 W
WAkoma Ntoso is an international technical standard for representing executive, legislative and judiciary documents in a structured manner using a domain specific, legal XML vocabulary.
 W
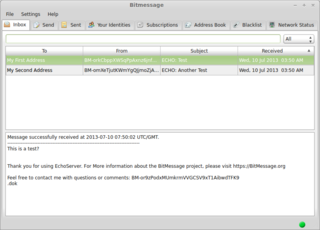
WBitmessage is a decentralized, encrypted, peer-to-peer, trustless communications protocol that can be used by one person to send encrypted messages to another person, or to multiple subscribers.
 W
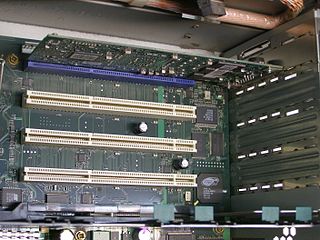
WCompactPCI is a computer bus interconnect for industrial computers, combining a Eurocard-type connector and PCI signaling and protocols. Boards are standardized to 3U or 6U sizes, and are typically interconnected via a passive backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. The connectors and the electrical rules allow for eight boards in a PCI segment. Multiple bus segments are allowed with bridges.
 W
WDigital Radio Mondiale is a set of digital audio broadcasting technologies designed to work over the bands currently used for analogue radio broadcasting including AM broadcasting, particularly shortwave, and FM broadcasting. DRM is more spectrally efficient than AM and FM, allowing more stations, at higher quality, into a given amount of bandwidth, using xHE-AAC audio coding format. Various other MPEG-4 and Opus codecs are also compatible, but the standard now specifies xHE-AAC.
 W
WDigital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
 W
WEMVA1288 is an electronic measurement standard developed by the European Machine Vision Association (EMVA). Its purpose is to define the methods to measure and characterize image sensors and cameras that are used in machine vision. It also provides rules and guidelines on how to report results and how to write device datasheets.
 W
WThe Enthusiast System Architecture (ESA) specification is a royalty-free protocol for two-way communication of PC components. Announced in 2007, ESA is used for monitoring temperature of computer hardware components such as the computer case and power supply unit. The first and last official release of the ESA specification is version 1.0, released in 2007. The ESA USB specification was created by a joint venture between Microsoft, Nvidia, Logitech and several other companies. The protocol remains open and royalty-free; but, no manufacturers are currently utilizing its specification at this time. The last known devices to utilize the ESA specifications were the Dell XPS 730x and Alienware Area-51 ALX computer systems that utilized the ESA specification to control its fans, LEDs, and motorized doors as well as the monitoring of available Water cooling systems such as the Dell XPS 730x's Dell H2Ceramic Cooling System.
 W
WKisekae Set System is a blending of art with computers originally designed to allow creation of virtual "paper dolls". Kisekae is short for "kisekae ningyou"; a Japanese term meaning "dress-up dolls". Unlike "computer art" which creates or displays traditional art via a computer, KiSS uses the computer as the medium, allowing the art to be not only animated, but also interactive.
 W
WMultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens AG, MMC is based on a surface-contact low pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack substrate assembly, and is therefore much smaller than earlier systems based on high pin-count parallel interfaces using traditional surface-mount assembly such as CompactFlash. Both products were initially introduced using SanDisk NOR-based flash technology. MMC is about the size of a postage stamp: 24 mm × 32 mm × 1.4 mm. MMC originally used a 1-bit serial interface, but newer versions of the specification allow transfers of 4 or 8 bits at a time. MMC can be used in many devices that can use Secure Digital (SD) cards.
 W
WThe Open Handset Alliance (OHA) is a consortium of 84 firms to develop open standards for mobile devices. Member firms include HTC, Sony, Dell, Intel, Motorola, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, Google, Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, T-Mobile, Sprint Corporation, Nvidia, and Wind River Systems.
 W
WPCI-X, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI local bus for higher bandwidth demanded mostly by servers and workstations. It uses a modified protocol to support higher clock speeds, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation. PCI-X 2.0 added speeds up to 533 MHz, with a reduction in electrical signal levels.
 W
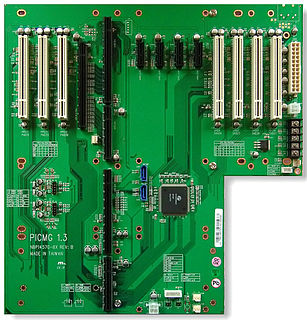
WPICMG 1.3 is a PICMG specification which is commonly referred to as SHB Express. SHB Express is a modernization of PICMG 1.0 single board computer specification. SHB Express, or System Host Board – Express, uses the same physical form factor as PICMG 1.0 boards. The board-to-backplane interfaces are PCI Express instead of PCI and ISA, although the use of PCI remains as an option.
 W
WQi is an open interface standard that defines wireless power transfer using inductive charging over distances of up to 4 cm, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium. The system uses a charging pad and a compatible device, which is placed on top of the pad, charging via resonant inductive coupling.
 W
WThe RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched interconnect technology. RapidIO supports messaging, read/write and cache coherency semantics. RapidIO fabrics guarantee in-order packet delivery, enabling power- and area- efficient protocol implementation in hardware. Based on industry-standard electrical specifications such as those for Ethernet, RapidIO can be used as a chip-to-chip, board-to-board, and chassis-to-chassis interconnect. The protocol is marketed as: RapidIO - the unified fabric for Performance Critical Computing, and is used in many applications such as Data Center & HPC, Communications Infrastructure, Industrial Automation and Military & Aerospace that are constrained by at least one of size, weight, and power (SWaP).
 W
WRezence is an interface standard developed by the Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) for wireless electrical power transfer based on the principles of magnetic resonance. The Rezence system consists of a single power transmitter unit (PTU) and one or more power receiver units (PRUs). The interface standard supports power transfer up to 50 watts, at distances up to 5 centimeters. The power transmission frequency is 6.78 MHz, and up to eight devices can be powered from a single PTU depending on transmitter and receiver geometry and power levels. A Bluetooth Smart link is defined in the A4WP system intended for control of power levels, identification of valid loads and protection of non-compliant devices.
 W
WThe RVU Alliance (RVUA) is a standards body created to manage the RVU protocol standard as used by manufacturers of consumer electronics to allow entertainment devices within the home to share their content with each other across a home network.
 W
WITU-T Recommendation X.1035 specifies a password-authenticated key agreement protocol that ensures mutual authentication of two parties by using a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to establish a symmetric cryptographic key. The use of Diffie-Hellman exchange ensures perfect forward secrecy—a property of a key establishment protocol that guarantees that compromise of a session key or long-term private key after a given session does not cause the compromise of any earlier session.
 W
WExtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is a communication protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML. It enables the near-real-time exchange of structured yet extensible data between any two or more network entities. Originally named Jabber, the protocol was developed by the eponymous open-source community in 1999 for near real-time instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Designed to be extensible, the protocol has been used also for publish-subscribe systems, signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming, the Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as the smart grid, and social networking services.