 W
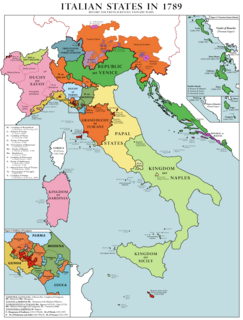
WThe Cisalpine Republic was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that lasted from 1797 to 1802.
 W
WThe Battle of Faenza, also known as the Battle of Castel Bolognese on February 3, 1797 saw a 7,000 troops from the Papal Army commanded by Michelangelo Alessandro Colli-Marchi facing 9,000 troops from the French Army under the command of Claude Victor-Perrin. The veteran French troops quickly overran the Papal army, inflicting disproportionate casualties. The town of Castel Bolognese was located on the banks of the Senio River 40 kilometres (25 mi) southeast of Bologna, and the city of Faenza was also nearby. The action took place during the War of the First Coalition, as part of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WThe Fall of the Republic of Venice was a series of events that culminated on 12 May 1797 that led to the dissolution and dismemberment of the Republic of Venice at the hands of Napoleon Bonaparte and Habsburg Austria.
 W
WThe Lombard Legion was a military unit of the Cisalpine Republic which existed from 1796 until the Republic's fall in 1799. The Lombard Legion was the first Italian military department to equip itself, as a banner, with an Italian tricolor flag.
 W
WThe Battle of Tarvis was fought during 21–23 March 1797 near present-day Tarvisio in far northeast Italy, about 12 kilometres (7 mi) west-by-southwest of the three-border conjunction with Austria and Slovenia. In the battle, three divisions of a First French Republic army commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte attacked several columns of the retreating Habsburg Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. In three days of confused fighting, French divisions directed by André Masséna, Jean Joseph Guieu, and Jean-Mathieu-Philibert Sérurier succeeded in blocking the Tarvis Pass and capturing 3,500 Austrians led by Adam Bajalics von Bajahaza. The engagement occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WThe Transpadane Republic was a revolutionary, provisional and internationally unrecognized government established in Milan by General Napoleon Bonaparte.
 W
WThe Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The treaty followed the armistice of Leoben, which had been forced on the Habsburgs by Napoleon's victorious campaign in Italy. It ended the War of the First Coalition and left Great Britain fighting alone against revolutionary France.
 W
WThe Treaty of Leoben was a general armistice and preliminary peace agreement between the Holy Roman Empire and the First French Republic that ended the War of the First Coalition. It was signed at Eggenwaldsches Gartenhaus, near Leoben, on 18 April 1797 by General Maximilian von Merveldt and the Marquis of Gallo on behalf of the Emperor Francis II and by General Napoléon Bonaparte on behalf of the French Directory. Ratifications were exchanged in Montebello on 24 May, and the treaty came into effect immediately.
 W
WThe Battle of Valvasone saw a First French Republic army led by Napoleon Bonaparte attack a Habsburg Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. The Austrian army fought a rear guard action at the crossing of the Tagliamento River but was defeated and withdrew to the northeast. The next day, a French division cut off and captured an Austrian column in the Capitulation of Gradisca. The actions occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Valvasone is located on the west bank of the Tagliamento 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Udine, Italy. Gradisca d'Isonzo lies on the Isonzo River 14 kilometres (9 mi) southwest of Gorizia, Italy.
 W
WThe Veronese Easter was a rebellion during the Italian campaign of 1797, in which inhabitants of Verona and the surrounding areas revolted against the French occupying forces under Antoine Balland, while Napoleon Bonaparte was fighting in Austria. The uprising received its name through association with the anti-French uprising of the Sicilian Vespers of the 13th century. Incited by oppressive behaviour by the French, it began on the morning of 17 April 1797, the second day of Easter: the enraged population succeeded in defeating more than a thousand French soldiers in the first hour of fighting, forcing them to take refuge in the town's fortifications, which the mob then captured by force. The revolt ended on 25 April 1797 with the encirclement and capture of the town by 15,000 soldiers, who then forced it to pay a huge fine and hand over various assets, including artwork.