 W
WThe music industry consists of the individuals and organizations that earn money by writing songs and musical compositions, creating and selling recorded music and sheet music, presenting concerts, as well as the organizations that aid, train, represent and supply music creators. Among the many individuals and organizations that operate in the industry are: the songwriters and composers who write songs and musical compositions; the singers, musicians, conductors, and bandleaders who perform the music; the record labels, music publishers, recording studios, music producers, audio engineers, retail and digital music stores, and performance rights organizations who create and sell recorded music and sheet music; and the booking agents, promoters, music venues, road crew, and audio engineers who help organize and sell concerts.
 W
WThe A-side and B-side are the two sides of phonograph records and cassettes; these terms have often been printed on the labels of two-sided music recordings. The A-side usually features a recording that its artist, producer, or record company intends to be the initial focus of promotional efforts and radio airplay and hopefully become a hit record. The B-side is a secondary recording that typically receives less attention, although some B-sides have been as successful as, or more so than, their A-sides.
 W
WThe album-equivalent unit is a measurement unit in music industry to define the consumption of music that equals the purchase of one album copy. This consumption includes streaming and song downloads in addition to traditional album sales. The album-equivalent unit was introduced in the mid-2010s as an answer to the drop of album sales in the 21st century. Album sales more than halved from 1999 to 2009, declining from a $14.6 to $6.3 billion industry. For instance, the only albums that went platinum in the United States in 2014 were the Frozen soundtrack and Taylor Swift's 1989, whereas several artists' works had in 2013.
 W
WMastering, a form of audio post production, is the process of preparing and transferring recorded audio from a source containing the final mix to a data storage device, the source from which all copies will be produced. In recent years digital masters have become usual, although analog masters—such as audio tapes—are still being used by the manufacturing industry, particularly by a few engineers who specialize in analog mastering.
 W
WBig in Japan is an expression that can be used to describe Western musical groups who achieve success in Japan but not necessarily in other parts of the world. However, the expression is commonly used ironically to mean successful in a limited, potentially comical, oddly specific, or possibly unverifiable way.
 W
WA bootleg recording is an audio or video recording of a performance not officially released by the artist or under other legal authority. Making and distributing such recordings is known as bootlegging. Recordings may be copied and traded among fans without financial exchange, but some bootleggers have sold recordings for profit, sometimes by adding professional-quality sound engineering and packaging to the raw material. Bootlegs usually consist of unreleased studio recordings, live performances or interviews without the quality control of official releases.
 W
WIn popular music, a cover version, cover song, remake, revival, or simply cover, is a new performance or recording by a musician other than the original performer or composer of the song.
 W
WIn the recording industry, a cut-out refers to a deeply discounted or remaindered copy of an LP, 45 RPM single, cassette tape, compact disc, or other item.
 W
WFree music or libre music is music that, like free software, can freely be copied, distributed and modified for any purpose. Thus free music is either in the public domain or licensed under a free license by the artist or copyright holder themselves, often as a method of promotion. It does not mean that there should be no fee involved. The word free refers to freedom, not to price.
 W
WThe G.V. Series were a series of 10 inch 78 rpm Gramophone records produced in Europe and the United States from 1933 to 1958, and exported to colonial Tropical Africa. They are credited with introducing Afro-Cuban music into modern African popular culture. The resulting re-interpretations influenced the creation of several genres of African popular music.
 W
WThe Galleria del Corso is a major shopping arcade in the historic center of Milan, Italy, one of five built in the city in the interwar period (1919–39), along with the Galleria del Toro, Galleria Mazzini, Galleria Meravigli and the Galleria Gonzaga.
 W
WThe Global Recording Artist of the Year is an award presented by the International Federation of the Phonographic Industry (IFPI) to honor the best-performing recording artist based on a total of album-equivalent units, which include music downloads, streaming and physical format sales. It has been awarded every year since January 2014, with British boy band One Direction becoming the first act to receive the accolade for Global Recording Artist of 2013. This success was attributed to the band's third studio album, Midnight Memories, which became the best-selling album of the year with sales of 4 million copies worldwide. Taylor Swift was awarded the Global Recording Artist of 2014 after the commercial success of her fifth studio album, 1989. During the year, the album became the second global bestseller with sales of 6 million copies, and spawned two international number-one singles, "Shake It Off" and "Blank Space".
 W
WMusic publishing is the business of creating, producing and distributing printed musical scores, parts, and books in various types of music notation, while ensuring that the composer, songwriter and other creators receive credit and royalties or other payment. This article outlines the early history of the industry.
 W
WHow Music Works is a non-fiction book by David Byrne, a musician, composer, and writer best known for his work with the group Talking Heads. He discusses the form and influence of music in a non-linear narrative fashion, using a variety of experiences from his career to create something part autobiography and part music theory. The book was published through McSweeney's on September 12, 2012, and was named as one of Amazon.com's "Best Books of the Month" in that same month. It has received mainly positive reviews.
 W
WThe COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the music industry, mirroring its impacts across all arts sectors. Numerous music events, including music festivals, concert tours, and award shows, have been cancelled or postponed. While some musicians and composers were able to use the time to create new works, there were flow-on effects on the many supporting people who relied on performers for their income. Various album releases have been delayed as well. Pollstar estimated the total lost revenue for the live music industry in 2020 at more than $30 billion.
