 W
WThe ExoLife Finder Telescope (ELF) is a proposed hybrid interferometric telescope intended to directly detect and image the surface of potentially Earth-like planets.
 W
WA telescope is an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, by using glass lenses. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy.
 W
W400 Years of the Telescope: A Journey of Science, Technology and Thought is a 2009 American documentary film that was created to coincide with the International Year of Astronomy in 2009. Directed by Kris Koenig, it chronicles the history of the telescope from the time of Galileo and features interviews with leading astrophysicists and cosmologists from around the world, who explain concepts ranging from Galileo's first use of the telescope to view the moons of Jupiter, to the latest discoveries in space, including new ideas about life on other planets and dark energy, a mysterious vacuum energy that is accelerating the expansion of the universe.
 W
WActive optics is a technology used with reflecting telescopes developed in the 1980s, which actively shapes a telescope's mirrors to prevent deformation due to external influences such as wind, temperature, mechanical stress. Without active optics, the construction of 8 metre class telescopes is not possible, nor would telescopes with segmented mirrors be feasible.
 W
WAdaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.
 W
WAn altazimuth or alt-azimuth mount is a simple two-axis mount for supporting and rotating an instrument about two perpendicular axes – one vertical and the other horizontal. Rotation about the vertical axis varies the azimuth of the pointing direction of the instrument. Rotation about the horizontal axis varies the altitude of the pointing direction.
 W
WAn astrograph is a telescope designed for the sole purpose of astrophotography. Astrographs are mostly used in wide-field astronomical surveys of the sky and for detection of objects such as asteroids, meteors, and comets.
 W
WThe Astroscan was a wide-field 4⅛" clear-inch (105mm) diameter reflecting telescope, originally produced by the Edmund Scientific Corporation, that was for sale from 1976 to 2013.
 W
WThe Automated Planet Finder Telescope (APF) a.k.a. Rocky Planet Finder, is a fully robotic 2.4-meter optical telescope at Lick Observatory, situated on the summit of Mount Hamilton, east of San Jose, California, USA. It is designed to search for extrasolar planets in the range of five to twenty times the mass of the Earth. The instrument will examine about 10 stars per night. Over the span of a decade, the telescope is expected to study 1,000 nearby stars for planets. Its estimated cost was $10 million. The total cost-to-completion of the APF project was $12.37 million. First light was originally scheduled for 2006, but delays in the construction of the major components of the telescope pushed this back to August 2013. It was commissioned in August 2013.
 W
WThe Bahtinov mask is a device used to focus small astronomical telescopes accurately. Although masks have long been used as focusing aids, the distinctive pattern was invented by Russian amateur astrophotographer Pavel Bahtinov in 2005. Precise focusing of telescopes and astrographs is critical to performing astrophotography.
 W
WThe Birmingham Solar Oscillations Network (BiSON) consists of a network of six remote solar observatories monitoring low-degree solar oscillation modes. It is operated by the High Resolution Optical Spectroscopy group of the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Birmingham, UK, in collaboration with Sheffield Hallam University, UK. They are funded by the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC).
 W
WThe Canopus Hill Observatory, located approximately 12 km from Hobart in Tasmania Australia, is an optical astronomy observatory belonging to the University of Tasmania (UTAS). Due to the high southern latitude, the Canopus Hill Observatory is able to observe and study the Magellanic clouds. However, the observatory has closed down due to the "encroaching light pollution from the Hobart suburbs". According to the Astronomical Society, light pollution reduces the vision of the night sky, becoming a "major menace to amateur and professional astronomers alike".
 W
WA Carey mask is a focusing aid for astronomical telescopes. The mask is in the form of a thin card or sheet that is placed over the front aperture of the telescope. There are four series of slits in the mask which form a diffraction pattern in the image plane.
 W
WChabot Space and Science Center, located in Oakland, California, is a center for science learning featuring interactive exhibits, planetariums, a large screen theater, hands-on activities and three powerful telescopes.
 W
WA comet seeker is a type of small telescope adapted especially to searching for comets: commonly of short focal length and large aperture, in order to secure the greatest brilliancy of light. This style of telescope was used to discover the asteroid 9 Metis in 1848.Design
 W
WA Compton telescope is a gamma-ray detector which utilizes Compton scattering to determine the origin of the observed gamma rays.
