 W
WThe Artificio de Juanelo was the name of two devices built in Toledo in the 16th century by Juanelo Turriano. They were designed to supply the city with a source of readily available water by lifting it from the Tagus (Tajo) river to the Alcázar. Now in ruins, the precise details of the operation of the devices are unknown, but at the time they were considered engineering wonders.
 W
WAn autogyro, also known as a gyroplane or gyrocopter, is a type of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. Forward thrust is provided independently, by an engine-driven propeller. While similar to a helicopter rotor in appearance, the autogyro's rotor must have air flowing across the rotor disc to generate rotation, and the air flows upwards through the rotor disc rather than down.
 W
WA capstan is a vertical-axled rotating machine developed for use on sailing ships to multiply the pulling force of seamen when hauling ropes, cables, and hawsers. The principle is similar to that of the windlass, which has a horizontal axle.
 W
WEl Ajedrecista is an automaton built in 1912 by Leonardo Torres y Quevedo, one of the first autonomous machines capable of playing chess. As opposed to the human-operated The Turk and Ajeeb, El Ajedrecista was a true automaton built to play chess without human guidance. It played an endgame with three chess pieces, automatically moving a white king and a rook to checkmate the black king moved by a human opponent.
 W
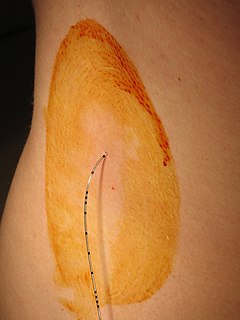
WEpidural administration is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians and nurse anesthetists to administer local anesthetic agents, analgesics, diagnostic medicines such as radiocontrast agents, and other medicines such as glucocorticoids. Epidural administration involves the placement of a catheter into the epidural space, which may remain in place for the duration of the treatment. The technique of intentional epidural administration of medication was first described in 1921 by Spanish military surgeon Fidel Pagés. In the United States, over 50% of childbirths involve the use of epidural anesthesia.
 W
WA farthingale is one of several structures used under Western European women's clothing in the 16th and 17th centuries to support the skirts in the desired shape and enlarge the lower half of the body. It originated in Spain in the fifteenth century. Farthingales served important social and cultural functions for women in Renaissance Europe as they were used, primarily by court women, to show their high social position and wealth. This is because these structures increased the amount of expensive fabrics used in the gowns that covered them.
 W
WThe full-rigged pinnace was the larger of two types of vessel called a pinnace in use from the sixteenth century.
 W
WThe guitarra morisca or mandora medieval is a plucked string instrument. It is a lute that has a bulging belly and a headstock as sickle. Part of that characterization came from a c. 1330 poem, Libra de Buen Amor by Juan Ruiz, which described the "Moorish gittern" as "corpulent". The use of the adjective morisca tacked to guitarra may have been to differentiate it from the commonly seen Latin European variety, when the morisca was seen on a limited basis during the 14th century.
 W
WThe Hiriko is a folding two-seat urban electric car that was under development by the Hiriko Driving Mobility consortium in the Basque Country of northern Spain. The electric car was to be the commercial implementation of the CityCar project developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Media Lab since 2003. The name Hiriko comes from the Basque word for "urban" or "from the city".
 W
WIctíneo I was a pioneering submarine constructed in Barcelona, Spain in 1858–1859 by engineer Narcís Monturiol.
 W
WIctíneo II was a pioneering submarine launched in 1864 by the Spanish engineer Narcís Monturiol and was the first air independent and combustion powered submarine and was the first submarine to overcome the basic problems of machine powered underwater navigation.
 W
WLaryngoscopy is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during general anaesthesia or cardiopulmonary resuscitation or for surgical procedures on the larynx or other parts of the upper tracheobronchial tree.
 W
WThe Libélula Viblandi, or Libélula Española was an early helicopter developed from 1924 by Federico Cantero Villamil, a Spanish civil engineer also known for the dams he constructed and planned along the river Duero.
