 W
WA compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
 W
WAn air compressor is a pneumatic device that converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. By one of several methods, an air compressor forces more and more air into a storage tank, increasing the pressure. When the tank's pressure reaches its engineered upper limit, the air compressor shuts off. The compressed air, then, is held in the tank until called into use. The energy contained in the compressed air can be used for a variety of applications, utilizing the kinetic energy of the air as it is released and the tank depressurizes. When tank pressure reaches its lower limit, the air compressor turns on again and re-pressurizes the tank. An air Compressor must be differentiated from a pump because it works for any gas/air, while pumps work on a liquid.
 W
WAjax is a brand of integral engine / compressor manufactured by the original equipment manufacturer, Cooper Machinery Services ). Ajax is the oldest continuous engine product line manufactured in the United States and has been utilized in the oil and gas industry for 130+ years.
 W
WAtlas Machine and Supply, Inc., founded in 1907, is one of the largest heavy-capacity industrial machinery engineering, manufacturing and remanufacturing centers in the United States. The firm also designs and repairs industrial compressed air systems compressors and related equipment, and offers full compressor rebuilding and rental engineering capabilities. The company had 210 employees as of January 2015. The headquarters are in Louisville, Kentucky, highlighted by a 100,000 sq. ft. facility. Additional plants and repair centers are located in Cincinnati, Ohio, Columbus, Ohio, and in Evansville, Indiana. In 2014 Atlas opened its fifth location, in Indianapolis, Indiana.
 W
WAn axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine.
 W
WA booster pump is a machine which will increase the pressure of a fluid. They may be used with liquids or gases, but the construction details will vary depending on the fluid. A gas booster is similar to a gas compressor, but generally a simpler mechanism which often has only a single stage of compression, and is used to increase pressure of a gas already above ambient pressure. Two-stage boosters are also made. Boosters may be used for increasing gas pressure, transferring high pressure gas, charging gas cylinders and scavenging.
 W
WBurckhardt Compression AG is a Winterthur-based Swiss firm specialising in reciprocating compressors. According to the enterprise, it is the world leader in this field, with its products being used around the world in various industrial applications.
 W
WCentrifugal compressors, sometimes called radial compressors, are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery.
 W
WCentrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exits.
 W
WThe relatively recently developed conical screw compressor is a type of rotary-screw compressor using a different topology from the typical dual-screw type, in effect it is a conical spiral extension of a gerotor. Because of this it does not have the inherent "blow-hole" leakage path which in typical screw compressors is responsible for significant leakage through the assembly and makes low-speed operation impractical. This theoretically allows much smaller rotors to have practical efficiency since at smaller sizes the leakage area does not become as large a portion of the pumping area as in straight screw compressors. In conjunction with the decreasing diameter of the cone shaped rotor this may also allows much higher compression ratios to be achieved in a single stage.
 W
WA diving air compressor is a gas compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a breathing gas.
 W
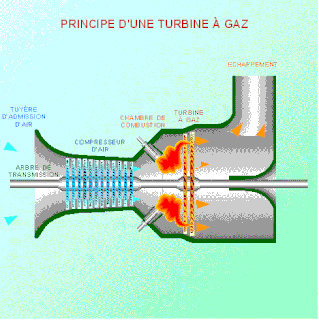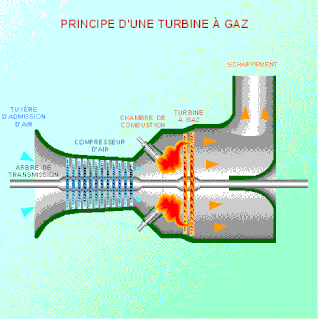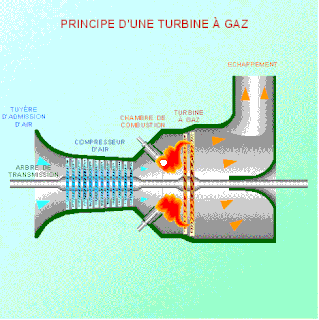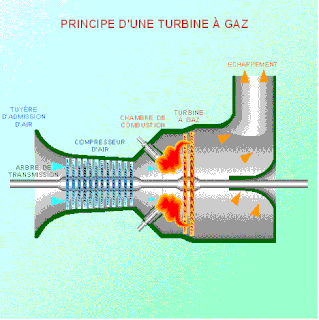
WAs the name suggests, gas turbine engine compressors provide the compression part of the gas turbine engine thermodynamic cycle. There are three basic categories of gas turbine engine compressor: axial compressor, centrifugal compressor and mixed flow compressor. A fourth, unusual, type is the free-piston gas generator, which combines the functions of compressor and combustion chamber in one unit.
