 W
WAchshaph was a royal city of the Canaanites, in the north of Canaan. The name means "sorcery".
 W
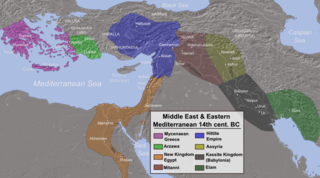
WAlashiya, also spelled Alasiya, also known as the Kingdom of Alashiya, was a state which existed in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, and was situated somewhere in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was a major source of goods, especially copper, for ancient Egypt and other states in the Ancient Near East. It is referred to in a number of the surviving texts and is now thought to be the ancient name of Cyprus, or an area of Cyprus. This was confirmed by the scientific analysis performed in the Tel Aviv University of the clay tablets which were sent from Alashiya to other rulers.
 W
WAmioun is the capital of the predominantly Greek Orthodox Koura District in the north of Lebanon.
 W
WArqa (Arabic: عرقا; canaanite: Irqata also in phonecian is a Sunni village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast.
 W
WArzawa was the name of a region and a political entity in Western Anatolia in the second half of the 2nd millennium BC. The core of Arzawa is believed to be along the Kaystros River, with its capital at Apasa, later known as Ephesus. When the Hittites conquered Arzawa, it was divided into three Hittite provinces: a southern province called Mira along the Maeander River, which would later become known as Caria; a northern province called the Seha River Land, along the Gediz River, which would later become known as Lydia; and an eastern province called Hapalla.
 W
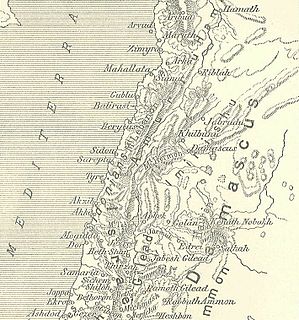
WAshkelon or Ashqelon, also known as Ascalon, is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Tel Aviv, and 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) north of the border with the Gaza Strip. The ancient seaport of Ashkelon dates back to the Neolithic Age. In the course of its history, it has been ruled by the Ancient Egyptians, the Canaanites, the Philistines, the Assyrians, the Babylonians, the Greeks, the Phoenicians, the Hasmoneans, the Romans, the Persians, the Arabs and the Crusaders, until it was destroyed by the Mamluks in 1270.
 W
W W
WBurqin is a Palestinian town in the northern West Bank located 5 km west of Jenin. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS) census, its population was 5,685 in 2007. The majority of Burqin's residents are Muslims, and 20 Christian families live in the town. The Byzantine-era Burqin Church or St. George's Church is one of the oldest churches in the world.
 W
WByblos is the largest city in the Mount Lebanon Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8800 and 7000 BC and continuously inhabited since 5000 BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WCanaan was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. The name "Canaan" appears throughout the Bible, where it corresponds to the Levant, in particular to the areas of the Southern Levant that provide the main setting of the narrative of the Bible: Phoenicia, Philistia, Israel, and other nations.
 W
WDamascus ( də-MASS-kəs; Arabic: دِمَشْق, romanized: Dimašq [diˈmaʃq], Syrian Arabic: [dɪˈmaʃʔ] is the capital of Syria; it became the country's largest city in the early 2010s, following the decline in population of Aleppo during the battle for the city. It is colloquially known in Syria as aš-Šām and titled the "City of Jasmine". Damascus is a major cultural center of the Levant and the Arab world. The city had an estimated population of 2,079,000 as of 2019.
 W
WEnfeh, or Enfe, Anfeh, Anfe, is a town in the Koura district of the North Governorate of Lebanon at Latitude 34°21'0"N and Longitude 35°44'0"E. Enfeh borders the towns of Chekka, Al-Qalamoun, Barghoun and Zakroun. It is located 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Beirut and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south of Tripoli. Its total area is 4.93 square kilometres (1.90 sq mi), and its population is around 6,500.