 W
WThe International Standard Music Number or ISMN is a thirteen-character alphanumeric identifier for printed music developed by ISO.
 W
WLANDR Audio is a cloud-based music creation platform developed by MixGenius, an artificial intelligence company based in Montreal, Quebec. Since launching with its flagship automated mastering service in 2014, LANDR has expanded its offerings to include distribution services, a music samples library, virtual studio technology (VSTs) and plug-ins, a service marketplace for musicians, and online video conferencing.
 W
WA lead sheet or fake sheet is a form of musical notation that specifies the essential elements of a popular song: the melody, lyrics and harmony. The melody is written in modern Western music notation, the lyric is written as text below the staff and the harmony is specified with chord symbols above the staff.
 W
WA music library contains music-related materials for patron use. Collections may also include non-print materials, such as digitized music scores or audio recordings. Use of such materials may be limited to specific patron groups, especially in private academic institutions. Music library print collections include dictionaries and encyclopedias, indexes and directories, printed music, music serials, bibliographies, and other music literature.
 W
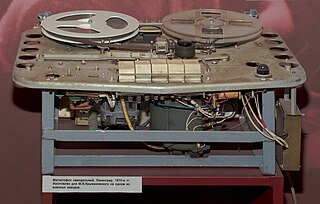
WMagnitizdat was the process of copying and distributing audio tape recordings that were not commercially available in the Soviet Union. It is analogous to samizdat, the method of disseminating written works that could not be officially published under Soviet political censorship. It is technically similar to bootleg recordings, except it has a political dimension not usually present in the latter term.
 W
WMusic recording certification is a system of certifying that a music recording has shipped, sold, or streamed a certain number of units. The threshold quantity varies by type and by nation or territory.
 W
WA music store or musical instrument store is a retail business that sells musical instruments and related equipment and accessories. Some music stores provide additional services for a fee, such as music lessons, instrument or equipment rental, or repair services.
 W
WThe Oahu Music Company was a music education program in the United States during the 1930s and 1940s to teach students to play the Hawaiian Guitar. Popular culture in America became fascinated with Hawaiian music during the first half of the twentieth century and in 1916, recordings of indigenous Hawaiian instruments outsold every other genre of music in the U.S. By 1920, sales of Hawaiian guitars and instruction had become well established and Oahu Music Company was the leading purveyor these programs. The organization canvassed nearly every city in the United States, often door-to-door, selling both their Oahu-brand instruments and lessons for young people to join their weekly classes.
 W
WA professional audio store is a retail business that sells, and in many cases rents, sound reinforcement system equipment and PA system components used in music concerts, live shows, dance parties and speaking events. This equipment typically includes microphones, power amplifiers, electronic effects units, speaker enclosures, monitor speakers, subwoofers and audio consoles (mixers). Some professional audio stores also sell sound recording equipment, DJ equipment, lighting equipment used in nightclubs and concerts and video equipment used in events, such as video projectors and screens. Some professional audio stores rent "backline" equipment used in rock and pop shows, such as stage pianos and bass amplifiers. While professional audio stores typically focus on selling new merchandise, some stores also sell used equipment, which is often the equipment that the company has previously rented out for shows and events.
 W
WA re-recording is a recording produced following a new performance of a work of music. This is most commonly, but not exclusively, by a popular artist or group. It differs from a reissue, which involves a second or subsequent release of a previously-recorded piece of music.
 W
WThe music industry consists of the individuals and organizations that earn money by writing songs and musical compositions, creating and selling recorded music and sheet music, presenting concerts, as well as the organizations that aid, train, represent and supply music creators. Among the many individuals and organizations that operate in the industry are: the songwriters and composers who write songs and musical compositions; the singers, musicians, conductors, and bandleaders who perform the music; the record labels, music publishers, recording studios, music producers, audio engineers, retail and digital music stores, and performance rights organizations who create and sell recorded music and sheet music; and the booking agents, promoters, music venues, road crew, and audio engineers who help organize and sell concerts.
 W
WRecord sales or music sales are activities related to selling music recordings through record shops or online music store. Record sales reached the peak in 1999, when 600 million people spent an average of $64 in buying records, bringing a total of $40 billion sales of recorded music. Sales continued declining in the 21st century. The collapse of record sales also made artists rely on touring for most of their income. By 2019, record sales had accounted for less than half of global recorded music revenue, overtaken by streaming. Following the inclusion of streaming into record charts in the mid-2010s, record sales are also referred to as traditional sales or pure sales.
 W
WSound Credit is a music credits platform with computer software applications for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. It includes the Sound Credit Publisher cross-platform desktop application, the Tracker cross-platform digital audio workstation (DAW) plug-in, physical kiosks, smart card check-in system, and online database.
 W
WSout El-Hob Records is an Egyptian record label founded in 1972 by Atef Montasser and owned by Dozzan Music Group. Sout El-Hob has the 4th largest Arabic music catalog in the Middle East & North Africa. It has also distributed many movies domestically and abroad under the name of “Sout El-Hob Movies." Mohsen also worked with Atef as a distributor before he set up his own company.
 W
WThe vinyl revival is the renewed interest and increased sales of vinyl records, or gramophone records, that has been taking place in the music industry. Since 2007, vinyl records have enjoyed renewed popularity in the West and in East Asia.
 W
WA white label record is a vinyl record with white labels attached. There are several variations each with a different purpose. Variations include test pressings, white label promos, and plain white labels.