 W
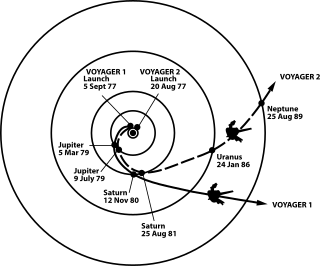
WThe Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic spaceprobes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Although their original mission was to study only the planetary systems of Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 2 continued on to Uranus and Neptune. The Voyagers now explore the outer boundary of the heliosphere in interstellar space; their mission has been extended three times and they continue to transmit useful scientific data. Neither Uranus nor Neptune has had a close-up picture taken by a probe other than Voyager 2.
 W
WVoyager 1 is a space probe that was launched by NASA on September 5, 1977. Part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System, Voyager 1 was launched 16 days after its twin, Voyager 2. Having operated for 43 years, 4 months and 2 days as of January 8, 2021 UTC [refresh], the spacecraft still communicates with the Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data is provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of 152.1 AU from Earth as of December 11, 2020, it is the most distant human-made object from Earth ⊕.
 W
WVoyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets. A part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, Voyager 1, on a trajectory that took longer to reach Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with Uranus and Neptune. It is the only spacecraft to have visited either of these two ice giant planets. Voyager 2 is the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve the Solar escape velocity, which will allow it to leave the Solar System.
 W
WThe Voyager Golden Record contains 116 images and a variety of sounds. The items for the record, which is carried on both the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft, were selected for NASA by a committee chaired by Carl Sagan of Cornell University. Included are natural sounds, musical selections from different cultures and eras, spoken greetings in 59 languages, human sounds like footsteps and laughter, and printed messages from President Jimmy Carter and U.N. Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim.
 W
WCosmic Ray Subsystem is an instrument aboard the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft of the NASA Voyager program, and it is an experiment to detect cosmic rays. The CRS includes a High-Energy Telescope System (HETS), Low-Energy Telescope System (LETS), and The Electron Telescope (TET). It is designed to detect energetic particles and some of the requirements were for the instrument to be reliable and to have enough charge resolution. It can also detect the energetic particles like protons from the Galaxy or Earth's Sun.
 W
WThe Farthest is an Irish documentary film that chronicles the history of the Voyager program and its two space probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, launched in 1977. In 2013, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the Solar System, reaching the interstellar space. This fact makes the program one of the humankind's greatest achievements. The story is presented through the testimonies of the NASA team involved. The film premiered on February 26, 2017 at the Dublin Film Festival where it won the Audience Award.
 W
WTimothy Ferris is an American science writer and the best-selling author of twelve books, including The Science of Liberty (2010) and Coming of Age in the Milky Way (1988), for which he was awarded the American Institute of Physics Prize and was nominated for the Pulitzer Prize. He also wrote The Whole Shebang: A State-of-the-Universe(s) Report (1997), a popular science book on the study of the universe. Ferris has produced three PBS documentaries - The Creation of the Universe, Life Beyond Earth, and Seeing in the Dark.
 W
WThe Voyager Golden Records are two phonograph records that were included aboard both Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977. The records contain sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth, and are intended for any intelligent extraterrestrial life form who may find them. The records are a sort of time capsule.
 W
WThe Grand Tour was a NASA program that would have sent two groups of robotic probes to all the planets of the outer Solar System. It called for four spacecraft, two of which would visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Pluto, while the other two would visit Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune. The enormous cost of the project, around $1 billion, led to its cancellation and replacement with Mariner Jupiter-Saturn, which became the Voyager program.
 W
WRaymond L. Heacock was an American engineer who spent his career at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory where he worked on the Ranger program in the 1960s and on the Voyager program in the 1970s and 1980s. A Caltech engineering graduate, he was the winner of the James Watt International Medal for 1979.
