A drop-down list is a graphical control element, similar to a list box, that allows the user to choose one value from a list. When a drop-down list is inactive, it displays a single value. When activated, it displays a list of values, from which the user may select one. When the user selects a new value, the control reverts to its inactive state, displaying the selected value. It is often used in the design of graphical user interfaces, including web design.
 W
WA frame, or group box, is a type of box within which a collection of graphical control elements can be grouped as a way to show relationships visually, either because the items are functionally related, or because they apply to related objects.
 W
WA label is a graphical control element which displays text on a form. It is usually a static control; having no interactivity. A label is generally used to identify a nearby text box or other widget. Some labels can respond to events such as mouse clicks, allowing the text of the label to be copied, but this is not standard user-interface practice. Labels usually cannot be given the focus.
 W
Wlarswm is a window manager for the X window system that follows the tiling window manager paradigm. Using ideas from the older 9wm window manager, it features automatic tiling and virtual desktops. It also borrows other ideas, for example a limited form of plumbing, from the Acme development environment. Objects are tiled into non-overlapping areas, instead of using windows that can be stacked, as this approach can result in lower memory and CPU requirements.
A list box is a graphical control element that allows the user to select one or more items from a list contained within a static, multiple line text box. The user clicks inside the box on an item to select it, sometimes in combination with the ⇧ Shift or Ctrl in order to make multiple selections. "Control-clicking" an item that has already been selected, unselects it.
 W
WA list builder, also known as a dual list, dual listbox, disjoint listbox, list shuttle, shuttle, swaplist, transfer list and two sided multi select is a graphical control element in which a user can select a set of text values by moving values between two list boxes, one representing selected values and the other representing unselected ones. Moving values back and forth is usually accomplished selecting values within one of the two lists and clicking buttons reading "Add" and "Remove", rather than by dragging and dropping them. Less traditionally, there may instead be an add or delete button individually next to each item. The widget can sometimes also include the ability to rearrange the selected values. There may also be buttons to add or remove all values, or a text field to filter the list.
 W
WA mnemonic is an underlined alphanumeric character, typically appearing in a menu title, menu item, or the text of a button or component of the user interface. A mnemonic indicates to the user which key to press to activate a command or navigate to a component.
 W
Wolwm was the default stacking window manager for OpenWindows, the original X11 desktop environment included with SunOS and Solaris. Its unique characteristic is its implementation of the OPEN LOOK look and feel.
 W
WA spinner or numeric updown is a graphical control element with which a user may adjust a value in an adjoining text box by either clicking on an up or down arrow, or by holding an arrow down, causing the value in the text box to increase or decrease. A spinner is typically oriented vertically. In most cases holding a button down causes the speed at which the associated value changes to increase. Usually, the value of the spinner is displayed in a text box next to the spinner, allowing the user to use the spinner to adjust the value, or to type the value into the text box. The combination of spinner and text box was coined as a Value Box.
 W
WIn computer interface design, a toolbar is a graphical control element on which on-screen buttons, icons, menus, or other input or output elements are placed. Toolbars are seen in many types of software such as office suites, graphics editors and web browsers. Toolbars are usually distinguished from palettes by their integration into the edges of the screen or larger windows, which results in wasted space if too many underpopulated bars are stacked atop each other or interface inefficiency if overloaded bars are placed on small windows.
 W
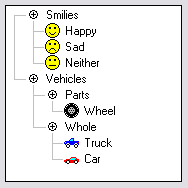
WA tree view or an outline view is a graphical control element that presents a hierarchical view of information. Each item can have a number of subitems. This is often visualized by indentation in a list.
 W
WX.desktop was an early desktop environment graphical user interface built on the X Window System. It was developed and sold during the late 1980s and early 1990s by IXI Limited, a British software house based in Cambridge. Versions of X.desktop were available for over 30 different UNIX operating system platforms and it was licensed to various vendors, including IBM, Compaq, Locus Computing Corporation, BiiN and Acorn Computers. Early version of X.desktop used Xlib and the Athena widgets; from version 2.0 onwards it was based on the Motif toolkit.
 W
WXynth is an embedded windowing system, released under LGPL, developed for systems with low resources, is an alternative for X Window System. The goal of the project is to release a soft but portable and powered Window Environment. The source language is C. A fork of the project exists as XFast.