees on or before January 31. This deadline gives these taxpayers about 2 months to prepare their returns before the April 15 income tax due date. The form is also used to report FICA taxes to the Social Security Administration. The Form W-2, along with Form W-3, generally must be filed by the employer with the Social Security Administration by the end of February. Relevant amounts on Form W-2 are reported by the Social Security Administration to the Internal Revenue Service. In territories, the W-2 is issued with a two letter code indicating which territory, such as W-2GU for Guam. If corrections are made, it can be done on a W-2c.
 W
WForm W-4 is an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) tax form completed by an employee in the United States to indicate his or her tax situation to the employer. The W-4 form tells the employer the correct amount of federal tax to withhold from an employee's paycheck.
 W
WForm W-9 is used in the United States income tax system by a third party who must file an information return with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It requests the name, address, and taxpayer identification information of a taxpayer.