 W
WDigital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical samples in a continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samples are taken 44,100 times per second, each with 16-bit sample depth. Digital audio is also the name for the entire technology of sound recording and reproduction using audio signals that have been encoded in digital form. Following significant advances in digital audio technology during the 1970s and 1980s, it gradually replaced analog audio technology in many areas of audio engineering and telecommunications in the 1990s and 2000s.
 W
WIn digital audio using pulse-code modulation (PCM), bit depth is the number of bits of information in each sample, and it directly corresponds to the resolution of each sample. Examples of bit depth include Compact Disc Digital Audio, which uses 16 bits per sample, and DVD-Audio and Blu-ray Disc which can support up to 24 bits per sample.
 W
WA CD player is an electronic device that plays audio compact discs, which are a digital optical disc data storage format. CD players were first sold to consumers in 1982. CDs typically contain recordings of audio material such as music or audiobooks. CD players may be part of home stereo systems, car audio systems, personal computers, or portable CD players such as CD boomboxes. Most CD players produce an output signal via a headphone jack or RCA jacks. To use a CD player in a home stereo system, the user connects an RCA cable from the RCA jacks to a hi-fi and loudspeakers for listening to music. To listen to music using a CD player with a headphone output jack, the user plugs headphones or earphones into the headphone jack.
 W
WDecibels relative to full scale is a unit of measurement for amplitude levels in digital systems, such as pulse-code modulation (PCM), which have a defined maximum peak level. The unit is similar to the units dBov and decibels relative to overload (dBO).
 W
WDear Reality GmbH is a German company specialising in 3D audio software and Virtual acoustics. They have developed Software tools for professional audio production of linear and interactive content in Augmented reality, Virtual reality, Video games, Sound design and Music.
 W
WDigital Audio Tape is a signal recording and playback medium developed by Sony and introduced in 1987. In appearance it is similar to a Compact Cassette, using 3.81 mm / 0.15" magnetic tape enclosed in a protective shell, but is roughly half the size at 73 mm × 54 mm × 10.5 mm. The recording is digital rather than analog. DAT can record at sampling rates equal to, as well as higher and lower than a CD at 16 bits quantization. If a comparable digital source is copied without returning to the analogue domain, then the DAT will produce an exact clone, unlike other digital media such as Digital Compact Cassette or non-Hi-MD MiniDisc, both of which use a lossy data reduction system.
 W
WA digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
 W
WThe Digital Compact Cassette (DCC) is a magnetic tape sound recording format introduced by Philips and Matsushita in late 1992 and marketed as the successor to the standard analog Compact Cassette. It was also a direct competitor to Sony's MiniDisc (MD), but neither format toppled the then-ubiquitous analog cassette despite their technical superiority, and DCC was discontinued in October 1996.
 W
WA digital media player is a type of consumer electronics device designed for the storage, playback, or viewing of digital media content. They are typically designed to be integrated into a home cinema configuration, and attached to a television and/or AV receiver.
 W
WIn professional audio, a digital mixing console (DMC) is an electronic device used to combine, route, and change the dynamics, equalization and other properties of multiple audio input signals, using digital signal processing rather than analog circuitry. The digital audio samples, which is the internal representation of the analog inputs, are summed to what is known as a master channel to produce a combined output. A professional digital mixing console is a dedicated desk or control surface produced exclusively for the task and is typically more robust in terms of user control, processing power and quality of audio effects. However, a computer can also perform the same function since it can mimic its interface, input and output.
 W
WDolby Laboratories, Inc. is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction and audio encoding/compression. Dolby licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers.
 W
WGroove Music is an audio player software application included with Windows 8, Windows 8.1, and Windows 10.
 W
WIn January 2004, Sony announced the Hi-MD media storage format as a further development of the MiniDisc format. With its release in later 2004, came the ability to use newly developed, high-capacity 1 gigabyte Hi-MD discs, sporting the same dimensions as regular MiniDiscs. The Hi-MD format can be considered obsolete as the last recorder/player was discontinued in 2011. The discs themselves were withdrawn from sale in September 2012, though regular MiniDiscs are still available.
 W
WFrancis Fan Lee is an inventor, entrepreneur, and professor emeritus of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Lee is the founder of Lexicon (company). He is best known for three inventions: the Digital Cardiac Monitor (1969), the Digital Audio Signal Processor (1971), and the Digital Time Compression System (1972). In 1984, Lexicon won an Emmy Award for Engineering Excellence for the Model 1200 Audio Time Compressor and Expander, widely used in the television industry.
 W
WMIL-CD or Music Interactive Live CD is a compact disc format created by the video game company Sega in 1999.
 W
WThe MiniDisc (MD) is a magneto-optical disc-based data storage format offering a capacity of 60, 74, and later, 80 minutes of digitized audio or 1 gigabyte of Hi-MD data. Sony brand audio players went on the market in September 1992.
