 W
WThe Antichrist is a book by the philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, originally published in 1895. Although it was written in 1888, its controversial content made Franz Overbeck and Heinrich Köselitz delay its publication, along with Ecce Homo. The German title can be translated into English as either The Anti-Christ or The Anti-Christian, depending on how the German word Christ is translated.
 W
WThe Class Struggles in France, 1848 to 1850 was a set of articles written by Karl Marx for the newspaper Neue Rheinische Zeitung in 1850. The works were collated and republished in 1895 by Friedrich Engels.
 W
WThe Criterion for Religions, the English rendering of Mi‘yarul Madhahib, was written and published in 1895 by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad, founder of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community. This English edition was published in 2007, by Islam International Publications
 W
WThe Crowd: A Study of the Popular Mind is a book authored by Gustave Le Bon that was first published in 1895.
The Development of the Monist View of History is the major work of the Russian philosopher Georgi Plekhanov, published in 1895. Plekhanov gives an account of modern social and philosophical thought as culminating in Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel and Karl Marx and seen through the materialism of Ludwig Feuerbach.
 W
WForerunners of Modern Socialism is a four volume work that documents the history of primitive communist and socialist ideas, edited by Karl Kautsky and including contributions by a number of prominent intellectuals of the Second International, including Eduard Bernstein, Paul Lafargue, C. Hugo, Franz Mehring, and Georgii Plekhanov. The first volume was published in 1895.
 W
WHistory of the Kinetograph, Kinetoscope, and Kinetophonograph is a book written by siblings William Kennedy Dickson and Antonia Dickson about the history of film. The brother Dickson wrote from his experiences working for Thomas Edison at his "Black Maria" studio in West Orange, New Jersey; Edison himself prefaced the book. Emphasis is placed on the eponymous devices: the kinetograph, the kinetoscope, and the kinetophonograph. Dickson helped to develop these devices, which facilitate the capturing and exhibition of motion pictures.
 W
WThe Life and Morals of Jesus of Nazareth, commonly referred to as the Jefferson Bible, is one of two religious works constructed by Thomas Jefferson. The first, The Philosophy of Jesus of Nazareth, was completed in 1804, but no copies exist today. The second, The Life and Morals of Jesus of Nazareth, was completed in 1820 by cutting and pasting with a razor and glue numerous sections from the New Testament as extractions of the doctrine of Jesus. Jefferson's condensed composition excludes all miracles by Jesus and most mentions of the supernatural, including sections of the four gospels that contain the Resurrection and most other miracles, and passages that portray Jesus as divine.
 W
WThe Life of Sir William Petty 1623-1687 is a book, written by Lord Edmond Fitzmaurice, and published in 1895. It is a biography of Sir William Petty, the 17th-century scientist, known for his inventions, his charting of large parts of Ireland, in the Down Survey, and his publications on many different topics, like "political arithmetic" and political economy.
 W
WThe Rules of Sociological Method is a book by Émile Durkheim, first published in 1895. It is recognized as being the direct result of Durkheim's own project of establishing sociology as a positivist social science. Durkheim is seen as one of the fathers of sociology, and this work, his manifesto of sociology. Durkheim distinguishes sociology from other sciences and justifies his rationale. Sociology is the science of social facts. Durkheim suggests two central theses, without which sociology would not be a science:It must have a specific object of study. Unlike philosophy or psychology, sociology's proper object of study are social facts. It must respect and apply a recognized objective scientific method, bringing it as close as possible to the other exact sciences. This method must at all cost avoid prejudice and subjective judgment.
 W
WThe Salmon Fly - How to Dress It and How to Use It is a fly fishing book written by George M. Kelson published in London in 1895 by Messers. Wyman & Sons, Limited. This Victorian guide to fly fish tying built up the illusion that angling for salmon required feathers of exotic bird species.
 W
WStudies on Hysteria is an 1895 book by Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, and the physician Josef Breuer. It consists of a joint introductory paper ; followed by five individual studies of "hysterics" – Breuer's famous case of Anna O., seminal for the development of psychoanalysis, and four more by Freud— including his evaluation of Emmy von N— and finishing with a theoretical essay by Breuer and a more practice-oriented one on therapy by Freud.
 W
WThe Times Atlas of the World, rebranded The Times Atlas of the World: Comprehensive Edition in its 11th edition and The Times Comprehensive Atlas of the World from its 12th edition, is a world atlas currently published by HarperCollins Publisher L.L.C. Its most recent edition, the fifteenth, was published on 6 September 2018.
 W
WThe Valley of Kashmir (1895) is a travel book by the English writer Sir Walter Roper Lawrence. The author served in the Indian Civil Service in British India during which he was appointed as a first Settlement Commissioner of Kashmir.
 W
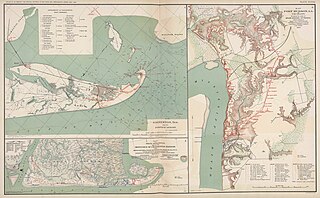
WThe Atlas to Accompany the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies was published as a companion piece to the Official Records of the American Civil War. It contains maps and other images derived from materials generated by both Union and Confederate military personnel during the American Civil War.
 W
WWhy I Am a Vegetarian is an 1895 pamphlet based on an address delivered by J. Howard Moore before the Chicago Vegetarian Society. It was reprinted several times by the society and other publishers.
 W
WThe Woman's Bible is a two-part non-fiction book, written by Elizabeth Cady Stanton and a committee of 26 women, published in 1895 and 1898 to challenge the traditional position of religious orthodoxy that woman should be subservient to man. By producing the book, Stanton wished to promote a radical liberating theology, one that stressed self-development. The book attracted a great deal of controversy and antagonism at its introduction.