 W
WIn telecommunications, an acoustic coupler is an interface device for coupling electrical signals by acoustical means—usually into and out of a telephone.
 W
WIntegrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking system with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance.
 W
WMultichannel Multipoint Distribution Service (MMDS), formerly known as Broadband Radio Service (BRS) and also known as Wireless Cable, is a wireless telecommunications technology, used for general-purpose broadband networking or, more commonly, as an alternative method of cable television programming reception.
 W
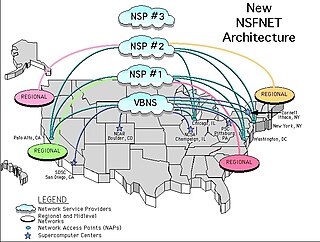
WA Network Access Point (NAP) was a public network exchange facility where Internet service providers (ISPs) connected with one another in peering arrangements. The NAPs were a key component in the transition from the 1990s NSFNET era to the commercial Internet providers of today. They were often points of considerable Internet congestion.
 W
WThe Open Base Station Architecture Initiative (OBSAI) was a trade association created by Hyundai, LG Electronics, Nokia, Samsung and ZTE in September 2002 with the aim of creating an open market for cellular network base stations. The hope was that an open market would reduce the development effort and costs traditionally associated with creating base station products.
 W
WThe Seattle Internet Exchange (SIX) is an Internet exchange point in Seattle, USA. Its switch fabric is centered at the Westin Building and extended to KOMO Plaza, Sabey Intergate, and other locations. The SIX is one of the most successful examples of neutral and independent peering points, created as a free exchange point originally sponsored only by donations. The SIX is the most frequently cited model upon which other neutral Internet exchanges are based, and its financial and governance models are often cited as inspiration for other exchanges. It continues to run without any recurring charges to the participants and current major funding comes from one-time 10 and 100 Gbit/s port fees. The SIX is a 501(c)(6) tax-exempt non-profit corporation.
 W
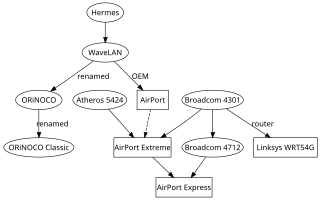
WWaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
 W
WcnPilot Xirrus. is a Wi-Fi technology company based in Thousand Oaks, California, US, that designs and sells wireless networking equipment based on the IEEE standards 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac. The company was founded in 2004.
 W
WWiMAX is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide multiple physical layer (PHY) and Media Access Control (MAC) options.
 W
WWiMAX MIMO refers to the use of Multiple-input multiple-output communications (MIMO) technology on WiMAX, which is the technology brand name for the implementation of the standard IEEE 802.16.
 W
WIn computer networking, a wireless access point (WAP), or more generally just access point (AP), is a networking hardware device that allows other Wi-Fi devices to connect to a wired network. As a standalone device, the AP may have a wired connection to a router, but, in a wireless router, it can also be an integral component of the router itself. An AP is differentiated from a hotspot which is a physical location where Wi-Fi access is available.