 W
WDennis Vincent Brutus was a South African activist, educator, journalist and poet best known for his campaign to have South Africa banned from the Olympic Games due to its controversial racial policy of apartheid.
 W
WClimate justice is a term used to frame global warming as an ethical and political issue, rather than one that is purely environmental or physical in nature. This is done by relating the causes and effects of climate change to concepts of justice, particularly environmental justice and social justice. Climate justice examines concepts such as equality, human rights, collective rights, and the historical responsibilities for climate change. Climate justice actions can include the growing global body of legal action on climate change issues. In 2017, a report of the United Nations Environment Programme identified 894 ongoing legal actions worldwide.
 W
WCompassionate conservation is a discipline which aims to combine the fields of conservation and animal welfare. Historically, these two fields have been considered separate and sometimes contradictory to each other. The foundational principles of compassionate conservation are: "Do No Harm; Individuals Matter; Inclusivity; Peaceful Coexistence".
 W
WNature conservation is the moral philosophy and conservation movement focused on protecting species from extinction, maintaining and restoring habitats, enhancing ecosystem services, and protecting biological diversity. A range of values underlie conservation, which can be guided by biocentrism, anthropocentrism, ecocentrism, and sentientism. There has recently been a movement towards evidence-based conservation which calls for greater use of scientific evidence to improve the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
 W
WDegrowth is a term used for both a political, economic, and social movement as well as a set of theories that critiques the paradigm of economic growth. It is based on ideas from a diverse range of lines of thought such as political ecology, ecological economics, feminist political ecology, and environmental justice. Degrowth emphasizes the need to reduce global consumption and production and advocates a socially just and ecologically sustainable society with well-being replacing GDP as the indicator of prosperity. Degrowth highlights the importance of autonomy, care work, self-organization, commons, community, localism, work sharing, happiness and conviviality.
 W
WDeep ecology is an environmental philosophy which promotes the inherent worth of all living beings regardless of their instrumental utility to human needs, plus the restructuring of modern human societies in accordance with such ideas.
 W
WEnvironmental personhood is a legal concept which designates certain environmental entities the status of a legal person. This assigns to these entities, the rights, protections, privileges, responsibilities and legal liability of a legal personality. Environmental personhood emerged from the evolution of legal focus in pursuit of the protection of nature. Over time, focus has evolved from human interests in exploiting nature, to protecting nature for future human generations, to conceptions that allow for nature to be protected as intrinsically valuable. This concept can be used as a vehicle for recognising Indigenous peoples' relationships to natural entities, such as rivers. Environmental personhood, which assigns nature certain rights, concurrently provides a means to individuals or groups such as Indigenous peoples to fulfill their human rights.
 W
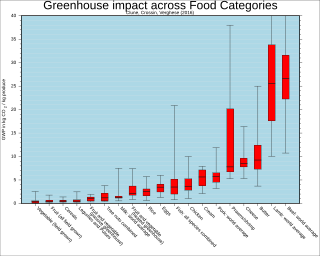
WEnvironmental vegetarianism is the practice of vegetarianism when motivated by the desire to create a sustainable diet that avoids the negative environmental impact of meat production. Livestock as a whole is estimated to be responsible for around 18% of global greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, significant reduction in meat consumption has been advocated by, among others, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in their 2019 special report and as part of the 2017 World Scientists' Warning to Humanity.
 W
WThe ethics of uncertain sentience refers to questions surrounding the treatment of and moral obligations towards individuals whose sentience—the capacity to subjectively sense and feel—and resulting ability to experience pain is uncertain; the topic has been particularly discussed within the field of animal ethics, with the precautionary principle frequently invoked in response.
 W
WPeter H. Gleick is an American scientist working on issues related to the environment. He works at the Pacific Institute in Oakland, California, which he co-founded in 1987. In 2003 he was awarded a MacArthur Fellowship for his work on water resources. Among the issues he has addressed are conflicts over water resources, water and climate change, development, and human health.
 W
WIndividual action on climate change can include personal choices in many areas, such as diet, means of long- and short-distance travel, household energy use, consumption of goods and services, and family size. Individuals can also engage in local and political advocacy around issues of climate change.
 W
WLeave No Trace is a set of outdoor ethics created by the Leave No Trace Center of Outdoor Ethics promoting conservation in the outdoors. It consists of seven principles:plan ahead and prepare, travel and camp on durable surfaces, dispose of waste properly, leave what you find, minimize campfire impacts, respect wildlife, be considerate of other visitors.
 W
WThe Millennium Seed Bank Partnership, formerly known as the Millennium Seed Bank Project, is the largest ex situ plant conservation programme in the world coordinated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. After being awarded a Millennium Commission grant in 1995, the project commenced in 1996, and is now housed in the Wellcome Trust Millennium Building situated in the grounds of Wakehurst Place, West Sussex. Its purpose is to provide an "insurance policy" against the extinction of plants in the wild by storing seeds for future use. The storage facilities consist of large underground frozen vaults preserving the world's largest wild-plant seedbank or collection of seeds from wild species. The project had been started by Dr Peter Thompson and run by Paul Smith after the departure of Roger Smith. Roger Smith was awarded the OBE in 2000 in the Queen's New Year Honours for services to the Project.
