 W
W1-Click, also called one-click or one-click buying, is the technique of allowing customers to make purchases with the payment information needed to complete the purchase having been entered by the user previously. More particularly, it allows an online shopper using an Internet marketplace to purchase an item without having to use shopping cart software. Instead of manually inputting billing and shipping information for a purchase, a user can use one-click buying to use a predefined address and credit card number to purchase one or more items.
 W
WAbove the fold is the upper half of the front page of a newspaper or tabloid where an important news story or photograph is often located. Papers are often displayed to customers folded so that only the top half of the front page is visible. Thus, an item that is "above the fold" may be one that the editors feel will entice people to buy the paper. Alternatively, it reflects a decision, on the part of the editors, that the article is one of the day's most important. By extension, the space above the fold is also preferred by advertisers, since it is the most prominent and visible even when the newspaper is on stands.
 W
WActive users is a measurement metric that is commonly used to measure the level of engagement a particular product or object has on the internet, by quantifying the number of active interactions from visitors within a relevant range of time . The metric has many uses in both commerce and academia, such as in a social networking service, online game, or mobile app. Although having extensive uses in digital behavioural learning, prediction and reporting, it also has impacts on the privacy and security, and ethical factors should be considered thoroughly. Like any metric, active users may have limitations and criticisms. Active Users is relatively new or neologistic in nature, that became important with the rise of the commercialised internet, with uses in communication and social-networking. It measures how many users visit or interact with the product or service over a given interval or period. This metric is commonly assessed per month as monthly active users (MAU), per week as weekly active users (WAU), per day as daily active users (DAU) or peak concurrent users (PCU).
 W
WAsymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem can provide. ADSL differs from the less common symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL). In ADSL, bandwidth and bit rate are said to be asymmetric, meaning greater toward the customer premises (downstream) than the reverse (upstream). Providers usually market ADSL as an Internet access service primarily for downloading content from the Internet, but not for serving content accessed by others.
 W
WIn the context of the World Wide Web, a bookmark is a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that is stored for later retrieval in any of various storage formats. All modern web browsers include bookmark features. Bookmarks are called favorites or Internet shortcuts in Internet Explorer, and by virtue of that browser's large market share, these terms have been synonymous with bookmark since the first browser war. Bookmarks are normally accessed through a menu in the user's web browser, and folders are commonly used for organization. In addition to bookmarking methods within most browsers, many external applications offer bookmark management.
 W
WClearnet is a term typically referring to the publicly accessible Internet, the opposite of the term darknet which typically describes the services built on Tor or other anonymity networks, the connection to which is encrypted and anonymized.
 W
WClickbait is a text or a thumbnail link that is designed to attract attention and to entice users to follow that link and read, view, or listen to the linked piece of online content, with a defining characteristic of being deceptive, typically sensationalized or misleading. A "teaser" aims to exploit the "curiosity gap", providing just enough information to make readers of news websites curious, but not enough to satisfy their curiosity without clicking through to the linked content. Click-bait headlines add an element of dishonesty, using enticements that do not accurately reflect the content being delivered. The "-bait" part of the term makes an analogy with fishing, where a hook is disguised by an enticement (bait), presenting the impression to the fish that it is a desirable thing to swallow.
 W
WConversation threading is a feature used by many email clients, bulletin boards, newsgroups, and Internet forums in which the software aids the user by visually grouping messages with their replies. These groups are called a conversation, topic thread, or simply a thread. A discussion forum, e-mail client or news client is said to have a "conversation view", "threaded topics" or a "threaded mode" if messages can be grouped in this manner.
 W
WHoward G. Cunningham is an American computer programmer who developed the first wiki and was a co-author of the Manifesto for Agile Software Development. A pioneer in both design patterns and extreme programming, he started coding the WikiWikiWeb in 1994, and installed it on c2.com on March 25, 1995, as an add-on to the Portland Pattern Repository. He co-authored a book about wikis, entitled The Wiki Way, and invented the Framework for Integrated Tests.
 W
WThe term digital native describes a young person who has grown up in the digital age, in close contact with computers, the Internet, and video game consoles, and later mobile phones, social media, and tablets. The term is often used to refer to millennials, Generation Z, and Generation Alpha; the latter two are sometimes described as distinct "neo-digital natives", "true" digital natives, or "digital integrators".
 W
WElectronic mail is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email entered limited use in the 1960s, but users could only send to users of the same computer, and some early email systems required the author and the recipient to both be online simultaneously, similar to instant messaging. Ray Tomlinson is credited as the inventor of email; in 1971, he developed the first system able to send mail between users on different hosts across the ARPANET, using the @ sign to link the user name with a destination server. By the mid-1970s, this was the form recognized as email.
 W
WGodwin's law, short for Godwin's law of Nazi analogies, is an Internet adage asserting that "as an online discussion grows longer, the probability of a comparison involving Nazis or Hitler approaches 1". That is, if an online discussion goes on long enough, sooner or later someone will compare someone or something to Adolf Hitler or his deeds, the point at which effectively the discussion or thread often ends.
 W
WIn Internet activism, hacktivism, or hactivism, is the use of computer-based techniques such as hacking as a form of civil disobedience to promote a political agenda or social change. With roots in hacker culture and hacker ethics, its ends are often related to free speech, human rights, or freedom of information movements.
 W
WInternet Relay Chat (IRC) is an application layer protocol that facilitates communication in the form of text. The chat process works on a client/server networking model. IRC clients are computer programs that users can install on their system or web based applications running either locally in the browser or on a third party server. These clients communicate with chat servers to transfer messages to other clients. IRC is mainly designed for group communication in discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat and data transfer, including file sharing.