 W
WEnišasi, was a city, or city-state located in the Beqaa Valley-(called Amqu, or Amka) of Lebanon, during the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Of the 382–Amarna letters, Enišasi is only referenced in two letters. Enišasi was located near Hašabu,, and Hasi,, southwest of Baalbek.
 W
WGezer, or Tel Gezer, in Arabic Tell Jezer or Tell el-Jazari, the site of the abandoned Arab village of Abu Shusheh, is an archaeological site in the foothills of the Judaean Mountains at the border of the Shfela region roughly midway between Jerusalem and Tel Aviv. It is now an Israeli national park. In the Hebrew Bible, Gezer is associated with Joshua and Solomon.
 W
WByblos is the largest city in the Mount Lebanon Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8800 and 7000 BC and continuously inhabited since 5000 BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WTel Hanaton is a Bronze Age tel situated at the Western edge of the Beit Netofa Valley, in the western Lower Galilee region of Israel, 2 km South of the Town of Kfar Manda and 1 km ENE of the modern settlement which took its name, Kibbutz Hanaton.
 W
WTel Hazor, also Chatsôr, translated in LXX as Hasōr and Tell el-Qedah, is an archaeological tell at the site of ancient Hazor, located in Israel, Upper Galilee, north of the Sea of Galilee, in the northern Korazim Plateau. In the Middle Bronze Age and the Israelite period, Hazor was the largest fortified city in the country and one of the most important in the Fertile Crescent. It maintained commercial ties with Babylon and Syria, and imported large quantities of tin for the bronze industry. In the Book of Joshua, Hazor is described as “the head of all those kingdoms”.
 W
WArqa (Arabic: عرقا; canaanite: Irqata also in phonecian is a Sunni village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast.
 W
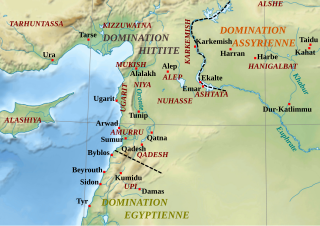
WKadesh, or Qadesh, was an ancient city of the Levant on or near the headwaters or a ford of the Orontes River. It was of some importance during the Late Bronze Age and is mentioned in the Amarna letters. It was the site of the Battle of Kadesh between the Hittite and Egyptian empires in the 13th century BC.
 W
WKamid al lawz is located in West Bekaa, Lebanon. Its population numbers several thousand, mostly Sunni, people.
 W
WKarduniaš, also transcribed Karduniash, Karaduniyaš or Karaduniše), is a Kassite term used for the kingdom centered on Babylonia and founded by the Kassite dynasty. It is used in the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence, and is also used frequently in Middle-Assyrian and Neo-Assyrian texts to refer to the kingdom of Babylon. The name Karaduniyaš is mainly used in the letters written between Kadashman-Enlil I, or Burna-Buriash, the Kings of Babylon, and the Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt-(called: Mizri), letters EA 1-EA 11, a subcorpus of letters,. Much later, a version of the name was used in the Babylonian Talmud as Kardunya referring to similar locations.
 W
WKeilah, meaning Citadel, was a city in the lowlands of Judah. It is now a ruin, known as Kh. Qeila, near the modern village of Qila, 7 miles (11 km) east of Beit Gubrin, and about 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) west of Kharas.
 W
WKfarhazir is a village in the Koura District of Lebanon. It is 350 meters above sea level, and has an area of 12.1 square kilometres (4.69 sq mi) - the largest town in Koura by size, with a population of about 2000. The population are Greek Orthodox and Maronite.
 W
WTel Megiddo is the site of the ancient city of Megiddo, the remains of which form a tell, situated in northern Israel near Kibbutz Megiddo, about 30 km south-east of Haifa. Megiddo is known for its historical, geographical, and theological importance, especially under its Greek name Armageddon. During the Bronze Age, Megiddo was an important Canaanite city-state and during the Iron Age, a royal city in the Kingdom of Israel. Megiddo drew much of its importance from its strategic location at the northern end of the Wadi Ara defile, which acts as a pass through the Carmel Ridge, and from its position overlooking the rich Jezreel Valley from the west. Excavations have unearthed 26 layers of ruins since the Chalcolithic phase, indicating a long period of settlement. The site is now protected as Megiddo National Park and is a World Heritage Site.