 W
WModule file is a family of music file formats originating from the MOD file format on Amiga systems used in the late 1980s. Those who produce these files and listen to them form the worldwide MOD scene, a part of the demoscene subculture.
 W
WAn MP3 player is an electronic device that can play MP3 digital audio files. It is a type of digital audio player (DAP), or portable media player. Most players play more than the MP3 file format, such as Windows Media Audio (WMA), Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), Vorbis, FLAC, Speex and Ogg.
 W
WMP3 Surround is an extension of MP3 for multi-channel audio support including 5.1 surround sound. It was developed by Fraunhofer IIS in collaboration with Thomson and Agere Systems, and released in December 2004.
 W
WMusicStation is a music service platform developed by Omnifone. The cloud based platform works across a number of different digital device platforms and is tailored specifically for various partners including rara.com, RIM, Sony, Sony Ericsson, HP, BSkyB, Vodafone, Telenor, Hutchison Telecom and Vodacom.
 W
WNon-linear editing is a form of offline editing for audio, video, and image editing. In offline editing, the original content is not modified in the course of editing. In non-linear editing, edits are specified and modified by specialized software. A pointer-based playlist, effectively an edit decision list (EDL), for video and audio, or a directed acyclic graph for still images, is used to keep track of edits. Each time the edited audio, video, or image is rendered, played back, or accessed, it is reconstructed from the original source and the specified editing steps. Although this process is more computationally intensive than directly modifying the original content, changing the edits themselves can be almost instantaneous, and it prevents further generation loss as the audio, video, or image is edited.
 W
WA PCM adaptor is a device that encodes digital audio as video for recording on a videocassette recorder. The adapter also has the ability to decode a video signal back to digital audio for playback. This digital audio system was used for mastering early compact discs.
 W
WA piano roll is a music storage medium used to operate a player piano, piano player or reproducing piano. Piano rolls, like other music rolls, are continuous rolls of paper with perforations (holes) punched into them. The perforations represent note control data. The roll moves over a reading system known as a 'tracker bar' and the playing cycle for each musical note is triggered when a perforation crosses the bar and is read.
 W
WA podcast is an episodic series of spoken word digital audio files that a user can download to a personal device for easy listening. Streaming applications and podcasting services provide a convenient and integrated way to manage a personal consumption queue across many podcast sources and playback devices.
 W
WPono was a portable digital media player and music download service for high-resolution audio. It was developed by musician Neil Young and his company PonoMusic, which raised money for development and initial production through a crowd-funding campaign on Kickstarter. Production and shipments to backers started in October 2014, and shipments to the general public began in Q1 2015.
 W
WPOW-R is a set of commercial dithering and noise shaping algorithms used in digital audio bit-depth reduction. Developed by a consortium of four companies – The POW-R Consortium – the algorithms were first made available in 1999 in digital audio hardware products. POW-R is now licensed for use by many companies, particularly those in the Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) arena, where it currently has significant market share.
 W
WPray As You Go is a daily prayer website, podcast and application that was created in 2006 by the Jesuits in the United Kingdom. Since its founding it has been adapted into nine other languages and as of 2020, it is used 30 million times a year.
 W
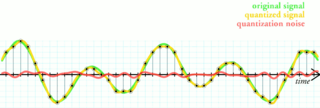
WQuantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and truncation are typical examples of quantization processes. Quantization is involved to some degree in nearly all digital signal processing, as the process of representing a signal in digital form ordinarily involves rounding. Quantization also forms the core of essentially all lossy compression algorithms.
 W
WLyra is a series of portable media players developed and sold by RCA.
 W
WThe RVU Alliance (RVUA) is a standards body created to manage the RVU protocol standard as used by manufacturers of consumer electronics to allow entertainment devices within the home to share their content with each other across a home network.
 W
WStyle Jukebox was a hi-fi high-resolution audio cloud music streaming and storage player for the Windows, iOS, Android and Windows Phone platforms. A Web Player was also available for Mac, Windows and Linux.
 W
WThe Technics Digital Link interface was introduced by Panasonic at the Internationale Funkausstellung 2014 in Berlin as an integral part of the new "R1 Reference Class" of audio components. At the same time, Panasonic relaunched the Technics brand itself.
 W
WVirtual Audio Cable is a software product based on WDM multimedia driver that allows a user to transfer audio streams from one application to another. Any application is able to send an audio stream to the input side of a "virtual cable" while a corresponding application can receive this stream from the output side. Since all transfers are made digitally, there is no loss in sound quality. VAC is the audio equivalent of a MIDI loopback device such as MultiMid or Hubi, and can be used instead of "Stereo Mix" or "What U Hear" features of audio adapters.
 W
WWiMP was a music streaming service available on mobiles, tablets, network players and computers. Music in WiMP was streamed using the AAC+ file format in a bitrate of 96 kbit/s or the AAC file format in a bitrate of 320 kbit/s if the high quality streaming option is selected. WiMP also offered a HiFi-product with FLAC/ALAC. WiMP has since been merged into Tidal.