 W
W3LCD is the name and brand of a major LCD projection color image generation technology used in modern digital projectors. 3LCD technology was developed and refined by Japanese imaging company Epson in the 1980s and was first licensed for use in projectors in 1988. In January 1989, Epson launched its first 3LCD projector, the VPJ-700.
 W
WThe ANS synthesizer is a photoelectronic musical instrument created by Russian engineer Evgeny Murzin from 1937 to 1957. The technological basis of his invention was the method of graphical sound recording used in cinematography, which made it possible to obtain a visible image of a sound wave, as well as to realize the opposite goal—synthesizing a sound from an artificially drawn sound spectrogram.
 W
WCorona poling is a technique in optoelectronics.
 W
WDigital Light Processing (DLP) is a set of chipsets based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It was originally developed in 1987 by Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. While the DLP imaging device was invented by Texas Instruments, the first DLP-based projector was introduced by Digital Projection Ltd in 1997. Digital Projection and Texas Instruments were both awarded Emmy Awards in 1998 for the DLP projector technology. DLP is used in a variety of display applications from traditional static displays to interactive displays and also non-traditional embedded applications including medical, security, and industrial uses.
 W
WThe digital micromirror device, or DMD, is the microoptoelectromechanical system (MOEMS) that is the core of the trademarked DLP projection technology from Texas Instruments (TI). Texas Instrument's DMD was created by solid state physicist and TI Fellow Emeritus Dr. Larry Hornbeck in 1987. However, the technology goes back to 1973 with Harvey C. Nathanson's use of millions of microscopically small moving mirrors to create a video display of the type now found in digital projectors.
 W
WIn semiconductor physics, the band gap of a semiconductor can be of two basic types, a direct band gap or an indirect band gap. The minimal-energy state in the conduction band and the maximal-energy state in the valence band are each characterized by a certain crystal momentum (k-vector) in the Brillouin zone. If the k-vectors are different, the material has an "indirect gap". The band gap is called "direct" if the crystal momentum of electrons and holes is the same in both the conduction band and the valence band; an electron can directly emit a photon. In an "indirect" gap, a photon cannot be emitted because the electron must pass through an intermediate state and transfer momentum to the crystal lattice.
 W
WIn computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives.
 W
WAn electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element exhibiting an electro-optic effect is used to modulate a beam of light. The modulation may be imposed on the phase, frequency, amplitude, or polarization of the beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser-controlled modulators.
 W
WA fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example, long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
 W
WGallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.
 W
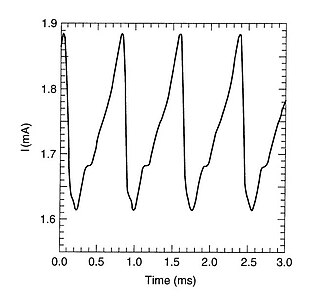
WA high-field domain is a band of elevated field orthogonal to the equi-current lines, and seen in photoconductive CdS and monochromatic light at the band edge as dark band was discovered by Böer, using the Franz-Keldysh effect. Such domains must appear whenever the conductivity decreases stronger than linearly. This can be caused by the field dependence of the carrier density, as observed in copper-doped CdS caused by Frenkel Poole excitation of holes, causing faster electron recombination, known as field quenching. These high-field domains, now referred to as Böer domains, or by field dependence of the mobility, caused by excitation of electrons into higher conduction bands with lower mobility as observed in GaAs, called the Gunn effect. The high-field domains can be identified by periodical field oscillations between high and low values, as shown in Fig. 1.
 W
WIndium phosphide (InP) is a binary semiconductor composed of indium and phosphorus. It has a face-centered cubic ("zincblende") crystal structure, identical to that of GaAs and most of the III-V semiconductors.
 W
WLED art is a form of light art constructed from light-emitting diodes. LEDs are very inexpensive to purchase and have become a new way to make street art. Many artists who use LEDs are guerrilla artists, incorporating LEDs to produce temporary pieces in public places. LEDs may be used in installation art, sculptural pieces and interactive artworks.
 W
WIn computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material on one of its flat surfaces.
 W
WAlthough research into optical data storage has been ongoing for many decades, the first popular system was the Compact Disc, introduced in 1982, adapted from audio (CD-DA) to data storage with the 1985 Yellow Book, and re-adapted as the first mass market optical storage medium with CD-R and CD-RW in 1988. Compact Disc is still the de facto standard for audio recordings, although its place for other multimedia recordings and optical data storage has largely been superseded by DVD.
 W
WAn opto-isolator is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/μs.
 W
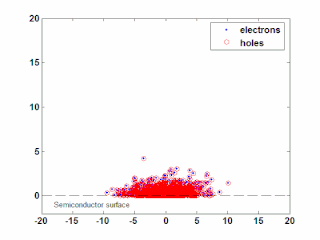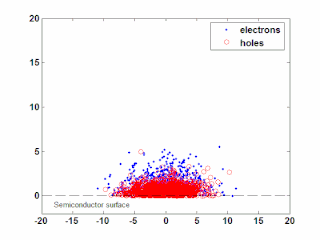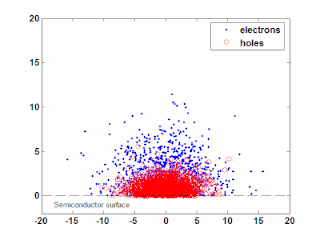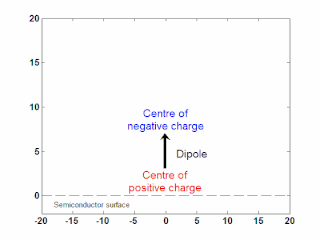
WIn semiconductor physics, the photo–Dember effect is the formation of a charge dipole in the vicinity of a semiconductor surface after ultra-fast photo-generation of charge carriers. The dipole forms owing to the difference of mobilities for holes and electrons which combined with the break of symmetry provided by the surface lead to an effective charge separation in the direction perpendicular to the surface. In an isolated sample, where the macroscopic flow of an electric current is prohibited, the fast carriers are slowed and the slow carriers are accelerated by an electric field, called the Dember field.