 W
WThe 50th Anniversary National Wilderness Conference is the culminating commemorative event for the 50th anniversary of the Wilderness Act. The conference was held in Albuquerque, NM, from October 15-19, 2014.
 W
WNIMBY, an acronym for the phrase "not in my back yard", or Nimby, is a characterization of opposition by residents to proposed developments in their local area, as well as support for strict land use regulations. It carries the connotation that such residents are only opposing the development because it is close to them and that they would tolerate or support it if it were built farther away. The residents are often called Nimbys, and their viewpoint is called Nimbyism.
 W
WJadav "Molai" Payeng is an environmental activist and forestry worker from Majuli, popularly known as the Forest Man of India. Over the course of several decades, he has planted and tended trees on a sandbar of the river Brahmaputra turning it into a forest reserve. The forest, called Molai forest after him, is located near Kokilamukh of Jorhat, Assam, India and encompasses an area of about 1,360 acres / 550 hectares. In 2015, he was honoured with Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award in India. He was born in the indigenous Mising tribe of Assam.
 W
WPower Shift is an annual youth summit which has been held in New Zealand, Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States. Other Power Shift Conferences are also being organised by members of the International Youth Climate Movement including Africa, Japan and India. The focus of the events is on climate change policy.
 W
WPractical Ethics is a 1979 book by the moral philosopher Peter Singer, which is an introduction to applied ethics. The book has been translated into a number of languages.
 W
WThe predation problem or predation argument refers to the consideration of the harms experienced by animals due to predation as a moral problem, that humans may or may not have an obligation to work towards preventing. Discourse on this topic has, by and large, been held within the disciplines of animal and environmental ethics. The issue has particularly been discussed in relation to animal rights and wild animal suffering. Some critics have considered an obligation to prevent predation as untenable or absurd and have used the position as a reductio ad absurdum to reject the concept of animal rights altogether. Others have criticized any obligation implied by the animal rights position as environmentally harmful.
 W
WAlicia Helda Puleo García is an Argentine-born feminist philosopher based in Spain. She is known for the development of ecofeminist thinking. Among her main publications is Ecofeminismo para otro mundo posible.
 W
WPhilip David Radford is an American activist who served as the executive director of Greenpeace USA. He is the founder and President of Progressive Power Lab, an organization that incubates companies and non-profits that build capacity for progressive organizations, including the Progressive Multiplier Fund and Membership Drive. Radford is a co-founder of the Democracy Initiative, was founder and executive director of Power Shift, and is a board member of the Mertz Gilmore Foundation. He has a background in grassroots organizing, corporate social responsibility, climate change, and clean energy.
 W
WThe relationship between animal ethics and environmental ethics concerns the differing ethical consideration of individual nonhuman animals—particularly those living in spaces outside of direct human control—and conceptual entities such as species, populations and ecosystems. The intersection of these two fields is a prominent component of vegan discourse.
 W
WShark tourism is a way for tourists to see sharks in the ocean rather than in an aquarium. It is a form of eco-tourism intended to show that local shark species are more valuable alive than dead. Instead of opting for a one time economic benefit of harvesting sharks for their body parts, communities are enabled to assist tourists who want to see live sharks. People can get close to the sharks by free- or scuba diving or entering the water in a protective cage.
 W
WSwami Sundaranand was an Indian Yogi, photographer, author and mountaineer who lectured widely in India on threats to the Ganges River and the loss of Himalayan glaciers due to global warming.
 W
WTrail ethics define appropriate ranges of behavior for hikers on a public trail. It is similar to both environmental ethics and human rights in that it deals with the shared interaction of humans and nature. There are multiple agencies and groups that support and encourage ethical behavior on trails.
 W
WIn 1944, uranium mining under the U.S military's Manhattan Project began on Navajo Nation lands and on Lakota Nation lands. On August 1, 1946, the responsibility for atomic science and technology was transferred from the military to the United States Atomic Energy Commission. Afterward, widespread uranium mining began on Navajo and Lakota lands in a nuclear arms race with the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
 W
WWild animal suffering is the suffering experienced by nonhuman animals living outside of direct human control, due to harms such as disease, injury, parasitism, starvation and malnutrition, dehydration, weather conditions, natural disasters, and killings by other animals, as well as psychological stress. Some estimates indicate that the vast majority of individual animals in existence live in the wild. A vast amount of natural suffering has been described as an unavoidable consequence of Darwinian evolution and the pervasiveness of reproductive strategies which favor producing large numbers of offspring, with a low amount of parental care and of which only a small number survive to adulthood, the rest dying in painful ways, has led some to argue that suffering dominates happiness in nature.
 W
WWildlife management is the management process influencing interactions among and between wildlife, its habitats and people to achieve predefined impacts. It attempts to balance the needs of wildlife with the needs of people using the best available science. Wildlife management can include wildlife conservation, gamekeeping and pest control. Wildlife management draws on disciplines such as mathematics, chemistry, biology, ecology, climatology and geography to gain the best results.
 W
WWildness, in its literal sense, is the quality of being wild or untamed. Beyond this, it has been defined as a quality produced in nature, as that which emerges from a forest, and as a level of achievement in nature. More recently, it has been defined as "a quality of interactive processing between organism and nature where the realities of base natures are met, allowing the construction of durable systems". A wilderness is a place where wildness occurs.