 W
WVayeira, Vayera, or Va-yera is the fourth weekly Torah portion in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes Genesis 18:1–22:24. The parashah tells the stories of Abraham's three visitors, Abraham's bargaining with God over Sodom and Gomorrah, Lot's two visitors, Lot's bargaining with the Sodomites, the flight of Lot, the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, how Lot's daughters became pregnant by their father, how Abraham once again passed off his wife Sarah as his sister, the birth of Isaac, the expulsion of Hagar, disputes over wells, and the binding of Isaac.
 W
WAbimelech was the name of multiple Philistine kings mentioned in the Hebrew Bible.
 W
WAbraham is the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the covenant of the pieces, the special relationship between the Hebrews and God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, Jewish or Gentile; and in Islam he is seen as a link in the chain of prophets that begins with Adam and culminates in Muhammad.
 W
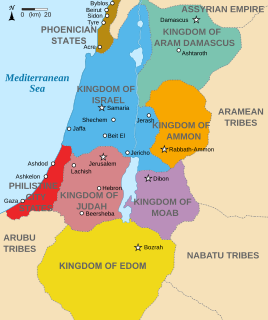
WAmmon was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was Rabbah or Rabbath Ammon, site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital. Milcom and Molech are named in the Hebrew Bible as the gods of Ammon. The people of this kingdom are called "Children of Ammon" or "Ammonites".
 W
WBethuel, in the Hebrew Bible, was an Aramean man, the youngest son of Nahor and Milcah, the nephew of Abraham, and the father of Laban and Rebecca.
 W
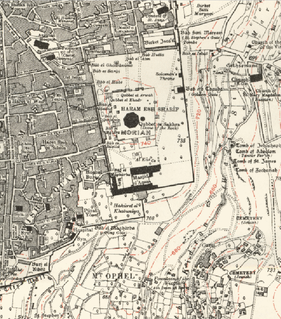
WThe Binding of Isaac Aqedat Yitzhaq, in Hebrew also simply "the Binding", הָעֲקֵידָה Ha-Aqedah, -Aqeidah) is a story from the Hebrew Bible found in Genesis 22. In the biblical narrative, God tells Abraham to sacrifice his son, Isaac, on Moriah. Abraham begins to comply, when a messenger from God interrupts him. Abraham then sees a ram and sacrifices it instead.
 W
WGerar was a Philistine town and district in what is today south central Israel, mentioned in the Book of Genesis and in the Second Book of Chronicles of the Hebrew Bible.
 W
WHagar is a biblical person in the Book of Genesis. She was an Ancient Egyptian servant of Sarah, who gave her to Abraham to bear a child. The product of the union was Abraham's firstborn, Ishmael, the progenitor of the Ishmaelites, generally taken to be the Arabians. Various commentators have connected her to the Hagrites, perhaps claiming her as their eponymous ancestor.
 W
WIsaac is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and is an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the son of Abraham and Sarah, the father of Jacob, and the grandfather of the twelve tribes of Israel.
 W
WLot was a patriarch in the biblical Book of Genesis, chapters 11–14 and 19. Notable events in his life include his journey with his uncle Abram (Abraham) and his flight from the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, during which Lot's wife became a pillar of salt, and Lot was made drunk by his daughters so that they could have children with him.
 W
WIn the Bible, Lot's wife is a figure first mentioned in Genesis 19. The Book of Genesis describes how she became a pillar of salt after she looked back at Sodom. She is not named in the Bible but is called "Ado" or "Edith" in some Jewish traditions. She is also referred to in the deuterocanonical books at Wisdom 10:7 and the New Testament at Luke 17:32. Islamic accounts also talk about the wife of Prophet Lut (Lot) when mentioning 'People of Lut'.
 W
WMoab is the name of an ancient kingdom whose territory is today located in the modern state of Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archaeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel, an episode also noted in 2 Kings 3. The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Hebrew Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west.
 W
WMoriah is the name given to a mountainous region by the Book of Genesis, in which context it is the location of the sacrifice of Isaac. Through association with the biblical Mount Moriah, Mount Moriah has been interpreted as the name of the specific mountain at which this occurred.
 W
WRebecca appears in the Hebrew Bible as the wife of Isaac and the mother of Jacob and Esau. According to biblical tradition, Rebecca's father was Bethuel the Aramean from Paddan Aram, also called Aram-Naharaim. Rebecca's brother was Laban the Aramean, and she was the granddaughter of Milcah and Nahor, the brother of Abraham. Rebecca and Isaac were one of the four couples that some believe are buried in the Cave of the Patriarchs, the other three being Adam and Eve, Abraham and Sarah, and Jacob and Leah.
 W
WSarah is a biblical matriarch and prophetess, a major figure in Abrahamic religions. While some discrepancies exist in how she is portrayed by the different faiths, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam all depict her character similarly, as that of a pious woman, renowned for her hospitality and beauty, the wife and half-sister of Abraham, and the mother of Isaac.
 W
WSodom and Gomorrah were two cities mentioned in the Book of Genesis and throughout the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament, and in the deuterocanonical books, as well as in the Quran and the hadith.