 W
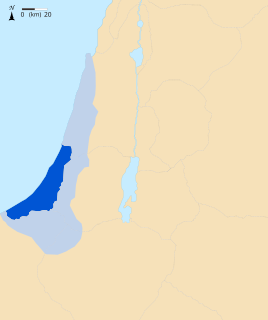
WPhilistia was a confederation of cities in the Southwest Levant. Its appearance follows the invasion of Egypt by the foreign sea People, of which Philistines or Peleset are part, and their alleged relocation to the southern abandoned coast of Canaan by Ramesses III following his victory over them. Philistia northern boundary was the Yarkon River with the Mediterranean Sea on the west, the Kingdom of Judah to the east and the Wadi El-Arish to the south. Philistia consisted of the Five Lords of the Philistines, described in the Book of Joshua and the Books of Samuel, comprising Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, Gath, and Gaza, in the south-western Levant.
 W
WThe Philistines were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their state, after having already been subjugated for centuries by Assyria, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylonia, and after becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called Peleset ; the parallel Assyrian term is Palastu, Pilišti, or Pilistu.
 W
WAbimelech was the name of multiple Philistine kings mentioned in the Hebrew Bible.
 W
WAl-Muzayri'a was a Palestinian village in the Ramle Subdistrict. It was depopulated in 1948. In 1998 the new Israeli city of El'ad was built over the ruins.
 W
WDeir al-Balah or Deir al Balah is a Palestinian city in the central Gaza Strip and the administrative capital of the Deir el-Balah Governorate. It is located over 14 kilometers (8.7 mi) south of Gaza City. The city had a population of 54,439 in 2007. The city is known for its date palms, after which it is named.
 W
WDelilah is a woman mentioned in the sixteenth chapter of the Book of Judges in the Hebrew Bible. She is loved by Samson, a Nazirite who possesses great strength and serves as the final Judge of Israel. Delilah is bribed by the lords of the Philistines to discover the source of his strength. After three failed attempts at doing so, she finally goads Samson into telling her that his vigor is derived from his hair. As he sleeps, Delilah orders a servant to cut Samson's hair, thereby enabling her to turn him over to the Philistines.
 W
WThe Ekron Royal Dedicatory Inscription, or simply the Ekron inscription, is a royal dedication inscription found in its primary context in the ruins of a temple during the 1996 excavations of Ekron. It is known as KAI 286.
 W
WGoliath is described in the biblical Book of Samuel as a Philistine giant defeated by the young David in single combat. The story signified Saul's unfitness to rule, as Saul himself should have fought for Israel. Scholars today believe that the original listed killer of Goliath was Elhanan, son of Jair, and that the authors of the Deuteronomic history changed the original text to credit the victory to the more famous character, David.
 W
WJimzu, also known as Gimzo, was a Palestinian village, located three miles southeast of Lydda. Under the 1947 UN Partition Plan of Mandatory Palestine, Jimzu was to form part of the proposed Arab state. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the village was depopulated in a two-day assault by Israeli forces.
 W
WMuseum of Philistine Culture is an archaeological museum in Ashdod (Israel). Museum is dedicated to the culture of the Philistines, the ancient people who inhabited the maritime part of Israel from the XII century BC. It is the only museum in the world completely dedicated to this topic.
 W
WPhilistine Bichrome ware is an archaeological term coined by William F. Albright in 1924 which describes pottery production in a general region associated with the Philistine settlements during the Iron Age I period in ancient Canaan. The connection of the pottery type to the "Philistines" is still held by many scholars, although some question its methodological validity.
 W
WThe Philistine captivity of the Ark was an episode described in the biblical history of the Israelites, in which the Ark of the covenant was in the possession of the Philistines, who had captured it after defeating the Israelites in a battle at a location between Eben-ezer, where the Israelites encamped, and Aphek, where the Philistines encamped.
 W
WThe Philistine language is the extinct language of the Philistines. Very little is known about the language, of which a handful of words survived as cultural loanwords in Biblical Hebrew, describing specifically Philistine institutions, like the seranim, the "lords" of the Philistine five cities ("Pentapolis"), or the ’argáz receptacle, which occurs in 1 Samuel 6 and nowhere else, or the title padî.
 W
WTell Qasile is an archaeological site in Tel Aviv, Israel. Over 3,000 years old, the site contains the remains of a port city founded by the Philistines in the 12th century BC. It is located near the Yarkon River, on the grounds of the Eretz Israel Museum.
 W
WThe Tell es-Safi inscription was found in 2005 at the archaeological site at Tell es-Safi, identified with the biblical city of Gath. It was under the destruction layer at the beginning of Iron Age IIA.