 W
WIn Internet slang, a troll is a person who starts flame wars or intentionally upsets people on the Internet. Typically they do this by posting inflammatory and digressive, extraneous, or off-topic messages in an online community, with the intent of provoking readers into displaying emotional responses and normalizing tangential discussion. This is typically for the troll's amusement, or to achieve a specific result such as disrupting a rival's online activities or manipulating a political process.
 W
WLegion is a hacktivist group that has attacked some rich and powerful people in India by hacking their twitter handlers. The group claims to have access to many email servers in India and has the encryption keys used by Indian banks over the Internet.
 W
WA Let's Play (LP) is a video documenting the playthrough of a video game, usually including commentary or a camera view of the gamer's face. A Let's Play differs from a video game walkthrough or strategy guide by focusing on an individual's subjective experience with the game, often with humorous, irreverent, or critical commentary from the gamer, rather than being an objective source of information on how to progress through the game. While Let's Plays and live streaming of game playthroughs are related, Let's Plays tend to be curated experiences that include editing and narration, can be scripted, while streaming is an unedited experience performed on the fly.
 W
WHelen Lewis is a British journalist and a staff writer at The Atlantic. She is a former deputy editor of the New Statesman, and has also written for The Guardian and The Sunday Times.
 W
WIn computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database.
 W
WA photoblog is a form of photo sharing and publishing in the format of a blog. It differs from a blog through the predominant use of and focus on photographs rather than text. Photoblogging gained momentum in the early 2000s with the advent of the moblog and cameraphones.
 W
WRule 63 is an Internet meme that states that, as a rule, "for every given female character, there is a male version of that character" and vice versa. It is one of the "Rules of the Internet" that began in 2006 as a Netiquette guide on 4chan and were eventually expanded upon by including deliberately mocking rules, of which Rule 63 is an example. It began to see general use in fandom communities as a term to refer to both fan-made and official gender-swaps of existing fictional characters.
 W
WA search engine is a software system that is designed to carry out web searches, which means to search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a line of results, often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs) The information may be a mix of links to web pages, images, videos, infographics, articles, research papers, and other types of files. Some search engines also mine data available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain real-time information by running an algorithm on a web crawler. Internet content that is not capable of being searched by a web search engine is generally described as the deep web.
 W
WIn computing, and specifically peer-to-peer file sharing, seeding is the uploading of already downloaded content for others to download from. A peer, a computer that is connected to the network, becomes a seed when having acquired the entire set of data it tries to download. This data consists of small parts so that seeds can effectively share their content with other peers, handing out the missing pieces. A peer deliberately chooses to become a seed by leaving the upload task active once the content has downloaded. This means that there should be motivation to seed. The opposite of a seed is a leech, a peer that downloads more than they upload.
 W
W"A series of tubes" is a phrase coined originally as an analogy by then-United States Senator Ted Stevens (R-Alaska) to describe the Internet in the context of opposing network neutrality. On June 28, 2006, he used this metaphor to criticize a proposed amendment to a committee bill. The amendment would have prohibited Internet service providers such as AT&T, Comcast, Time Warner Cable and Verizon Communications from charging fees to give some companies' data a higher priority in relation to other traffic. The metaphor has been widely ridiculed, particularly because Stevens displayed an extremely limited understanding of the Internet, even though he was in charge of the Senate committee with the responsibility for regulating it. Edward Felten, Princeton University professor of computer science, pointed out the unfairness of some criticisms of Stevens's wording, while maintaining that the underlying arguments were rather weak.
 W
WMystery meat navigation is a disparaging term describing a web page where the destination of the link is not visible until the user points their cursor at it. Such interfaces lack a user-centered design, emphasizing aesthetic appearance, white space, and the concealment of relevant information over basic practicality and functionality. The term was coined in 1998 by Vincent Flanders, author and designer of the website Web Pages That Suck.
 W
WA sock puppet or sockpuppet is an online identity used for purposes of deception. The term, a reference to the manipulation of a simple hand puppet made from a sock, originally referred to a false identity assumed by a member of an Internet community who spoke to, or about, themselves while pretending to be another person.
 W
WThe term tribe or digital tribe is used as a slang term for an unofficial community or organization of people who share a common interest, and usually who are loosely affiliated with each other through social media or other Internet mechanisms. The term is related to "tribe", which traditionally refers to people closely associated in both geography and genealogy. Nowadays, it looks more like a virtual community or a personal network and it is often called global digital tribe. Most anthropologists agree that a tribe is a (small) society that practices its own customs and culture, and that these define the tribe. The tribes are divided into clans, with their own customs and cultural values that differentiate them from activities that occur in 'real life' contexts. People feel more inclined to share and defend their ideas on social networks than they would dare to say to someone face to face. For example, it would be ridiculous to 'poke' someone in real life.
 W
WWeb callback is a technology where a person can enter his or her telephone number in a form on a web site. The company who owns that Web site will then receive the Web callback request and a call center agent will call the person who made the request back on the number they entered.
 W
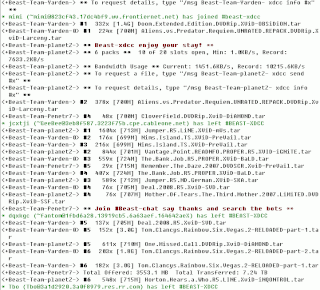
WXDCC is a computer file sharing method which uses the Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network as a host service.