 W
WErnst Karl Abbe HonFRMS was a German physicist, optical scientist, entrepreneur, and social reformer. Together with Otto Schott and Carl Zeiss, he developed numerous optical instruments. He was also a co-owner of Carl Zeiss AG, a German manufacturer of scientific microscopes, astronomical telescopes, planetariums, and other advanced optical systems.
 W
WGiovanni Battista Amici was an Italian astronomer, microscopist, and botanist.
 W
WHenry Baker was a British naturalist.
 W
WWynne Edwin Baxter FRMS FGS was an English lawyer, translator, antiquarian and botanist, but is best known as the Coroner who conducted the inquests on most of the victims of the Whitechapel Murders of 1888 to 1891 including three of the victims of Jack the Ripper in 1888, as well as on Joseph Merrick, the "Elephant Man".
 W
WRobert Eric Betzig is an American physicist who works as a Professor of Physics and Professor of Molecular and Cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also a Senior Fellow at the Janelia Farm Research Campus in Ashburn, Virginia.
 W
WGerd Binnig is a German physicist. He is most famous for having won the Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Heinrich Rohrer in 1986 for the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope.
 W
WMary Ann Allard Booth was an American microscopist.
 W
WThomas Benjamin Britton is a materials scientist and engineer based at Imperial College London. He is a specialist in micromechanics, electron microscopy and crystal plasticity. In 2014 he was awarded the Silver Medal of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (IOM3), a society of which he then became a Fellow in 2016.
 W
WSir Frank Crisp, Kt., 1st Baronet, was an English lawyer and microscopist. Crisp was an enthusiastic member, and sometime officer, of the Royal Microscopical Society. He was generous in his support of the Society, donating furniture, books and instruments in addition to his work on technical publications.
 W
WElena de Galantha was an Austro-Hungarian histologist. She is considered a pioneer in the field of modern histology and known for the de Galantha technique and the de Galantha stain.
 W
WFrancisco Javier "Frank" Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers and quantum optics. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory, has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations, and pioneered polymer-nanoparticle gain media. His contributions have found applications in a variety of fields including astronomical instrumentation, atomic vapor laser isotope separation, geodesics, gravitational lensing, laser medicine, laser microscopy, laser pulse compression, laser spectroscopy, nonlinear optics, and tunable diode lasers.
 W
WRafal Edward Dunin-Borkowski is a British experimental physicist. He is currently Director of the Institute for Microstructure Research (PGI-5) and the Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons (ER-C) in Forschungszentrum Jülich and Professor of Experimental Physics in RWTH Aachen University.
 W
WRichard Marshall Eakin, was an American zoologist and professor at the University of California, Berkeley. He was widely known for portraying prominent historical scientists during some of his lectures; dressing in costume and speaking in character to entertain and inform his students. A 1953 Guggenheim fellow, he wrote several books and more than 200 scientific papers. His research focused on eyes and vision in animals, especially the parietal eye or "third eye" of vertebrates, as well as animal embryology. He served as chairman of the UC Berkeley Department of Zoology for over 10 years, was elected president of the Western Society of Naturalists and American Society of Zoologists, and was a fellow of the California Academy of Sciences.
 W
WChristian Gottfried Ehrenberg, German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist, was one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Ehrenberg was an evangelist.
 W
WFred Enock aka Frederick Enock was an English microscopist, illustrator and naturalist.
 W
WHumberto Fernández-Morán Villalobos was a Venezuelan research scientist born in Maracaibo, Venezuela, renowned for inventing the diamond knife or scalpel, significantly advancing the development of electromagnetic lenses for electron microscopy based on superconducting technology, and many other scientific contributions.
 W
WKatharina Gaus is an Australian immunologist and molecular microscopist. She is currently an NHMRC Senior Research Fellow and founding head of the Cellular Membrane Biology Lab, part of the Centre for Vascular Research at the University of New South Wales. Gaus uses new super-resolution fluorescence microscopes to examine the plasma membrane within intact living cells, and study cell signalling at the level of single molecules to better understand how cells "make decisions". A key discovery of Gaus and her team was how T-cells decide to switch on the body's immune system to attack diseases. Her work is of importance to the development of drugs that can work with T-cells in support of the immune system.
 W
WPieter Harting was a Dutch biologist and naturalist, born in Rotterdam. He made contributions in a number of scientific disciplines, and is remembered for his work in the fields of microscopy, hydrology, botany, and biostratigraphy.
 W
WArthur Hill Hassall was a British physician, chemist and microscopist who is primarily known for his work in public health and food safety.
 W
WStefan Walter Hell HonFRMS is a Romanian born German physicist and one of the directors of the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen, Germany. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2014 "for the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy", together with Eric Betzig and William Moerner.
 W
WRichard Henderson is a Scottish molecular biologist and biophysicist and pioneer in the field of electron microscopy of biological molecules. Henderson shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2017 with Jacques Dubochet and Joachim Frank.
 W
WArchibald "Archie" Howie CBE HonFRMS FRS HonFRSE is a British physicist and Emeritus Professor at the University of Cambridge, known for his pioneering work on the interpretation of transmission electron microscope images of crystals. Born in 1934, he attended Kirkcaldy High School and the University of Edinburgh. He received his PhD from the University of Cambridge, where he subsequently took up a permanent post. He has been a fellow of Churchill College since its foundation, and was President of its Senior Combination Room (SCR) until 2010.
 W
WSumio Iijima is a Japanese physicist and inventor, often cited as the inventor of carbon nanotubes. Although carbon nanotubes had been observed prior to his "invention", Iijima's 1991 paper generated unprecedented interest in the carbon nanostructures and has since fueled intense research in the area of nanotechnology.
