 W
WAlbert Barnes & Co were Rhyl based manufacturers of miniature steam locomotives. A number of them are preserved at the Rhyl Miniature Railway. Albert Barnes was the owner of Rhyl Amusements Ltd. Six 4-4-2 locomotives were built.Locomotive list
 W
WBangladesh Railway Class 3200 is a class of metre-gauge diesel-hydraulic locomotive in Bangladesh, operated by Bangladesh Railway. They are the first metre-gauge diesel-hydraulic locomotives of Bangladesh.
 W
WA Bo-Bo-Bo or Bo′Bo′Bo′ is a locomotive with three independent two-axle bogies with all axles powered by separate traction motors. In the AAR system, this is simplified to B-B-B.
 W
WA boxcab, in railroad terminology, is a locomotive in which the machinery and crew areas are enclosed in a box-like superstructure. It is a term mostly used in North America while in Victoria (Australia), such locomotives have been nicknamed "butterboxes". Boxcabs may use any source of power but most are diesel or electric locomotives. Few steam locomotives are so described but the British SR Leader class was a possible exception. Most American boxcabs date from before World War II, when the earliest boxcabs were often termed "oil-electrics" to avoid the use of the German name "Diesel" due to propaganda purposes.
 W
WThe ČD Class 340 is a multisystem electric locomotive, designed for use between the Czech Republic and Austria. A total of three locomotives were rebuilt from the earlier 240 class. Since 2007, all three have been allocated to ČD Cargo.
 W
WCo-Bo or Co′Bo′ is a wheel arrangement in the UIC classification system for railway locomotives. It features two uncoupled bogies. The "Co" bogie has three driven axles and the "Bo" bogie has two.
 W
WThe ČSD Class ES 499.2 and DR Class 230 are multisystem electric locomotives, manufactured by Škoda Plzeň from 1988 to 1991. The locomotives were developed to work international trains between Czechoslovakia and the DDR. The locomotives are similar to the 163, 263 and 363 classes, but differ in electrical equipment, due to the need to operate across borders. 35 were produced, originally split between the Czechoslovak State Railways (ČSD) and the Deutsche Reichsbahn.
 W
WRailcar class M 290.0, named after an express train which it served as Slovenská strela was manufactured by Tatra Kopřivnice in 1936 for Czechoslovak State Railways.
 W
WThe ČSD Class T 466.2/3, later ČD and ZSSK class 742/3, are a class of diesel locomotives, constructed by ČKD Praha between 1977 and 1986.
 W
WA dock shunter, or "dock tank", is a locomotive used for shunting wagons in the vicinity of docks. It is usually of 0-4-0 or 0-6-0 wheel arrangement and has a short wheelbase and large buffers. These features make it suitable for negotiating sharp curves.
 W
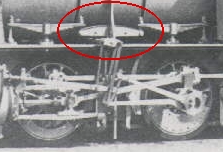
WAn equalising beam, equalising lever or equalising bar links the suspension of two or more adjacent axles of a vehicle with more than two axles, especially railway locomotives. Its job is to provide 'compensated' springing, i.e. to ensure an even and statically determinate distribution of load to all the axles on uneven terrain or poorly laid track. The function of an equalising lever thus corresponds roughly to that of axle compensators or rockers (Achswippen).
 W
WJumper cables are electric cables to connect two rail or road vehicles.
 W
WSS Lichtenfels was an early example of a modern heavy-lift ship. She was launched in 1929 in Germany for DDG Hansa. She was equipped with a 120 t boom crane capable of lifting fully assembled railway locomotives, which were shipped to India.
 W
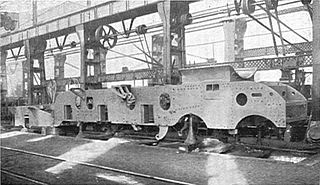
WA locomotive frame is the structure that forms the backbone of the railway locomotive, giving it strength and supporting the superstructure elements such as a cab, boiler or bodywork. The vast majority of locomotives have had a frame structure of some kind. The frame may in turn be supported by axles directly attached to it, or it may be mounted on bogies (UK) / trucks (US), or a combination of the two. The bogies in turn will have frames of their own.
 W
WThe M-497 was an experimental jet-powered railcar test bed of the New York Central Railroad, developed and tested in 1966 in the United States. Two second-hand General Electric J47-19 jet engines, originally used as boosters for the Convair B-36 Peacemaker intercontinental bomber, were mounted atop an existing Budd Rail Diesel Car, an RDC-3 of coach and baggage-mail configuration which had received a streamlined front cowling. The construct was then successfully sent on test runs over the existing tracks between Butler, Indiana, and Stryker, Ohio. The line had been chosen for its arrow-straight layout and good condition, but otherwise unmodified track. On July 23, 1966, the car reached a speed of 183.68 mph (295.6 km/h), an American rail speed record that still stands today.
 W
WThe Multi-purpose vehicle is a purpose built departmental derivative of a diesel multiple unit constructed for use as a rail adhesion vehicle by NI Railways in Northern Ireland.
 W
WThe ÖBB 1014 and 1114 classes are multi system electric locomotives, constructed between 1993 and 1994. The locomotives were designed to operate from Austria, to the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary.
 W
WIn rail transport, the expression power car may refer to either of two distinct types of rail vehicle:a vehicle that propels, and commonly also controls, a passenger train or tram, often as the lead vehicle; a vehicle equipped with machinery for supplying heat or electrical power to other parts of a train.
 W
WThe SNCF Class A1AA1A 68500 is a class of 28 mixed traffic diesel locomotives originally intended for operating main line freight services on the Paris – Chalindrey – Belfort route. They are similar to the Class A1AA1A 68000 but with an AGO engine rather than the Sulzer fitted to the latter. 5 members of the class were rebuilt as A1AA1A 68000 by replacing the AGO prime mover with Sulzer engines, thought to be those formerly used in the BR Class 48 locomotives, D1702–1706. Subsequently, 13 members of the class 68000 were rebuilt as 68500 in 1993. The last was withdrawn from traffic in July 2011.
 W
WThe Stadler SPATZ or Schmalspur Panorama Trieb Zug is a narrow gauge multiple unit manufactured by Stadler Rail. It consists of three articulated sections. The centre section is high floor and contains the motors and traction equipment. The centre section is fitted with extra large panoramic windows. The end sections are similar to those of the Stadler GTW. They are low-floor and have a bogie at the outer end and are supported by the central section at the inner end.
 W
WA turbojet train is a train powered by turbojet engines. Like a jet aircraft, but unlike a gas turbine locomotive, the train is propelled by the jet thrust of the engines, rather than by its wheels. Only a handful of jet-powered trains have been built, for experimental research in high-speed rail.
 W
WThe W44 Concentrate Train conveyed lead and zinc concentrates from the Zinc Corporation owned mines at Broken Hill, New South Wales to the Sulphide Corporation Cockle Creek Smelter south of Newcastle.
 W
WWagon Pars is an Iranian train and locomotive manufacturer established in 1974, in Arak. Products include locomotives, trains, metros, freight and fuel railroad cars, and equipment for passenger boarding of aircraft. It is the largest rolling stock manufacturer in the Middle East.
 W
WA work train or departmental train is one or more rail cars intended for internal non-revenue use by the railroad's operator. Work trains serve functions such as track maintenance, maintenance of way, revenue collection, system cleanup and waste removal, heavy duty hauling, and crew member transport.