 W
WThe Craig telescope was a large telescope built in the 1850s, and while much larger than previous refracting telescopes, it had some problems that hampered its use. Its unique design and potential caused a great deal of excitement in its day. The telescope was ready in August 1852 and was visited by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, famous for the Leviathan of Parsonstown, a reflecting telescope and the largest telescope of this age with a six foot mirror.
 W
WThe Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is a scientific research instrument for conducting a spectrographic astronomical surveys of distant galaxies. Its main components are a focal plane containing 5,000 fiber-positioning robots, and a bank of spectrographs which are fed by the fibers. The new instrument will enable an experiment to probe the expansion history of the universe and the mysterious physics of dark energy.
 W
WThe resolution of an optical imaging system – a microscope, telescope, or camera – can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited.
 W
WGreat refractor refers to a large telescope with a lens, usually the largest refractor at an observatory with an equatorial mount. The preeminence and success of this style in observational astronomy defines an era in modern telescopy in the 19th and early 20th century. Great refractors were large refracting telescopes using achromatic lenses. They were often the largest in the world, or largest in a region. Despite typical designs having smaller apertures than reflectors, great refractors offered a number of advantages and were popular for astronomy. It was also popular to exhibit large refractors at international exhibits, and examples of this include the Trophy Telescope at the 1851 Great Exhibition, and the Yerkes Great Refractor at the 1893 World's Fair in Chicago.
 W
WAn equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that compensates for Earth's rotation by having one rotational axis parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. This type of mount is used for astronomical telescopes and cameras. The advantage of an equatorial mount lies in its ability to allow the instrument attached to it to stay fixed on any celestial object with diurnal motion by driving one axis at a constant speed. Such an arrangement is called a sidereal or clock drive.
 W
WAn equatorial platform or equatorial table is an equatorial telescope mount in the form of a specially designed platform that allows any device sitting on it to track astronomical objects in the sky on an equatorial axis. They are used to give equatorial tracking to any device sitting on them, from small cameras up to entire observatory buildings. They are often used with altazimuth mounted telescopes, such as the common Dobsonian telescope type, to overcome that type of mount's inability to track the night sky. With careful polar alignment sub-arc second precision CCD imaging is entirely possible. Roeser Observatory, Luxembourg have contributed hundreds of astrometric measurements of Near Earth Asteroids to the Minor Planet Center using a home-built 20" Dobsonian telescope on an Osypowski equatorial platform.
 W
WAn equatorial room, in astronomical observatories, is the room which contains an equatorial mounted telescope. It is usually referred to in observatory buildings that contain more than one type of instrument: for example buildings with an "equatorial room" containing an equatorial telescope and a "transit room" containing a transit telescope. Equatorial rooms tend to be large circular rooms to accommodate all the range of motion of a long telescope on an equatorial mount and are usually topped with a dome to keep out the weather.
 W
WAn eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is so named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.
 W
WIn astronomy, first light is the first use of a telescope to take an astronomical image after it has been constructed. This is often not the first viewing using the telescope; optical tests will probably have been performed in daylight to adjust the components.
 W
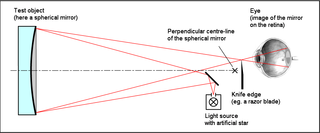
WThe Foucault knife-edge test is an optical test developed 150 years ago to accurately measure the shape of concave curved mirrors. It is commonly used by amateur telescope makers for figuring primary mirrors in reflecting telescopes. It uses a relatively simple, inexpensive apparatus compared to other testing techniques.
 W
WThe Galaxy Hα Fabry-Perot System for WHT (GHaFaS) is an astronomical instrument installed on the 4.2 metre William Herschel Telescope (WHT) at Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the Canary island of La Palma. First light was on 6 July 2007. Its name is a play on the acronym: Galaxy Hα Fabry-Perot System and the Spanish word "gafas" meaning spectacles. It produces maps, in intensity and velocity, of extended objects in the sky, which radiate in the H-alpha line, emitted by ionized hydrogen in interstellar space. It can also be used for a variety of other lines.