 W
WPhotoinduced electron transfer (PET) is an excited state electron transfer process by which an excited electron is transferred from donor to acceptor. Due to PET a charge separation is generated, i.e., redox reaction takes place in excited state.
 W
WPhotonic curing is the high-temperature thermal processing of a thin film using pulsed light from a flashlamp. When this transient processing is done on a low-temperature substrate such as plastic or paper, it is possible to attain a significantly higher temperature than the substrate can ordinarily withstand under an equilibrium heating source such as an oven. Since the rate of most thermal curing processes generally increase exponentially with temperature, this process allows materials to be cured much more rapidly than with an oven.
 W
WA photonics mast is a sensor on a submarine which functions similarly to a periscope without requiring a periscope tube, thus freeing design space during construction and limiting risks of water leakage in the event of damage. A photonics mast replaces the mechanical, line-of-sight viewing system with digital equipment, similar to a digital camera array, and it has fewer locational and dimensional constraints than a traditional periscope.
 W
WPhotovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially utilized for electricity generation and as photosensors.
 W
WPilkington is a Japanese-owned glass-manufacturing company which is based in Lathom, Lancashire, United Kingdom. In the UK it includes several legal entities and is a subsidiary of Japanese company NSG Group.
 W
WResistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol, analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.
 W
WGagik Shmavonyan is Professor at National Polytechnic University of Armenia, PhD in Physics, D.Sc in Engineering., President of "NanoHiTech" Association (Nanotechnology), International Expert in Nanotechnology and Chief Scientific Coordinator of multidisciplinary research group of scientific experts from different countries at LarrainVial Investment and Advisory Company, Expert/Project Peer Reviewer at Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia, as well as Advisor at Ministery of High-Tech Industry of Armenia and Science Committee of Armenia.
 W
WSilicon photomultipliers, often called "SiPM" in the literature, are solid-state single-photon-sensitive devices based on Single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) implemented on common silicon substrate. The dimension of each single SPAD can vary from 10 to 100 micrometres, and their density can be up to 10000 per square millimeter. Every SPAD in SiPM operates in Geiger mode and is coupled with the others by a metal or polysilicon quenching resistor. Although the device works in digital/switching mode, most of SiPM are an analog device because all the microcells are read in parallel, making it possible to generate signals within a dynamic range from a single photon to 1000 photons for a device with just a square-millimeter area. More advanced readout schemes are utilized for the lidar applications. The supply voltage (Vb) depends on APD technology used and typically varies between 20 V and 100 V, thus being from 15 to 75 times lower than the voltage required for a traditional photomultiplier tube's (PMT) operation.
 W
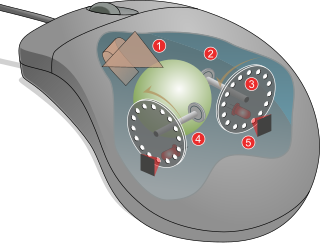
WThe slotted optical switch, sometimes known as opto switch or optical switch but not to be confused with the optical component, is a device comprising a photoemitter and a photodetector mounted in a single package so that the photoemitter normally illuminates the photodetector, but an opaque object can be inserted in a slot between them so as to break the beam. Associated circuitry is provided which changes state when the beam is interrupted. For example, the carriage of a computer printer may be fitted with a projection which interrupts the beam of a slotted switch when it reaches the end of its travel, causing circuitry to react appropriately. Another application of the slotted switch is in the type of computer mouse with a rotating ball. The ball measures distances moved by rotating orthogonal shafts which drive optical chopper wheels turning in the slots of slotted switches.
 W
WSmall molecule sensors are an effective way to detect the presence of metal ions in solution. Although many types exist, most small molecule sensors comprise a subunit that selectively binds to a metal that in turn induces a change in a fluorescent subunit. This change can be observed in the small molecule sensor's spectrum, which can be monitored using a detection system such as a microscope or a photodiode. Different probes exist for a variety of applications, each with different dissociation constants with respect to a particular metal, different fluorescent properties, and sensitivities. They show great promise as a way to probe biological processes by monitoring metal ions at low concentrations in biological systems. Since they are by definition small and often capable of entering biological systems, they are conducive to many applications for which other more traditional bio-sensing are less effective or not suitable.
 W
WThermopile laser sensors are used for measuring laser power from a few µW to several W. The incoming radiation of the laser is converted into heat energy at the surface. This heat input produces a temperature gradient across the sensor. Making use of the thermoelectric effect a voltage is generated by this temperature gradient. Since the voltage is directly proportional to the incoming radiation, it can be directly related to the irradiation power.
 W
WCarl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue, Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.