 W
WIn 2014, a new design was introduced for train tickets issued on the National Rail network in Great Britain. The pre-2014 design was similar to the APTIS design introduced in 1986 by British Rail.
 W
WAJENTS is one of the two original computer-based railway ticket issuing systems supplied to travel agencies in Britain. It allows agencies which are not connected to one of the major GDS networks to issue and print railway tickets from a standard personal computer, and submit revenue and accounting data securely to Rail Settlement Plan Ltd for allocation to the appropriate Train Operating Companies.
 W
WAmadeus IT Group, S.A. is a major Spanish IT provider for the global travel and tourism industry.
 W
WAPTIS was the Accountancy and Passenger Ticket Issuing System used on the British Rail/National Rail until 2007. It was originally called "Advanced Passenger Ticket Issuing System" as it was being developed at the time of the Advanced Passenger Train.
 W
WTickets issued from British Rail's APTIS system had a considerable amount of detail, presented in a consistent, standard format. The design for all tickets was created by Colin Goodall. This format has formed the basis for all subsequent ticket issuing systems introduced on the railway network – ticket-office based, self-service and conductor-operated machines alike.
 W
WAscom B8050, usually known by the name QuickFare, is an early example of a passenger-operated railway ticket issuing system, consisting of a series of broadly identical machines installed at British railway stations from 1989 onwards. The machines allow passengers to buy the most popular types of ticket themselves, without having to go to a booking office, and are therefore useful at unstaffed, partly staffed or busy stations. All QuickFare machines have now been replaced by more modern technology.
 W
WThe Ascom EasyTicket is a railway ticket issuing system used in Britain, consisting of a series of self-service (passenger-operated) machines at railway stations. Having been introduced in 2003 on a trial basis by several Train Operating Companies (TOCs) at various stations, the system did not spread into common usage, and most machines have since been removed.
 W
WAvantix B8070, more commonly known as Avantix MultiTicket was a passenger-operated railway ticket issuing system, installed at British railway stations from 1999 onwards. The machines were available as upgrades to the Ascom B8050 Quickfare or as new build.
 W
WAVANTIX Mobile ("AVB") is a portable railway ticket issuing system used across the British railway network from 2001 to 2017.
 W
WBYHOURS is a Spanish company and first hotelmicrostays booking platform where hotels can be booked by the hour. Guests can decide the time of arrival and pay for the time they need.
 W
WClock Software is a private limited company developing software and hardware solutions for the hospitality industry - property management system, restaurant point of sale, online booking engine, channel manager, self-service kiosk, mobile hotel app. Its headquarters is in London, UK.
 W
WJohn F. Davis III is an entrepreneur, educator, CEO of Room Key, and a member of the Texas Christian University Board of Trustees. He is a co-founder of 1-800-Flowers and former CEO of both Pegasus Solutions and Birch Street Systems.
 W
WAn electronic ticket, often called e-ticket, is the digital ticket equivalent of a paper ticket. The term is most commonly associated with airline issued tickets. Electronic ticketing for urban or rail public transport is usually referred to as travel card or transit pass. It is also used in ticketing in the entertainment industry.
 W
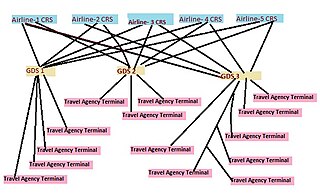
WA global distribution system (GDS) is a computerised network system owned or operated by a company that enables transactions between travel industry service providers, mainly airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and travel agencies. The GDS mainly uses real-time inventory to service providers. Travel agencies traditionally relied on GDS for services, products and rates in order to provide travel-related services to the end consumers. Thus, a GDS can link services, rates and bookings consolidating products and services across all three travel sectors: i.e., airline reservations, hotel reservations, car rentals.
 W
WIn-car entertainment (ICE), or in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), is a collection of hardware and software in automobiles that provides audio or video entertainment. In car entertainment originated with car audio systems that consisted of radios and cassette or CD players, and now includes automotive navigation systems, video players, USB and Bluetooth connectivity, Carputers, in-car internet, and WiFi. Once controlled by simple dashboards knobs and dials, ICE systems can include steering wheel audio controls and handsfree voice control.
 W
WIn-flight entertainment (IFE) refers to the entertainment available to aircraft passengers during a flight. In 1936, the airship Hindenburg offered passengers a piano, lounge, dining room, smoking room, and bar during the 2 1/2-day flight between Europe and America. After World War II, IFE was delivered in the form of food and drink services, along with an occasional projector movie during lengthy flights. In 1985 the first personal audio player was offered to passengers, along with noise cancelling headphones in 1989. During the 1990s, the demand for better IFE was a major factor in the design of aircraft cabins. Before then, the most a passenger could expect was a movie projected on a screen at the front of a cabin, which could be heard via a headphone socket at his or her seat. Now, in most aircraft, private IFE TV screens are offered.
 W
WInformation Systems Associates FZE is an aviation software house serving airlines, airports and travel agents. ISA is a privately owned company formed in 2005. The company produces a computer reservation system 'under the name "aeroMART SELL", formerly AccelAero,. The company is headquartered in Sharjah, UAE and the development center is based in Colombo, Sri Lanka. Software produced includes airline, airport, e-business suites, revenue management, crew & ground operations, and holidays etc.
