 W
WAdam's Bridge, also known as Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu, is a chain of limestone shoals, between Pamban Island, also known as Rameswaram Island, off the south-eastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island, off the north-western coast of Sri Lanka. Geological evidence suggests that this bridge is a former land connection between India and Sri Lanka.
 W
WAllahabad, officially known as Prayagraj, and also known as Ilahabad and Prayag, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of Allahabad district—the most populous district in the state and 13th most populous district in India—and the Allahabad division. The city is the judicial capital of Uttar Pradesh with Allahabad High Court being the highest judicial body in the state. As of 2011, Allahabad is the seventh most populous city in the state, thirteenth in Northern India and thirty-sixth in India, with an estimated population of 1.53 million in the city. In 2011 it was ranked the world's 40th fastest-growing city. Allahabad, in 2016, was also ranked the third most liveable city in the state and sixteenth in the country. Hindi is the most widely spoken language in the city.
 W
WAnjaneri, one of the forts in the mountain range of Nasik-Trimbakeshwar, is considered to be the birthplace of god Hanuman. Anjaneri is located 20 km away from Nasik by Trimbak Road. It has become a famous trekking spot for local Nashikites, specially in the rainy season.
 W
WAntarvedi, or Antarvedipalem, is a village in the Sakhinetipalle mandal, or tehsil, located in the East Godavari district of the Andhra Pradesh state in India. The village is situated at the place where the Bay of Bengal and Vashista Godavari, a tributary of the Godavari River, meet.
 W
WAshok Vatika was a garden in Lanka that was located in the kingdom of the Rakshasa king Ravana, as mentioned in the Vishnu Purana and the Hindu epic Ramayana of Valmiki, and all subsequent versions, including the Ramacharitamanas written by Tulsidas, where it finds mention in the Sundar Kand. The Vatika has garden houses around it, built by Vishwakarma himself.
 W
WAyodhya is a legendary city mentioned in the ancient Sanskrit-language texts, including the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. These texts describe it as the capital of the Ikshvaku kings, including Rama.
 W
WThe Bandhavgarh Fort is situated in Bandhavgarh in Umaria district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located on the Bandhavgarh hill, rising 811 meters above sea level at the centre of the Bandhavgarh National Park. It is surrounded by many smaller hills separated by gently sloping valleys. These valleys end in small, swampy meadows, locally known as 'bohera'. The fort is also home to many of the endangered species of Vulture in India.
 W
WChitrakoot is a famous pilgrimage centre and a nagar panchayat in the Satna district in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is a place of religious, cultural, historical and archaeological importance, situated in the Bundelkhand region. It borders the Chitrakoot district in Uttar Pradesh, whose headquarters Chitrakoot Dham is located nearby. The city lies in the historical Chitrakoot region, which is divided between the present-day Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. It is known for a number of temples and sites mentioned in Hindu scriptures.
 W
WDandakaranya is a historical region in India, mentioned in the Ramayana. It is identified with a territory roughly equivalent to the Bastar division in the Chhattisgarh state in the central-east part of India. It covers about 92,200 square kilometres (35,600 sq mi) of land, which includes the Abujhmar Hills in the west and the Eastern Ghats in the east, including regions of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Odisha states. It spans about 300 kilometres (200 mi) from north to south and about 500 kilometres (300 mi) from east to west. Dandakaranya roughly translates from Sanskrit to "The Jungle (aranya) of Punishment (dandakas"). The Balaghat district of Madhya Pradesh and Bhandara, Gondia and Gadchiroli districts of Maharashtra are part of the ancient region Dandakaranya.
 W
WDehradun, also rendered Dera Doon, is the winter capital and the most populous city in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and is governed by the Dehradun Municipal Corporation. Part of the Garhwal region, it lies along National Highway 7 with the distance of 236 kilometres (147 mi) north of India's capital New Delhi and is served by Dehradun railway station and Jolly Grant Airport. Dehradun is one of the "Counter Magnets" of the National Capital Region (NCR) being developed as an alternative centre of growth to help ease the migration and population explosion in the Delhi metropolitan area and to establish a smart city at Dehradun.
 W
WDhanushkodi is an abandoned town at the south-eastern tip of Pamban Island of the state of Tamil Nadu in India. It is south-east of Pamban and is about 24 kilometres (15 mi) west of Talaimannar in Sri Lanka. The town was destroyed during the 1964 Rameswaram cyclone and remains uninhabited in the aftermath.