 W
WIn amateur astronomy, "GoTo" refers to a type of telescope mount and related software that can automatically point a telescope at astronomical objects that the user selects. Both axes of a GoTo mount are driven by a motor and controlled by a computer. It may be either a microprocessor-based integrated controller or an external personal computer. This differs from the single-axis semi-automated tracking of a traditional clock-drive equatorial mount.
 W
WThe Greenland Telescope is a radio telescope that is currently installed and operating at the Thule Air Base in north-western Greenland. It will later be deployed at the Summit Station research camp, located at the highest point of the Greenland ice sheet at an altitude of 3,210 meters.
 W
WThe Hale Telescope is a 200-inch (5.1 m), f/3.3 reflecting telescope at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, US, named after astronomer George Ellery Hale. With funding from the Rockefeller Foundation in 1928, he orchestrated the planning, design, and construction of the observatory, but with the project ending up taking 20 years he did not live to see its commissioning. The Hale was groundbreaking for its time, with double the diameter of the second-largest telescope, and pioneered many new technologies in telescope mount design and in the design and fabrication of its large aluminum coated "honeycomb" low thermal expansion Pyrex mirror. It was completed in 1949 and is still in active use.
 W
WHartmann mask is a tool to help focusing telescopes, mainly used by amateur astronomers. It is named after the German astronomer Johannes Franz Hartmann (1865–1936), who developed it around 1900.
 W
WThe Hexapod-Telescope (HPT) is a telescope located at Cerro Armazones Observatory in northern Chile. The 1.5 metres (59 in) Ritchey-Chrétien reflecting telescope is notable for the design of the telescope mount. Instead of the typical mounting where the telescope moves on two rotating axes, the mirror end of the telescope is supported by six extensible struts, an arrangement known as a Stewart platform. This configuration allows the telescope to move in all six spatial degrees of freedom and also provides strong structural integrity. As a result, the ratio of bearing pressure and its own weight is very high. Furthermore, the six-leg structure allows for a very precise positioning and repeatability. The disadvantage of the system is that controlling and aiming a hexapod-mounted telescope is much more complex than with conventional telescope mounts.
 W
WThe history of the telescope can be traced to before the invention of the earliest known telescope, which appeared in 1608 in the Netherlands, when a patent was submitted by Hans Lippershey, an eyeglass maker. Although Lippershey did not receive his patent, news of the invention soon spread across Europe. The design of these early refracting telescopes consisted of a convex objective lens and a concave eyepiece. Galileo improved on this design the following year and applied it to astronomy. In 1611, Johannes Kepler described how a far more useful telescope could be made with a convex objective lens and a convex eyepiece lens. By 1655, astronomers such as Christiaan Huygens were building powerful but unwieldy Keplerian telescopes with compound eyepieces.
 W
WAn infinite-axis telescope is a telescope that can move freely in all directions. Such telescopes can be mechanically simple hand-guided versions with the mounting serving only to carry the weight of the telescope although there are equatorial versions.
 W
WLas Cumbres Observatory (LCO) is a network of astronomical observatories run by a non-profit private operating foundation directed by the technologist Wayne Rosing. Its offices are in Goleta, California. The telescopes are located at both northern and southern hemisphere sites distributed in longitude around the Earth. For some astronomical objects, the longitudinal spacing of telescopes allows continuous observations over 24 hours or longer. The operating network currently consists of two 2 meter telescopes, nine 1 meter telescopes, and seven 40 cm telescopes, placed at six astronomical observatories. The network operates as a single, integrated, observing facility, using a software scheduler that continuously optimizes the planned observing schedule of each individual telescope.
 W
WLiquid-mirror telescopes are telescopes with mirrors made with a reflective liquid. The most common liquid used is mercury, but other liquids will work as well. The liquid and its container are rotated at a constant speed around a vertical axis, which causes the surface of the liquid to assume a paraboloidal shape. This parabolic reflector can serve as the primary mirror of a reflecting telescope. The rotating liquid assumes the same surface shape regardless of the container's shape; to reduce the amount of liquid metal needed, and thus weight, a rotating mercury mirror uses a container that is as close to the necessary parabolic shape as possible. Liquid mirrors can be a low-cost alternative to conventional large telescopes. Compared to a solid glass mirror that must be cast, ground, and polished, a rotating liquid-metal mirror is much less expensive to manufacture.
