 W
WInformation technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT) components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components, but also various software and network components.
 W
WThis article contains a sortable list of countries by number of broadband Internet subscriptions and penetration rates, using data compiled by the International Telecommunication Union.
 W
WThis is the list of countries by number of Internet hosts, based on 2012 figures from the CIA World Factbook. Several dependent territories, not fully recognized states, and non-state territories are also listed. The European Union host (.eu) is mostly composed of French, Polish and German hosts.
 W
WThe Digital Nations or DN is a collaborative network of the world's leading digital governments with a common goal of harnessing digital technology to improve citizens' lives. Members share world-class digital practices, collaborate to solve common problems, identify improvements to digital services, and support and champion the group's growing digital economies. Through international cooperation, the Digital Nations aims to identify how digital government can provide the most benefit to citizens. The group embodies minilateral engagement, where small groups of states cooperate on specific topics with a global impact.
 W
WThe Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure, abbreviated BMVI, is a cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany.
 W
WAn information infrastructure is defined by Ole Hanseth (2002) as "a shared, evolving, open, standardized, and heterogeneous installed base" and by Pironti (2006) as all of the people, processes, procedures, tools, facilities, and technology which supports the creation, use, transport, storage, and destruction of information.
 W
WThe Internet backbone may be defined by the principal data routes between large, strategically interconnected computer networks and core routers of the Internet. These data routes are hosted by commercial, government, academic and other high-capacity network centers, as well as the Internet exchange points and network access points, that exchange Internet traffic between the countries, continents, and across the oceans. Internet service providers, often Tier 1 networks, participate in Internet backbone traffic by privately negotiated interconnection agreements, primarily governed by the principle of settlement-free peering.
 W
WLansweeper is an application that gathers hardware and software information of computers and other devices on a computer network for management and compliance and audit purposes. The application also encompasses a ticket based help desk system and capabilities for software updates on target devices.
 W
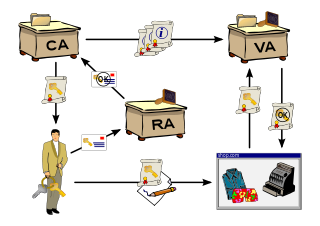
WA public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. It is required for activities where simple passwords are an inadequate authentication method and more rigorous proof is required to confirm the identity of the parties involved in the communication and to validate the information being transferred.