 W
WMiquelet lock is a modern term used by collectors and curators for a type of firing mechanism used in muskets and pistols. It is a distinctive form of snaplock, originally as a flint-against-steel ignition form, once prevalent in Spain, Portugal, Italy, the Balkans, North Africa, the Ottoman Empire and throughout Spain's colonies from the late 16th to the mid 19th centuries.
 W
WA Molotov cocktail, also known as a petrol bomb, gasoline bomb, bottle bomb, poor man's grenade, fire bomb, fire bottle or just Molotov, sometimes shortened as Molly, is a generic name used for a variety of bottle-based improvised incendiary weapons.
 W
WA rib vault or ribbed vault is an architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs. Variations were used in Roman architecture, Byzantine architecture, Islamic architecture, Romanesque architecture, and especially Gothic architecture. Thin stone panels fill the space between the ribs. This greatly reduced the weight and thus the outward thrust of the vault. The ribs transmit the load downward and outward to specific points, usually rows of columns or piers. This feature allowed architects of Gothic cathedrals to make higher and thinner walls and much larger windows.
 W
WSherry is a fortified wine made from white grapes that are grown near the city of Jerez de la Frontera in Andalusia, Spain. Sherry is produced in a variety of styles made primarily from the Palomino grape, ranging from light versions similar to white table wines, such as Manzanilla and fino, to darker and heavier versions that have been allowed to oxidise as they age in barrel, such as Amontillado and oloroso. Sweet dessert wines are also made from Pedro Ximénez or Moscatel grapes, and are sometimes blended with Palomino-based sherries.
 W
WSpanish-suited playing cards or Spanish-suited cards have four suits and a deck is usually made up of 40 or 48 cards. It is categorized as a Latin-suited deck and has strong similarities with the Italian-suited deck and less to the French deck. Spanish-suited cards are used in Spain, southern Italy, parts of France, Hispanic America, North Africa, and the Philippines.
 W
WStamped paper is an often-foolscap piece of paper which bears a pre-printed revenue stamp. Stamped papers are not a form of postal stationery. The use of stamped paper in the American colonies was so unpopular that it has been credited with sowing the seeds of the American Revolution.
 W
WThe stratonautical space suit was a pressurised suit designed by Colonel Emilio Herrera in 1935 to be worn during a stratospheric flight using an open basket balloon scheduled for the following year. It is considered one of the antecedents of the space suit.
 W
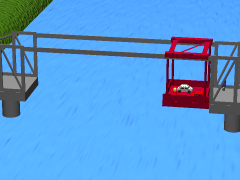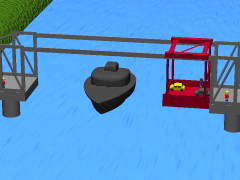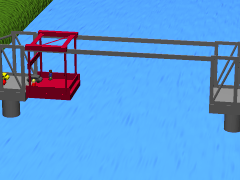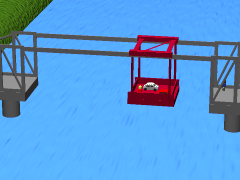
WA transporter bridge, also known as a ferry bridge or aerial transfer bridge, is a type of movable bridge that carries a segment of roadway across a river. The gondola is slung from a tall span by wires or a metal frame. The design has been used to cross navigable rivers or other bodies of water, where there is a requirement for ship traffic to be able to pass. This has been a rare type of bridge, with fewer than two dozen built. There are just twelve that continue to be used today, including one converted into a lift bridge and one designed as, but not yet operating as, a transporter bridge.
 W
WThe Whirlpool Aero Car or Spanish Aero Car is a cable car located in Niagara Falls, Ontario that transports passengers over a section of the Niagara River referred to as the Niagara Whirlpool. The system was designed by Spanish engineer Leonardo Torres Quevedo and has been upgraded several times since 1916. The system uses one car that carries 35 standing passengers over a one-kilometre trip.