 W
WThe Maunakea Spectroscopic Explorer (MSE) is a collaborative project by a new and enlarged partnership to revitalize the Canada-France-Hawai‘i Telescope (CFHT) observatory through replacing the existing 1970-vintage optical telescope with a modern segmented-mirror telescope and dedicated science instrumentation, while substantially re-using the existing Maunakea summit building and facility. At the highest level the objectives of MSE are to enhance scientific research and education for the partner communities. MSE will use an 11.25 meter aperture telescope and dedicated multiobject fibre spectroscopy instrumentation to perform survey science observations, collecting spectra from more than 4,000 astronomical targets simultaneously.
 W
WThe meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis.
 W
WThe Narrabri Stellar Intensity Interferometer (NSII) was the first astronomical instrument to measure the diameters of a large number of stars at visible wavelengths. It was designed by Robert Hanbury Brown, who received the Hughes Medal in 1971 for this work. It was built by University of Sydney School of Physics and was located near the town of Narrabri in north-central New South Wales, Australia. Many of the components were constructed in the UK. The design was based on an earlier optical intensity interferometer built by Hanbury Brown and Richard Q. Twiss at Jodrell Bank in the UK. Whilst the original device had a maximum baseline of 10m, the NSII device consisted of a large circular track that allowed the detectors to be separated from 10 to 188m. The NSII operated from 1963 until 1974, and was used to measure the angular diameters of 32 stars.
 W
WThe Next-Generation Transit Survey (NGTS) is a ground-based robotic search for exoplanets. The facility is located at Paranal Observatory in the Atacama desert in northern Chile, about 2 km from ESO's Very Large Telescope and 0.5 km from the VISTA Survey Telescope. Science operations began in early 2015. The astronomical survey is managed by a consortium of seven European universities and other academic institutions from Chile, Germany, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. Prototypes of the array were tested in 2009 and 2010 on La Palma, and from 2012 to 2014 at Geneva Observatory.
 W
WThe Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE) is a Polish astronomical project based at the University of Warsaw that runs a long-term variability sky survey (1992-present). The main goals are the detection and classification of variable stars, discovery of microlensing events, dwarf novae, and studies of the structure of the galaxy and the Magellanic Clouds. Since the project began in 1992, it has discovered a multitude of extrasolar planets, together with the first planet discovered using the transit method (OGLE-TR-56b) and gravitational microlensing. The project has been led by professor Andrzej Udalski since its inception.
 W
WAn optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.
 W
WThe Otto Struve Telescope was the first major telescope to be built at McDonald Observatory. Located in the Davis Mountains in West Texas, the Otto Struve Telescope was designed by Warner & Swasey Company and constructed between 1933 and 1939 by the Paterson-Leitch Company. Its 82-inch (2.1 m) mirror was the second largest in the world at the time. It was named after the Russian-American astronomer Otto Struve in 1966, three years after his death; Struve had been the director of McDonald Observatory from 1932–1950.
 W
WThe Palomar Testbed Interferometer (PTI) was a near infrared, long-baseline stellar interferometer located at Palomar Observatory in north San Diego County, California, United States. It was built by Caltech and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and was intended to serve as a testbed for developing interferometric techniques to be used at the Keck Interferometer. It began operations in 1995 and achieved routine operations in 1998, producing more than 50 refereed papers in a variety of scientific journals covering topics from high precision astrometry to stellar masses, stellar diameters and shapes. PTI concluded operations in 2008 and has since been dismantled.
 W
WA refracting telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image. The refracting telescope design was originally used in spy glasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece.
 W
WA rotating furnace is a device for making solid objects which have concave surfaces that are segments of axially symmetrical paraboloids. Usually, the objects are made of glass. The furnace makes use of the fact, which was known already to Newton, that the centrifugal-force-induced shape of the top surface of a spinning liquid is a concave paraboloid, identical to the shape of a reflecting telescope's primary focusing mirror.
