 W
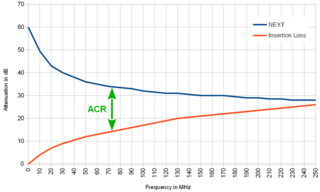
WAttenuation-to-crosstalk ratio (ACR) is a parameter that is measured when testing a communication link, which represents the overall performance of the cable. AcR is a mathematical formula that calculates the ratio of attenuation to near-end crosstalk for each combination of cable pairs. ACR is expressed as a figure in decibels (dB), between the signal attenuation produced by a wire or cable transmission medium and the near-end crosstalk (NEXT). In order for a signal to be received with an acceptable bit error rate, the attenuation and the crosstalk must both be minimized. Crosstalk can be reduced by ensuring that twisted-pair wiring is tightly twisted and is not crushed, and by ensuring that connectors between wire and cable media are properly rated and installed.
 W
WBandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to passband bandwidth or baseband bandwidth. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency.
 W
WIn electrical engineering and telecommunications, the center frequency of a filter or channel is a measure of a central frequency between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies. It is usually defined as either the arithmetic mean or the geometric mean of the lower cutoff frequency and the upper cutoff frequency of a band-pass system or a band-stop system.
 W
WA communication channel refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in telecommunications and computer networking. A channel is used to convey an information signal, for example a digital bit stream, from one or several senders to one or several receivers. A channel has a certain capacity for transmitting information, often measured by its bandwidth in Hz or its data rate in bits per second.
 W
WCommunication physics is one of the applied branches of physics. It deals with various kinds of communication systems.
 W
WIn telecommunications and electrical engineering, electrical length refers to the length of an electrical conductor in terms of the phase shift introduced by transmission over that conductor at some frequency.
 W
WIn telecommunications, extinction ratio (re) is the ratio of two optical power levels of a digital signal generated by an optical source, e.g., a laser diode. The extinction ratio may be expressed as a fraction, in dB, or as a percentage. It may be given by
 W
WA frequency band is an interval in the frequency domain, delimited by a lower frequency and an upper frequency. The term may refer to a radio band or an interval of some other spectrum.
 W
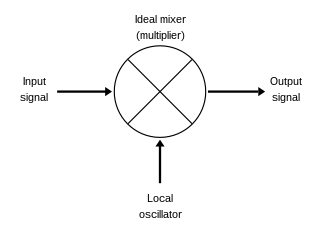
WIn electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is a nonlinear electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer.
 W
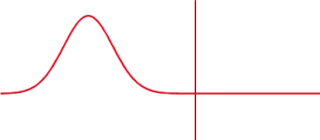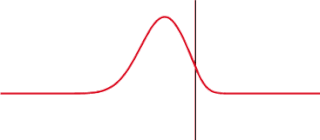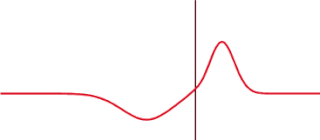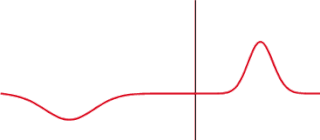
WIn a distribution, full width at half maximum (FWHM) is the difference between the two values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value. In other words, it is the width of a spectrum curve measured between those points on the y-axis which are half the maximum amplitude.
 W
WIn communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a communication channel, result in no intersymbol interference or ISI. It provides a method for constructing band-limited functions to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference.
 W
WIn signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, specifies a sampling rate. In units of samples per second its value is twice the highest frequency (bandwidth) in Hz of a function or signal to be sampled. With an equal or higher sampling rate, the resulting discrete-time sequence is said to be free of the distortion known as aliasing. Conversely, for a given sample rate, the corresponding Nyquist frequency in Hz is the largest bandwidth that can be sampled without aliasing, and its value is one-half the sample-rate. Note that the Nyquist rate is a property of a continuous-time signal, whereas Nyquist frequency is a property of a discrete-time system.
 W
WThe Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is a theorem in the field of signal processing which serves as a fundamental bridge between continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals. It establishes a sufficient condition for a sample rate that permits a discrete sequence of samples to capture all the information from a continuous-time signal of finite bandwidth.
 W
WPhase-fired control (PFC), also called phase cutting or "phase angle control", is a method for power limiting, applied to AC voltages. It works by modulating a thyristor, SCR, triac, thyratron, or other such gated diode-like devices into and out of conduction at a predetermined phase of the applied waveform.
 W
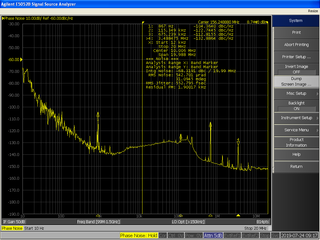
WIn signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity ("jitter"). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock.
 W
WIn signal processing and telecommunication, pulse duration is the interval between the time, during the first transition, that the amplitude of the pulse reaches a specified fraction (level) of its final amplitude, and the time the pulse amplitude drops, on the last transition, to the same level.
 W
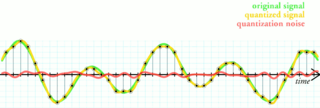
WQuantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and truncation are typical examples of quantization processes. Quantization is involved to some degree in nearly all digital signal processing, as the process of representing a signal in digital form ordinarily involves rounding. Quantization also forms the core of essentially all lossy compression algorithms.
 W
WIn physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of a wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave, with each expressed as phasors. For example, it is used in optics to calculate the amount of light that is reflected from a surface with a different index of refraction, such as a glass surface, or in an electrical transmission line to calculate how much of the electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient. The reflectance of a system is also sometimes called a "reflection coefficient".
 W
WIn signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. In electronics and telecommunications, it refers to any time varying voltage, current or electromagnetic wave that carries information. A signal may also be defined as an observable change in a quality such as quantity.
 W
WSignal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analysing, modifying, and synthesizing signals such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques can be used to improve transmission, storage efficiency and subjective quality and to also emphasize or detect components of interest in a measured signal.
 W
WA television channel is a terrestrial frequency or virtual number over which a television station or television network is distributed. For example, in North America, "channel 2" refers to the terrestrial or cable band of 54 to 60 MHz, with carrier frequencies of 55.25 MHz for NTSC analog video (VSB) and 59.75 MHz for analog audio (FM), or 55.31 MHz for digital ATSC (8VSB). Channels may be shared by many different television stations or cable-distributed channels depending on the location and service provider
 W
WA trellis is a graph whose nodes are ordered into vertical slices (time) with each node at each time connected to at least one node at an earlier and at least one node at a later time. The earliest and latest times in the trellis have only one node.