 W
WITA Software is a travel industry software division of Google, formerly an independent company, in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company was founded by Jeremy Wertheimer, a computer scientist from the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and Cooper Union, with his partner Richard Aiken in 1996. On July 1, 2010, ITA agreed to be acquired by Google. On April 8, 2011, the US Department of Justice approved the buyout. As part of the agreement, Google was required to license ITA software to other websites for five years.
 W
WMARS , which stands for Multi Access seat Reservation System, is a train ticket reservation system used by the railway companies of former Japanese National Railways, currently Japan Railways Group and travel agencies in Japan, developed jointly by Hitachi and the Railway Information Systems Co., Ltd, a JR Group company jointly owned by the seven members of the group.
 W
WThe National Public Transport Access Node (NaPTAN) database is a UK nationwide system for uniquely identifying all the points of access to public transport in the UK. The database is closely associated with the National Public Transport Gazetteer.
 W
WA passenger information system or passenger information display system is an automated system for supplying users of public transport with information about the nature and state of a public transport service, through visual, voice or other media. They are also known as Customer Information Systems and Operational Information Systems. Among the information provided by such systems, a distinction can be drawn between:Static or schedule information, which changes only occasionally and is typically used for journey planning prior to departure. Real time information, derived from automatic vehicle location systems, which changes continuously as a result of real-world events and is typically used during the course of a journey.
 W
WPickyourtrail.com, formerly Travel Troops Global Private Ltd, is an Indian travel and technology website and an online vacation packages booking platform and engine. The website uses global distribution systems such as Amadeus IT Group and Viator for flights, and Expedia for online hotel bookings.
 W
WRadixx was founded in 1993 and was built to offer a retail-centric alternative solution to legacy PNR-based reservations systems. At its core, Radixx was built to leverage the technology industry's rapid advances which led to cloud-based solutions that quickly deploy and which traditional providers are unable to support due to their major investments in legacy technology. Historically the provider for low-cost Carrier (LCC), hybrid, and retail-focused carriers, Radixx today supports all airline business models, in ticketed and tickletless capacity. Sabre acquired Radixx in October 2019 as part of the technology company's entrance into the fast growing LCC segment.
 W
WStarting in 1946, American Airlines developed a number of automated airline booking systems known as Reservisor. Although somewhat successful, American's unhappiness with the Reservisor systems led them to develop the computerized Sabre system used to this day.
 W
WThe Atos Worldline FASTticket system is a passenger-operated, self-service railway ticket issuing system, developed by the Guildford-based company Shere Ltd and first introduced on a trial basis in Britain in 1996, shortly after privatisation. It has been developed and upgraded consistently since then, and is now used by seven Train Operating Companies (TOCs) as their primary self-service ticket issuing system. Other TOCs have FASTticket machines at some of their stations, sometimes supplementing other systems.
 W
WThe Shere SMART is a desktop-based railway ticket issuing system, developed by the Guildford-based company Shere Ltd, utilising Newbury Data ND4020 ticket printer, first introduced in Britain in 2003. Since the first trial installation of the system in the ticket office at London Bridge station, approximately 300 terminals have been installed at stations on the Southern and former Thameslink networks.
 W
WTicketer is the brand name for a range of electronic ticket machines provided by British company Corvia Ltd, primarily for usage on buses. The "innovative" cloud-based system, first marketed on a small scale in 2008, has since developed into a rival to the three major ticket issuing systems used by bus companies throughout Britain.
 W
WTimatic is a database containing documentation requirements for passengers traveling internationally via air, e.g. passport and visa requirements. Timatic, an abbreviation for Travel Information Manual Automatic, is used by airlines and their representatives, airport staff, and travel agents to determine whether a passenger can be carried, as well as by airlines and travel agents to provide this information to travellers at the time of booking. This is critical for airlines due to the fines levied by immigration authorities every time a passenger is carried who does not have the correct travel documentation, as well as the airline's costs to return the incorrectly-boarded passenger to the original airport from which the passenger departed.
 W
WTravel Technology Interactive Group is a French-based international company. It is specialized in IT software for the management of airlines. It provides an Airline Reservations System with an integrated Global Distribution System (GDS).
 W
WTravelport Worldwide Ltd provides distribution, technology, payment solutions for the travel and tourism industry. It is the smallest, by revenue, of the top three global distribution systems (GDS) after Amadeus IT Group and Sabre Corporation.
 W
WTravelSky Technology Limited is a Chinese listed company on the Hong Kong share market and the dominant provider of information technology solutions to People's Republic of China's air travel and tourism industries. Its clients include airlines, airports, air travel suppliers, travel agencies, individual and corporate travel consumers and cargo services. Its majority shareholder or parent group is the China TravelSky Holding Company a State-owned enterprise (SOE) in China.
 W
WWorldTicket was founded in 2002 and is a global provider of IT and Software to airlines. WorldTicket has developed the passenger service system called Sell-More-Seats. Sell-More-Seats is integrated with the global distribution systems and is built on HTML 5 technology and follows IATA e-ticket standards.