 W
WNaziba, was a small 'city', or 'city-state' south of Dimašqu-(Damascus), in the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. The town of Naziba was located near Amarna letters Qanu, now named Qanawat, and biblical Kenath.
 W
WNuhašše, also Nuhašša, was a region in northwestern Syria that flourished in the 2nd millennium BC. It was a federacy ruled by different kings who collaborated and probably had a high king. Nuhašše changed hands between different powers in the region such as Egypt, Mitanni and the Hittites. It rebelled against the latter which led Šuppiluliuma I to attack and annex the region.
 W
WNuhašše, also Nuhašša, was a region in northwestern Syria that flourished in the 2nd millennium BC. It was a federacy ruled by different kings who collaborated and probably had a high king. Nuhašše changed hands between different powers in the region such as Egypt, Mitanni and the Hittites. It rebelled against the latter which led Šuppiluliuma I to attack and annex the region.
 W
WQatna was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about 18 km (11 mi) northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an important center through most of the second millennium BC and in the first half of the first millennium BC. It contained one of the largest royal palaces of Bronze Age Syria and an intact royal tomb that has provided a great amount of archaeological evidence on the funerary habits of that period.
 W
WRuhizzi, was a city, or city-state located in northern Canaan or southern Amurru territories, in the foothills of Mount Hermon during the time of the Amarna letters correspondence. During the 15-20 year Amarna letters of 1350-1335 BC, Arsawuya was the 'mayor' of Ruhizzi and corresponded with the Egyptian pharaoh.
 W
WThe Salhi is a region/city-state in the vicinity of Ugarit during the 15-20 year Amarna letters correspondence of 1350-1335 BC.
 W
WShimron is a nature reserve in Northern Israel.
 W
WThe land of Subartu or Subar is mentioned in Bronze Age literature. The name also appears as Subari in the Amarna letters, and, in the form Šbr, in Ugarit.
 W
WTel Lachish, known in Arabic as Tell ed-Duweir, is the site of an ancient Near Eastern city, now an archaeological site and an Israeli national park. The park was established on lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Qobebet Ibn ‘Awwad.
 W
WTel Yokneam, also spelled Yoqne'am or Jokneam, is an archaeological site located between the modern city of Yokneam Illit and the town of Yokneam Moshava. It was known in Arabic by a variant name, Tell Qamun, believed to be a corruption of the Hebrew name. The site is an elevated mound, or tel, spanning around 40 dunams and rising steeply to a height of 60 meters (200 ft). With a few brief interruptions, Yokneam was occupied for 4,000 years, from the Middle Bronze Age to the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WTell Ashtara is an archaeological mound south of Damascus. The Bronze Age city that once stood here was mentioned in the Amarna letters correspondence of 1350 BC as Aštartu, and is usually identified with the Biblical city of Ashtaroth.
 W
WTubu is the town east of the Sea of Galilee referred to in the (body) of the Amarna letters.
 W
WTunip was a city-state in western Syria in 1350–1335 BC, the period of the Amarna letters. The name "Syria" did not yet exist, though this was already the time of ancient Assyria. The regions were: Amurru, Nuhašše, the Amqu, Nii, etc.
 W
WTyre is one of the oldest continually inhabited cities in the world, though in medieval times for some centuries by just a tiny population. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix, as well as Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to UNESCO's list of World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins".
 W
WUgarit was an ancient port city in northern Syria, in the outskirts of modern Latakia, discovered by accident in 1928 together with the Ugaritic texts. Its ruins are often called Ras Shamra after the headland where they lie.
 W
WShaizar or Shayzar is a town in northern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located northwest of Hama. Nearby localities include, Mahardah, Tremseh, Kafr Hud, Khunayzir and Halfaya. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Shaizar had a population of 5,953 in the 2004 census.