 W
WA 3D city model is digital model of urban areas that represent terrain surfaces, sites, buildings, vegetation, infrastructure and landscape elements in three-dimensional scale as well as related objects belonging to urban areas. Their components are described and represented by corresponding two-dimensional and three-dimensional spatial data and geo-referenced data. 3D city models support presentation, exploration, analysis, and management tasks in a large number of different application domains. In particular, 3D city models allow "for visually integrating heterogeneous geoinformation within a single framework and, therefore, create and manage complex urban information spaces."
 W
WAerial video is an emerging form of data acquisition for scene understanding and object tracking. The video is captured by low flying aerial platforms that integrate Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and automated image processing to improve the accuracy and cost-effectiveness of data collection and reduction. Recorders can incorporate in-flight voice records from the cockpit intercom system. The addition of audio narration is an extremely valuable tool for documentation and communication. GPS data is incorporated with a text-captioning device on each video frame. Helicopter platforms enable "low and slow" flights, acquiring a continuous visual record without motion blur.
 W
WThe Dimensionally Extended 9-Intersection Model (DE-9IM) is a topological model and a standard used to describe the spatial relations of two regions, in geometry, point-set topology, geospatial topology, and fields related to computer spatial analysis. The spatial relations expressed by the model are invariant to rotation, translation and scaling transformations.
 W
WSpatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data.
 W
WA geotagged photograph is a photograph which is associated with a geographic position by geotagging. Usually this is done by assigning at least a latitude and longitude to the image, and optionally altitude, compass bearing and other fields may also be included.
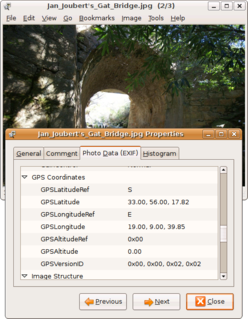 W
WGeotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RSS feeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, though they can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp.
 W
WINSPIRE is "an EU initiative to establish an infrastructure for spatial information in Europe that is geared to help to make spatial or geographical information more accessible and interoperable for a wide range of purposes supporting sustainable development".
 W
WLinear referencing, also called linear reference system or linear referencing system (LRS), is a method of spatial referencing in engineering and construction, in which the locations of physical features along a linear element are described in terms of measurements from a fixed point, such as a milestone along a road. Each feature is located by either a point or a line. If a segment of the linear element or route is changed, only those locations on the changed segment need to be updated. Linear referencing is suitable for management of data related to linear features like roads, railways, oil and gas transmission pipelines, power and data transmission lines, and rivers.
 W
WRandonautica is an app launched on February 22, 2020 founded by Joshua Lengfelder. It randomly generates coordinates that enables the user to explore their local area and report on their findings. According to its creators, the app is "an attractor of strange things," letting one choose specific coordinates based on a certain theme. It has gained controversy after several reports on the app generating coordinates, seemingly coincidentally, where disturbing things were present. The app is currently in its Beta version.
 W
WSatellite images are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell images by licensing them to governments and businesses such as Apple Maps and Google Maps. It should not be confused for astronomy images collected by space telescope.
 W
WSpatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data.
 W
WA triangulated irregular network (TIN) is a representation of a continuous surface consisting entirely of triangular facets, used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in primary elevation modeling.