 W
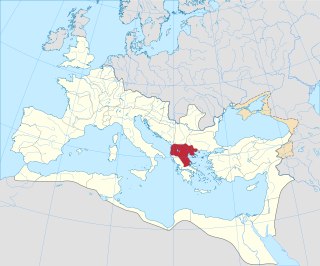
WThe Roman province of Macedonia was officially established in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled king of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia in 148 BC, and after the four client republics established by Rome in the region were dissolved. The province incorporated the former kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. This created a much larger administrative area, to which the name of 'Macedonia' was still applied.
 W
WThe Amphitheatre of Durrës is a Roman amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Durrës, Albania. Construction began under the emperor Trajan in the 2nd century AD and it was destroyed twice by earthquakes in the 6th and 10th centuries. It is the largest amphitheatre ever built in the Balkan Peninsula with once having a capacity of 20,000 people.
 W
WThe baptistery at Butrint, an archeological site in Vlorë County, Albania and part of the Butrint National Park, is a late antique structure known for its well-preserved mosaic pavement. The centrally planned, circular baptistery is also notable as an ancient Roman monument adapted to the needs of Christianity.
 W
WThe Battle of Dyrrachium on 10 July 48 BC was a battle during Caesar's Civil War that took place near the city of Dyrrachium. It was fought between Julius Caesar and an army led by Gnaeus Pompey who had the backing of the majority of the Roman Senate. The battle was a victory for Pompey, albeit not a decisive one. The Battle at Dyrrachium preceded the Battle of Pharsalus which was the decisive turning point in the Civil War leading to a Caesarian victory.
 W
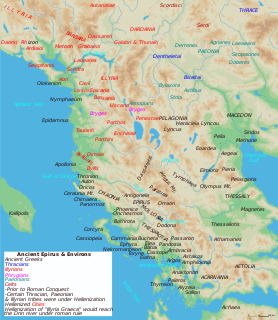
WButrint was an ancient Greek and later Roman city and bishopric in Epirus. Perhaps inhabited since prehistoric times, Buthrotum was a city of the Epirote tribe of the Chaonians, later a Roman colony and a bishopric. It entered into decline in Late Antiquity, before being abandoned during the Middle Ages after a major earthquake flooded most of the city. In modern times it is an archeological site in Vlorë County, Albania, some 14 kilometres south of Sarandë and close to the Greek border. It is located on a hill overlooking the Vivari Channel and is part of the Butrint National Park. Today Bouthrotum is a Latin Catholic titular see and also features the Ali Pasha Castle.
 W
WByllis or Bullis or Boullis (Βουλλίς) was an ancient city located in the region of Illyria. The remains of Byllis are situated north-east of Vlorë, 25 kilometers from the sea in Hekal, Fier County, Albania.
 W
WPelion, also Pellion or Pelium was a fortified settlement of the Dassaretae located on the borderlands between southern Illyria and Macedonia in classical and Roman antiquity. The precise location of Pelion is uncertain and various theories been proposed for the site of the settlement in the Dassaretis region, in Epirus Nova and in Illyricum. It passed different phases of control: the Chaonian tribe of Dexaroi, a coalition of Illyrian tribes, the Macedonian kingdom and finally Rome since at least 198 BCE.
 W
WPhoenice or Phoenike was an ancient Greek city in Epirus and capital of the Chaonians. It was also the location of the Treaty of Phoenice which ended the First Macedonian War, as well as one of the wealthiest cities in Epirus until the Roman conquest. During the early Byzantine period, Phoenice was the see of a bishopric. The city is an archaeological park of Albania and is located on a hill above a modern town which bears the same name, Finiq, in modern southern Albania.
 W
WThe praetorian prefecture of Illyricum was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.
 W
WPraevalitana was a Late Roman province that existed between c. 284 and c. 600. It included parts of present-day Montenegro, northern Albania, and part of present-day Kosovo. Its capital city was Scodra.
 W
WThe Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a continuation of the Via Appia.