 W
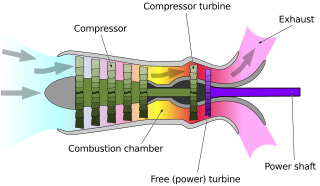
WA gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous and internal combustion engine. The main elements common to all gas turbine engines are:an upstream rotating gas compressor a combustor a downstream turbine on the same shaft as the compressor.
 W
WThe Chrysler turbine engine is a series of gas turbine engines developed by Chrysler intended to be used in road vehicles. In 1954, Chrysler Corporation disclosed the development and successful road testing of a production model Plymouth sport coupe which was powered by a turbine engine.
 W
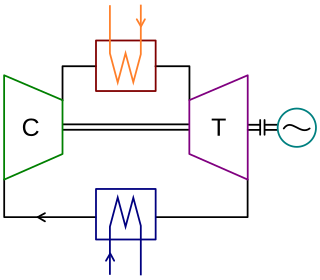
WA closed-cycle gas turbine is a turbine that uses a gas for the working fluid as part of a closed thermodynamic system. Heat is supplied from an external source. Such recirculating turbines follow the Brayton cycle.
 W
WIn aviation, exhaust mixer is a feature of many turbofan engines, where the bypass (cold/slow) air is mixed with the core (hot/fast) exhaust gases, before exhausting to atmospheric pressure through a common propelling nozzle.
 W
WA free-turbine turboshaft is a form of turboshaft or turboprop gas turbine engine where the power is extracted from the exhaust stream of a gas turbine by an independent turbine, downstream of the gas turbine and is not connected to the gas turbine. This is opposed to the power being extracted from the power spool via a gear box.
 W
WThe General Electric LM2500 is an industrial and marine gas turbine produced by GE Aviation. The LM2500 is a derivative of the General Electric CF6 aircraft engine.
 W
WThe General Electric LM6000 is a turboshaft aeroderivative gas turbine engine. The LM6000 is derived from the CF6-80C2 aircraft turbofan. It has additions and modifications designed to make it more suitable for marine propulsion, industrial power generation, and marine power generation use. These include an expanded turbine section to convert thrust into shaft power, supports and struts for mounting on a steel or concrete deck, and reworked controls packages for power generation. It has found wide use including peaking power plants, fast ferries and high speed cargo ship applications.
 W
WThe HAL HTFE-25 is a 25 kn turbofan engine under development by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The engine can be used in single engine trainer jets, business jets and UAVs weighing up to 5 tonnes and in twin engine configuration for same weighing up to 9 tonnes. Based on the technical feasibility, the market potential for engine is of 200-250 units.
 W
WThe Honeywell AGT1500 is a gas turbine engine. It is the main powerplant of the M1 Abrams series of tanks. The engine was originally designed and produced by the Lycoming Turbine Engine Division in the Stratford Army Engine Plant. In 1995, production was moved to the Anniston Army Depot in Anniston, Alabama, after the Stratford Army Engine Plant was shut down.
 W
WA jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an airbreathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, or pulse jet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.
 W
WThe Rolls-Royce Marine Olympus is a marine gas turbine based on the Rolls-Royce Olympus aircraft turbojet engine.
 W
WThe Rolls-Royce Marine Spey is a marine gas turbine based on the Rolls-Royce Spey and TF41 aircraft turbofan engines. The Marine Spey currently powers seven ship classes including the Royal Navy's Type 23 frigates and provides a power output of 19.5 MW. The Marine Spey incorporates technology from the Tay and RB211.
 W
WThe turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the turbo portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and the fan, a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to accelerate air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the turbine, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses the turbine. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust.
 W
WTurbine inlet air cooling is a group of technologies and techniques consisting of cooling down the intake air of the gas turbine. The direct consequence of cooling the turbine inlet air is power output augmentation. It may also improve the energy efficiency of the system. This technology is widely used in hot climates with high ambient temperatures that usually coincides with on-peak demand period.
 W
WThe turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the turbo portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and the fan, a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the gas turbine to accelerate air rearwards. Thus, whereas all the air taken in by a turbojet passes through the turbine, in a turbofan some of that air bypasses the turbine. A turbofan thus can be thought of as a turbojet being used to drive a ducted fan, with both of these contributing to the thrust.
 W
WThe turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine, typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.
 W
WA turboprop engine is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
 W
WA turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaftpower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.
 W
WThe Rolls-Royce WR-21 is an advanced gas turbine marine engine, designed with a view to powering the latest naval surface combatants of the partner nations, and currently fitted to the Type 45 destroyer of the Royal Navy.