 W
WAlfred Detlef Fritz Kahl was a German schoolteacher who took up microscopy in mid-life and became a leading authority on ciliated protozoa. In a burst of scientific productivity that lasted just nine years, he published 1800 pages of scholarly work, in which he described 17 new ciliate families, 57 genera, and about 700 previously unknown species. During his brief career as a protozoologist, he redescribed and illustrated nearly all the species of ciliates known in his time, and fit them into a taxonomic scheme that remains influential today.
 W
WSergei V. Kalinin is a corporate fellow at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences (CNMS) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. He is also a Joint Associate Professor at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the University of Tennessee-Knoxville.
 W
WAugust Karl Johann Valentin Köhler was a German professor and early staff member of Carl Zeiss AG in Jena, Germany. He is best known for his development of the microscopy technique of Köhler illumination, an important principle in optimizing microscopic resolution power by evenly illuminating the field of view. This invention revolutionized light microscope design and is widely used in traditional as well as modern digital imaging techniques today.
 W
WSnježana Kordić ; born 29 October 1964) is a Croatian linguist. In addition to her work in syntax, she has written on sociolinguistics. Kordić is known among non-specialists for numerous articles against the puristic and prescriptive language policy in Croatia. Her 2010 book on language and nationalism popularises the theory of pluricentric languages in the Balkans.
 W
WAntonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch businessman and scientist in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as "the Father of Microbiology", and one of the first microscopists and microbiologists. Van Leeuwenhoek is best known for his pioneering work in microscopy and for his contributions toward the establishment of microbiology as a scientific discipline.
 W
WBenjamin Martin was a lexicographer who compiled one of the early English dictionaries, the Lingua Britannica Reformata (1749). He also was a lecturer on science and maker of scientific instruments.
 W
WMatthew Fontaine Maury was an American astronomer, naval officer, historian, oceanographer, meteorologist, cartographer, author, geologist, and educator.
 W
WWilliam Esco Moerner is an American physical chemist and chemical physicist with current work in the biophysics and imaging of single molecules. He is credited with achieving the first optical detection and spectroscopy of a single molecule in condensed phases, along with his postdoc, Lothar Kador. Optical study of single molecules has subsequently become a widely used single-molecule experiment in chemistry, physics and biology. In 2014, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
 W
WLori Anne Passmore is a Canadian/British cryo electron microscopist and structural biologist who works at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) at the University of Cambridge. She is known for her work on multiprotein complexes involved in gene expression. and development of new supports for cryo-EM.
 W
WNatalie Porat-Shliom is an Israeli-American cell biologist and microscopist specialized in intravital microscopy to research mitochondrial structure. She is a NIH Stadtman Investigator and head of the cell biology and imaging section at the National Cancer Institute.
 W
WJohn Thomas Quekett was an English microscopist and histologist.
 W
WJohn Ralfs was an English botanist. Born in Millbrook, near Southampton, he was the second son of Samuel Ralfs, a yeoman of an old family in Hampshire. He has been commemorated in the names of many plant groups and taxa at many levels.
 W
WHeinrich Rohrer was a Swiss physicist who shared half of the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics with Gerd Binnig for the design of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM). The other half of the Prize was awarded to Ernst Ruska. The Heinrich Rohrer Medal is presented triennially by the Surface Science Society of Japan with IBM Research – Zurich, Swiss Embassy in Japan, and Ms. Rohrer in his memory. The medal is not to be confused with the Heinrich Rohrer Award presented at the Nano Seoul 2020 conference.
 W
WErnst August Friedrich Ruska was a German physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986 for his work in electron optics, including the design of the first electron microscope.
 W
WHenry Clifton Sorby, was an English microscopist and geologist. His major contribution was the development of techniques for studying iron and steel with microscopes. This paved the way for the mass production of steel.
 W
WJohn Charles Howorth Spence ForMemRS HonFRMS is Richard Snell Professor of Physics at Arizona State University and Director of Science at the National Science Foundation BioXFEL Science and Technology Center.
 W
WJan Swammerdam was a Dutch biologist and microscopist. His work on insects demonstrated that the various phases during the life of an insect—egg, larva, pupa, and adult—are different forms of the same animal. As part of his anatomical research, he carried out experiments on muscle contraction. In 1658, he was the first to observe and describe red blood cells. He was one of the first people to use the microscope in dissections, and his techniques remained useful for hundreds of years.
 W
WWashington Teasdale was an engineer and photographer. He invented the field naturalist's microscope and was one of the first people to use lantern slides.
 W
WNestor J. Zaluzec is an American scientist and inventor who works at Argonne National Laboratory. He invented and patented the Scanning Confocal Electron Microscope. and the π Steradian Transmission X-ray Detector for Electron-Optical Beam Lines and Microscopes.
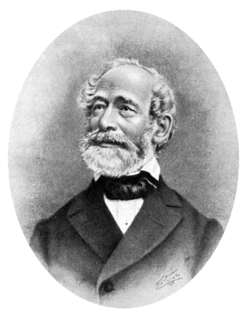 W
WCarl Zeiss was a German scientific instrument maker, optician and businessman who founded the workshop of Carl Zeiss in 1846, which is still in business today as Carl Zeiss AG. Zeiss gathered a group of gifted practical and theoretical opticians and glass makers to reshape most aspects of optical instrument production. His collaboration with Ernst Abbe revolutionized optical theory and practical design of microscopes. Their quest to extend these advances brought Otto Schott into the enterprises to revolutionize optical glass manufacture. The firm of Carl Zeiss grew to one of the largest and most respected optical firms in the world.
 W
WJoseph Zentmayer was a German-American maker of microscopes and other optical instruments.
 W
WFrits Zernike was a Dutch physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1953 for his invention of the phase-contrast microscope.