 W
WGandhamardan Hills or Gandhamardan parbat is a hill located in between Balangir and Bargarh district of Odisha, India. This hill is well known for medicinal plants. There is a Bauxite reserve which is planned for exploration by the state government through a private venture.
 W
WJanakpurdham or Janakpur is a sub-metropolitan city in Dhanusa District of Province No. 2 of Nepal. The city is a centre for religious and cultural tourism. It has been declared as the temporary capital for Province no. 2 until Province Assembly votes for a permanent capital.
 W
WKasur is a city to south of Lahore, in the Pakistani province of Punjab. The city serves as the headquarters of Kasur District. Kasur is the 24th largest city of Pakistan by population. It is also known for being the burial place of the 17th-century Sufi-poet Bulleh Shah. It is farther west of the border with neighbouring India, and bordered to Lahore, Sheikhupura, and the Okara District of Punjab Province.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Kashi was an ancient Indian kingdom located in the region around its capital Varanasi, the latter bounded by the Varuna and Asi rivers in the north and south and named after them. It was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas, great states that emerged in northern India at the start of the 6th century BCE. The kingdom of Kashi was bigger than Varanasi. Its easternmost border was the Son River, which was also the western border of erstwhile Magadh. It would have covered much of the area of Eastern UP centered around today's Varanasi and the contemporary southwestern part of Bihar that was Arrah (Shahabad) district. Today this area comprises Bhojpur, Rohtas, Kaimur and Buxar districts. Technically, the territory of Kashi today would dominated by people of the Bhojpuri language and culture. Kashi Mahajanpad would still be larger than what is covered within the Panch Krosh Kashi, as defined in the Puranas.
 W
WKingdom of Kosala was an ancient Indian kingdom, corresponding roughly in area with the region of Awadh in present-day Uttar Pradesh. It emerged as a small state during the late Vedic period, with connections to the neighboring realm of Videha. Kosala belonged to the Northern Black Polished Ware culture, and the Kosala region gave rise to the Sramana movements, including Jainism and Buddhism. It was culturally distinct from the Painted Grey Ware culture of the Vedic Aryans of Kuru-Pancala west of it, following independent development toward urbanisation and the use of iron.
 W
WMadhepura is a municipality in Madhepura district in the Indian state of Bihar.
 W
WMithila is a proposed state in India, comprising the Maithili speaking region of Bihar and Jharkhand. The Maithili language has own traditional script, known as Mithilakshar. It is part of the historical Mithila region. The proposed state will also include some Angika and Bajjika speaking districts which are considered by some to be dialects of Maithili. What will be the capital city of Mithila, India is still to be decided.
 W
WMukhed is and a municipal council in Nanded district in the Indian state of Maharashtra.
 W
WMuthathi is a settlement situated on the banks of the Kaveri river near Malavalli in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is surrounded by a dense forest which is the home of the Kaveri Wildlife Sanctuary. The location has associations with Sita and Anjaneya, and there is a small temple dedicated to Anjaneya near the town. This well connected hilly place is accessible from Bangalore through direct bus/private vehicles.
 W
WNashik is an ancient city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nasik is well known for being one of the Hindu pilgrimage sites, that of Kumbh Mela which is held every 12 years.
 W
WNuwara Eliya is a city in the hill country of the Central Province, Sri Lanka. Its name means "city on the plain " or "city of light". The city is the administrative capital of Nuwara Eliya District, with a picturesque landscape and temperate climate. It is at an altitude of 1,868 m (6,128 ft) and is considered to be the most important location for tea production in Sri Lanka. The city is overlooked by Pidurutalagala, the tallest mountain in Sri Lanka. Nuwara Eliya is known for its temperate, cool climate – the coolest area in Sri Lanka.
 W
WOshadhiparvata, that is, "the mountain of medicinal herbs," was a mythical mountain described in the Ramayana. Hanuman uproots the mountain and flies with it to the battlefield in Lanka. There the herbs are used by the Vaidyas to restore to life the dead, and to treat the wounded warriors fighting on the side of Rama.