 W
WA gerotor is a positive displacement pump. The name gerotor is derived from "generated rotor". A gerotor unit consists of an inner and outer rotor. The inner rotor has n teeth, while the outer rotor has n+1 teeth; with n defined as a natural number greater than or equal to 2. The axis of the inner rotor is offset from the axis of the outer rotor and both rotors rotate on their respective axes. The geometry of the two rotors partitions the volume between them into n different dynamically-changing volumes. During the assembly's rotation cycle, each of these volumes changes continuously, so any given volume first increases, and then decreases. An increase creates a vacuum. This vacuum creates suction, and hence, this part of the cycle is where the inlet is located. As a volume decreases compression occurs. During this compression period, fluids can be pumped, or, if they are gaseous fluids, compressed.
 W
WA hydride compressor is a hydrogen compressor based on metal hydrides with absorption of hydrogen at low pressure, releasing heat, and desorption of hydrogen at high pressure, absorbing heat, by raising the temperature with an external heat source like a heated waterbed or electric coil.
 W
WAn ionic liquid piston compressor, ionic compressor or ionic liquid piston pump is a hydrogen compressor based on an ionic liquid piston instead of a metal piston as in a piston-metal diaphragm compressor.
 W
WA jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an airbreathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, or pulse jet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.
 W
WA fan is a powered machine used to create a flow of air. A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades, which act on the air. The rotating assembly of blades and hub is known as an impeller, rotor, or runner. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing, or case. This may direct the airflow, or increase safety by preventing objects from contacting the fan blades. Most fans are powered by electric motors, but other sources of power may be used, including hydraulic motors, handcranks, and internal combustion engines.
 W
WA reciprocating compressor or piston compressor is a positive-displacement compressor that uses pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure.
 W
WThe Rotary Piston Machine is a proposed form of machine. It can be used either to transform pressure into rotational motion, or the converse - rotational motion into pressure (pump). It is still in development, but has possible applications in fields requiring oil, fuel or water pumps, as well as pumps for non-abrasive fluids when moderate or high pressure is required. For instance: Hydraulics, fluid and gas transport systems, presses, fuel injection, irrigation, heating systems, hydraulic lifts, water jet engines, hydro- and pneumatic engines, and medical pumps. The machine's inventor is Boris I. Schapiro, along with co-inventors Lev B. Levitin and Naum Kruk.
 W
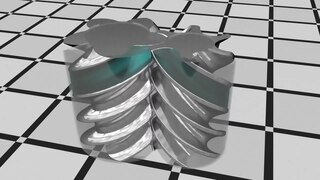
WA rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.
 W
WA scroll compressor is a device for compressing air or refrigerant. It is used in air conditioning equipment, as an automobile supercharger and as a vacuum pump. Many residential central heat pump and air conditioning systems and a few automotive air conditioning systems employ a scroll compressor instead of the more traditional rotary, reciprocating, and wobble-plate compressors.
 W
WA trompe is a water-powered air compressor, commonly used before the advent of the electric-powered compressor. A trompe is somewhat like an airlift pump working in reverse.