 W
WRTT-150 is a Russian-Turkish 1.5-m optical telescope. It is an international project, jointly led by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation and the Council for Technical and Scientific Research of Turkey. The main performers are Kazan Federal University and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences from the Russian side and the TUBITAK State Observatory from Turkey. Observational time of telescope is shared in the following proportion: 45% - KSU, 15% - IKI RAS, and another 40% - are shared between Turkish universities through the TUG.
 W
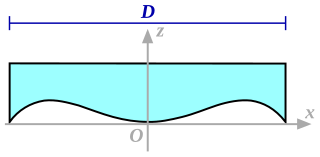
WThe Schiefspiegler, also called tilted-component telescopes (TCT) and off-axis reflecting telescopes, are a type of reflecting telescope featuring an off-axis secondary mirror, and therefore an obstruction-free light path. This is accomplished by tilting the primary mirror so that the secondary mirror does not block incoming light. William Herschel was one of the first to have tilted the mirror of his telescope in order to avoid light loss due to the low reflectivity of his speculum-metal mirror.
 W
WA Schmidt corrector plate is an aspheric lens which corrects the spherical aberration introduced by the spherical primary mirror of the Schmidt or Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope designs. It was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1931, although it may have been independently invented by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä in 1924. Schmidt originally introduced it as part of a wide-field photographic catadioptric telescope, the Schmidt camera. It is now used in several other telescope designs, camera lenses and image projection systems that utilise a spherical primary mirror.
 W
WA Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.
 W
WSetting circles are used on telescopes equipped with an equatorial mount to find astronomical objects in the sky by their equatorial coordinates often used in star charts or ephemerides.
 W
WSkyMapper is a fully automated 1.35 m (4.4 ft) wide-angle optical telescope at Siding Spring Observatory in northern New South Wales, Australia. It is one of the telescopes of the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics of the Australian National University (ANU). The telescope has a compact modified Cassegrain design with a large 0.69 m secondary mirror, which gives it a very wide field of view: its single, dedicated instrument, a 268-million pixel imaging camera, can photograph 5.7 square degrees of sky. The camera has six light filters which span from ultraviolet to near infrared wavelengths.
 W
WSubaru Telescope is the 8.2-meter (320 in) flagship telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, located at the Mauna Kea Observatory on Hawaii. It is named after the open star cluster known in English as the Pleiades. It had the largest monolithic primary mirror in the world from its commissioning until 2005.
 W
WA telescope mount is a mechanical structure which supports a telescope. Telescope mounts are designed to support the mass of the telescope and allow for accurate pointing of the instrument. Many sorts of mounts have been developed over the years, with the majority of effort being put into systems that can track the motion of the fixed stars as the Earth rotates.
 W
WThe Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) is a proposed extremely large telescope (ELT) that has become controversial due to its planned location on Mauna Kea, on the island of Hawaii, the most sacred mountain in Native Hawaiian culture. The TMT would become the largest visible-light telescope on Mauna Kea.
 W
WThe Transient Array Radio Telescope (TART) is a low-cost open-source array radio telescope consisting of 24 all-sky GNSS receivers operating at the L1-band (1.575 GHz). TART was designed as an all-sky survey instrument for detecting radio bursts, as well as providing a test-bed for the development of new synthesis imaging and calibration algorithms. All of the telescope hardware including radio receivers, correlators and operating software are open source. A TART-2 radio-telescope can be built for approximately 1000 Euros, and the telescope antenna array requires 4m x 4m area for deployment.
 W
WThe Vacuum Tower Telescope is an evacuated-optics solar telescope located at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It is operated by the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik (KIS).
 W
WThe Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, also known as the Blanco 4m, is a 4-metre aperture telescope located at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, Chile. Commissioned in 1974 and completed in 1976, the telescope is identical to the Mayall 4m telescope located on Kitt Peak. In 1995 it was dedicated and named in honour of Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel Blanco. It was the largest optical telescope in the Southern hemisphere from 1976 until 1998, when the first 8-metre telescope of the ESO Very Large Telescope opened.
 W
WA zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length (FFL) lens.