 W
WPampa Sarovar is a lake in Koppal district near Hampi in Karnataka. To the south of the Tungabhadra River, it is considered sacred by Hindus and is one of the five sacred sarovars, or lakes in India. According to Hindu theology, there are five sacred lakes; collectively called Panch Sarovar; Mansarovar, Bindu Sarovar, Narayan Sarovar, Pampa Sarovar and Pushkar Sarovar. They are also mentioned in Shrimad Bhagavata Purana. In Hindu scriptures Pampa Sarovar is regarded as the place where Pampa, a form of Shiva's consort Parvati, performed penance to show her devotion to Shiva. It is also one of the Sarovar's that finds a mention in the Hindu epic, Ramayana as the place where Shabari, a devotee of Rama waited for the arrival of Ram.
 W
WNashik is an ancient city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nasik is well known for being one of the Hindu pilgrimage sites, that of Kumbh Mela which is held every 12 years.
 W
WPushkalavati IAST: Puṣkalāvatī, Greek: Peukelaotis), and later Shaikhan Dheri, was the capital of the Gandhara kingdom. Its ruins are located on the outskirts of the modern city of Charsadda, in Charsadda District, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, 28 kilometres northeast of Peshawar. Its ruins are located on the banks of Swat River, near its junction with Kabul River, with the earliest archaeological remains from 1400 to 800 BCE in Bala Hisar mound. Pushkalavati was the capital of the ancient Gandhara kingdom before the 6th century BCE. It later became an Achaemenid regional capital, and it remained an important city until the 2nd century CE.
 W
WRameswaram is a town and municipality in the Ramanathapuram district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is on Pamban Island separated from mainland India by the Pamban channel and is about 40 kilometres from Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. It is in the Gulf of Mannar, at the tip of the Indian peninsula. Pamban Island, also known as Rameswaram Island, is connected to mainland India by the Pamban Bridge. Rameswaram is the terminus of the railway line from Chennai and Madurai. Together with Varanasi, it is considered to be one of the holiest places in India to Hindus, and part of the Char Dham pilgrimage.
 W
WRamtek is a city and municipal council in Nagpur district of the Maharashtra, India.
 W
WRavana Falls is a popular sightseeing attraction in Sri Lanka. It currently ranks as one of the widest falls in the country.
 W
WSankissa was an ancient city in India. The city came into prominence at the time of Gautama Buddha. According to a Buddhist source, it was thirty leagues from Savatthi. After the Gautama Buddha's Mahaparinirvana king Ashoka developed this place and installed one of his famous Pillars of Ashoka in the city, from which the elephant capital survives. He also built a stupa and a temple commemorating the visit of the Buddha. This temple exists even today and the ruins of the stupa are also present as a temple of Vishari Devi. It is said that the name Visahari Devi is given to the mother of the Buddha.
 W
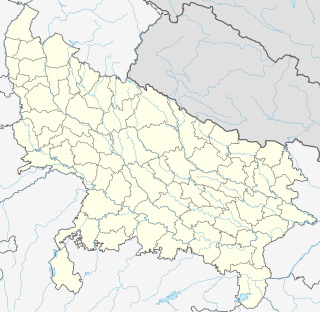
WShravasti was a city of ancient India and one of the six largest cities in India during Gautama Buddha's lifetime. The city was located in the fertile Gangetic plains in the present-day district of the same name, Shravasti, that belongs to Devipatan division of Uttar Pradesh near Balrampur, some 175 kilometres (109 mi) north-east of Lucknow. Earlier, it was a part of the Bahraich district, but the latter was split due to administrative reasons.
 W
WShringaverpur is a place 45 km from Prayagraj on Lucknow road. According to the local folklore, it was at this place that Rama crossed the river Ganges on his way to exile along with Sita and Lakshmana.
 W
WSitamarhi is a city and the district headquarters of the Sitamarhi district in the Mithila region of Bihar, India and is a part of the Tirhut Division. The Bihar government declared Sitamarhi a municipal corporation on 8 April 2020.
 W
WThe Tungabhadra River is a river in India that starts and flows through the state of Karnataka during most of its course, before flowing along the border between Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and ultimately joining the Krishna River near Sangameswaram village in Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh. In the epic Ramayana, the Tungabhadra River was known by the name of Pampa.
 W
WWalkeshwar is an affluent area in South Mumbai, India, at the north-western end of the Marine Drive loop. It is mostly known for Walkeshwar Temple, Banganga Tank and Jain temples.