 W
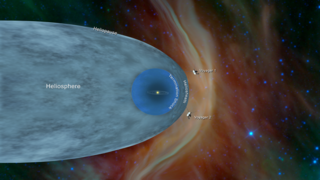
WThe heliosphere is the vast, bubble-like region of space that surrounds and is created by the Sun. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium. The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind. Outside the heliosphere, this solar plasma gives way to the interstellar plasma permeating the Milky Way. Radiation levels inside and outside the heliosphere differ; in particular, the galactic cosmic rays are less abundant inside the heliosphere, so that the planets inside are partly shielded from their impact. The word "heliosphere" is said to have been coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with first use of the word in scientific literature in 1967. The scientific study of the heliosphere is heliophysics, which includes space weather and space climate.
 W
WVoyager 1 is a space probe that was launched by NASA on September 5, 1977. Part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System, Voyager 1 was launched 16 days after its twin, Voyager 2. Having operated for 43 years, 4 months and 2 days as of January 8, 2021 UTC [refresh], the spacecraft still communicates with the Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data is provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of 152.1 AU from Earth as of December 11, 2020, it is the most distant human-made object from Earth ⊕.
 W
WVoyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets. A part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, Voyager 1, on a trajectory that took longer to reach Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with Uranus and Neptune. It is the only spacecraft to have visited either of these two ice giant planets. Voyager 2 is the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve the Solar escape velocity, which will allow it to leave the Solar System.
 W
WThe Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic spaceprobes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Although their original mission was to study only the planetary systems of Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 2 continued on to Uranus and Neptune. The Voyagers now explore the outer boundary of the heliosphere in interstellar space; their mission has been extended three times and they continue to transmit useful scientific data. Neither Uranus nor Neptune has had a close-up picture taken by a probe other than Voyager 2.
 W
WThe Multihundred-Watt radioisotope thermoelectric generators is a type of US radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for the Voyager spacecraft, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.
 W
WPale Blue Dot is a photograph of planet Earth taken on February 14, 1990, by the Voyager 1 space probe from a record distance of about 6 billion kilometers, as part of that day's Family Portrait series of images of the Solar System.
 W
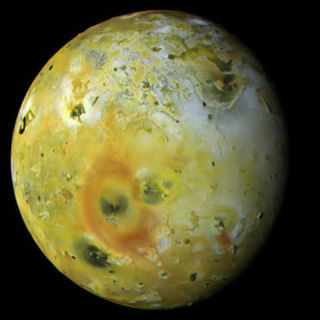
WPele is an active volcano on the surface of Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's trailing hemisphere at 18.7°S 255.3°W. A large, 300-kilometer (190 mi) tall volcanic plume has been observed at Pele by various spacecraft starting with Voyager 1 in 1979, though it has not been persistent. The discovery of the Pele plume on March 8, 1979 confirmed the existence of active volcanism on Io. The plume is associated with a lava lake at the northern end of the mountain Danube Planum. Pele is also notable for a persistent, large red ring circling the volcano resulting from sulfurous fallout from the volcanic plume.
 W
WPlasma Wave Subsystem, abbreviated PWS, is an instrument that is on board the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 unmanned probes of the Voyager program. The device is 16 channel step frequency receiver and a low-frequency waveform receiver that can measure electron density. The PWS uses the two long antenna in a V-shape on the spacecraft, which are also used by another instrument on the spacecraft. The instrument recorded data about the Solar System's gas giants, and about the outer reaches of the Heliosphere, and beyond. In the 2010s the PWS was used to play the "sounds of interstellar space" as the spacecraft can sample the local interstellar medium after they departed the Sun's heliosphere. The heliosphere is a region essentially under the influence of the Sun's solar wind, rather than the local interstellar environment, and is another way of understanding the Solar System in comparison to the objects gravitationally bound around Earth's Sun.
 W
WCarolyn C. Porco is an American planetary scientist who explores the outer Solar System, beginning with her imaging work on the Voyager missions to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in the 1980s. She led the imaging science team on the Cassini mission in orbit around Saturn. She is an expert on planetary rings and the Saturnian moon, Enceladus.
 W
WEdward Carroll Stone is an American space scientist, professor of physics at the California Institute of Technology, and former director of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
 W
W