 W
WGenome projects are scientific endeavours that ultimately aim to determine the complete genome sequence of an organism and to annotate protein-coding genes and other important genome-encoded features. The genome sequence of an organism includes the collective DNA sequences of each chromosome in the organism. For a bacterium containing a single chromosome, a genome project will aim to map the sequence of that chromosome. For the human species, whose genome includes 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, a complete genome sequence will involve 46 separate chromosome sequences.
 W
WThe Integrated Microbial Genomes system is a genome browsing and annotation platform developed by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)-Joint Genome Institute. IMG contains all the draft and complete microbial genomes sequenced by the DOE-JGI integrated with other publicly available genomes. IMG provides users a set of tools for comparative analysis of microbial genomes along three dimensions: genes, genomes and functions. Users can select and transfer them in the comparative analysis carts based upon a variety of criteria. IMG also includes a genome annotation pipeline that integrates information from several tools, including KEGG, Pfam, InterPro, and the Gene Ontology, among others. Users can also type or upload their own gene annotations and the IMG system will allow them to generate Genbank or EMBL format files containing these annotations.
 W
WMicrobesOnline is a publicly and freely accessible website that hosts multiple comparative genomic tools for comparing microbial species at the genomic, transcriptomic and functional levels. MicrobesOnline was developed by the Virtual Institute for Microbial Stress and Survival, which is based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California. The site was launched in 2005, with regular updates until 2011.
 W
WThe genome of a female Hereford cow was published in 2009. It was sequenced by the Bovine Genome Sequencing and Analysis Consortium, a team of researchers led by the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. It was part of an effort to improve livestock breeding and at the time was one of the largest genomes ever sequenced.
 W
WOregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant research university in Corvallis, Oregon. The university currently offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. Student enrollment averages near 32,000, making it the state's largest university. Since its founding over 230,000 students have graduated from OSU. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" with an additional, optional designation as a "Community Engagement" university.
 W
WThe Chimpanzee Genome Project is an effort to determine the DNA sequence of the chimpanzee genome. It is expected that by comparing the genomes of humans and other apes, it will be possible to better understand what makes humans distinct from other species from a genetic perspective. It will also aid in the study of diseases that affect various primate species.
 W
WHeather Dewey-Hagborg is an information artist and bio-hacker. She is best known for her project Stranger Visions, a series of portraits created from DNA she recovered from discarded items, such as hair, cigarettes and chewing gum while living in Brooklyn, New York. From the extracted DNA, she determined gender, ethnicity and other factors and then used face-generating software and a 3D printer to create a speculative, algorithmically determined 3D portrait. While critical of technology and surveillance, her work has also been noted as provocative in its lack of legal precedent.
 W
WThe Genome Project - Write is a large-scale collaborative research project that focuses on the development of technologies for the synthesis and testing of genomes of many different species of microbes, plants, and animals, including the human genome in a sub-project known as Human Genome Project-Write (HGP-Write). Formally announced on 2 June 2016, the project leverages two decades of work on synthetic biology and artificial gene synthesis.
 W
WGenomics England is a company set up and owned by the Department of Health and Social Care to run the 100,000 Genomes Project, which aims to sequence 100,000 genomes from NHS patients with a rare disease and their families, and patients with cancer. An infectious disease strand is being led by Public Health England.
 W
WThe Global Ocean Sampling Expedition (GOS) is an ocean exploration genome project whose goal is to assess genetic diversity in marine microbial communities and to understand their role in nature's fundamental processes. It was begun as a Sargasso Sea pilot sampling project in August 2003; Craig Venter announced the full expedition on 4 March 2004. The two-year journey, which used Craig Venter's personal yacht, originated in Halifax, Canada, circumnavigated the globe and terminated in the U.S. in January 2006. The expedition sampled water from Halifax, Nova Scotia to the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean. During 2007, sampling continued along the west coast of North America.
 W
WThe glucocorticoid receptor also known as NR3C1 is the receptor to which cortisol and other glucocorticoids bind.
 W
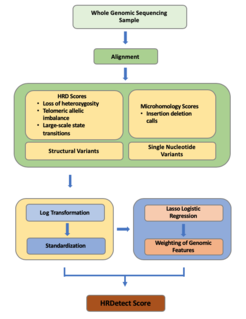
WHRDetect is a whole-genome sequencing (WGS)-based classifier designed to predict BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficiency based on six mutational signatures. Additionally, the classifier is able to identify similarities in mutational profiles of tumors to that of tumors with BRCA1 and BRCA2 defects, also known as BRCAness. This classifier can be applied to assess the implementation of PARP inhibitors in patients with BRCA1/BRCA2 deficiency. The final output is a probability of BRCA1/2 mutation.
 W
WThe Influenza Genome Sequencing Project (IGSP), initiated in early 2004, seeks to investigate influenza evolution by providing a public data set of complete influenza genome sequences from collections of isolates representing diverse species distributions.
 W
WThe New York Genome Center (NYGC) is an independent 501(c)(3) nonprofit academic research institution in New York, New York. It serves as a multi-institutional collaborative hub focused on the advancement of genomic science and its application to drive novel biomedical discoveries. NYGC’s areas of focus include the development of computational and experimental genomic methods and disease-focused research to better understand the genetic basis of cancer, neurodegenerative disease, and neuropsychiatric disease. In 2020, the NYGC also has directed its expertise to COVID-19 genomics research.
 W
WThe Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) was a USA based project that aimed at accelerating discovery in structural genomics and contribute to understanding biological function. Funded by the U.S. National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) between 2000 and 2015, its aim was to reduce the cost and time required to determine three-dimensional protein structures and to develop techniques for solving challenging problems in structural biology, including membrane proteins. Over a dozen research centers have been supported by the PSI for work in building and maintaining high-throughput structural genomics pipelines, developing computational protein structure prediction methods, organizing and disseminating information generated by the PSI, and applying high-throughput structure determination to study a broad range of important biological and biomedical problems.
 W
WA reference genome is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of the set of genes in one idealized individual organism of a species. As they are assembled from the sequencing of DNA from a number of individual donors, reference genomes do not accurately represent the set of genes of any single individual organism. Instead a reference provides a haploid mosaic of different DNA sequences from each donor. There are reference genomes for multiple species of viruses, bacteria, fungus, plants, and animals.
 W
WStructural genomics seeks to describe the 3-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by a given genome. This genome-based approach allows for a high-throughput method of structure determination by a combination of experimental and modeling approaches. The principal difference between structural genomics and traditional structural prediction is that structural genomics attempts to determine the structure of every protein encoded by the genome, rather than focusing on one particular protein. With full-genome sequences available, structure prediction can be done more quickly through a combination of experimental and modeling approaches, especially because the availability of large number of sequenced genomes and previously solved protein structures allows scientists to model protein structure on the structures of previously solved homologs.