 W
WLinzi, originally called Yingqiu, was the capital of the ancient Chinese state of Qi during the Zhou Dynasty. The ruins of the city lie in modern-day Linzi District, Shandong, China. The city was one of the largest and richest in China during the Spring and Autumn Period. With occupying Linzi in 221 BC, King Zheng of Qin completed his conquest of the Chinese rival states and declared himself the first emperor of Ancient China shortly afterwards. The ruins of the ancient city were excavated in 1926 by Japanese archaeologists and in 1964 by Chinese archaeologists.
 W
WChang'an was an ancient capital of more than ten dynasties in Chinese history, today known as Xi'an. Chang'an means "Perpetual Peace" in Classical Chinese since it was a capital that was repeatedly used by new Chinese rulers. During the short-lived Xin dynasty, the city was renamed "Constant Peace" ; the old name was later restored. By the time of the Ming dynasty, a new walled city named Xi'an, meaning "Western Peace", was built at the Sui and Tang dynasty city's site, which has remained its name to the present day.
 W
WFenghao is the modern name of the twin city formed by the Western Zhou capitals of Feng and Hao on opposite banks of the Feng River near its confluence with the Wei River in Shaanxi, China.
 W
WJiankang, or Jianye, as it was originally called, was the capital city of the Eastern Wu, the Jin dynasty and the Southern Dynasties. Its walls are extant ruins in the modern municipal region of Nanjing.
 W
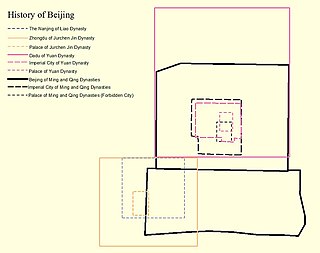
WKhanbaliq or Dadu (元大都) was the winter capital of the Yuan dynasty, the main center of the Mongol Empire founded by Kublai Khan in what is now Beijing, also the capital of China today. It was located at the center of modern Beijing. The Secretariat (中书省) directly administered the Central Region (腹裏) of the Yuan Empire and dictated policies for the other provinces. Kublai and his successors also claimed supremacy over the entire Mongol Empire following the death of Möngke Khan in 1259. Over time the unified empire gradually fragmented into a number of khanates.
 W
WLuoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of the final 2010 census, Luoyang had a population of 6,549,941 inhabitants with 1,857,003 people living in the built-up area made of the city's five urban districts, all of which except the Jili District are not urbanized yet.
 W
WNanjing was the name for modern Beijing during the Liao dynasty, when Khitan rulers made the city the southern capital. To distinguish Nanjing, which literally means "Southern Capital" in Chinese, from modern Nanjing in Jiangsu Province and Beijing Damingfu, the Northern Song Dynasty name for modern Daming County in Hebei Province, Chinese historians sometimes refer to Beijing during the Liao dynasty as Liao Nanjing. The Khitan rulers of the Liao acquired the city, then known as Youzhou, in the cession of the Sixteen Prefectures in 938 from the Later Jìn, one of the five shortlived dynasties that ruled northern China following the end of the Tang Dynasty. The city was officially renamed Nanjing, Youdu Fu (南京幽都府). In 1012, the city was renamed Nanjing, Xijin Fu (南京析津府). The city was also colloquially referred to at the time as Yanjing. In 1122, the city was captured by the Jurchen Jin dynasty and was officially renamed Yanjing, ending the use of Nanjing for what is today modern Beijing.
 W
WXianyang is a prefecture-level city in central Shaanxi province, situated on the Wei River a few kilometers upstream (west) from the provincial capital of Xi'an. Once the capital of the Qin dynasty, it is now integrated into the Xi'an metropolitan area, one of the main urban agglomerations in western China, with more than 7.17 million inhabitants, its built-up area made of 2 urban districts was 945,420 inhabitants at the 2010 census. It has a total area of 10,213 square kilometres (3,943 sq mi). Xianyang is home to the main campus of Northwest A&F University (NWAFU), one of the world's top universities in "Agriculture Science" related-fields and a member of "Project 985" club which is an organization of 39 reputable universities in China.
 W
WXuchang is a prefecture-level city in central Henan province in Central China. It borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the northwest, Kaifeng to the northeast, Zhoukou to the east, Luohe to the southeast, and Pingdingshan to the southwest.
 W
WYinxu is the site of one of the ancient and major historical capitals of China. It is the source of the archeological discovery of oracle bones and oracle bone script, which resulted in the identification of the earliest known Chinese writing. The archeological remnants known as Yinxu represent the ancient city of Yin, the last capital of China's Shang dynasty which existed through eight generations for 255 years, and through the reign of 12 kings. Yinxu was discovered, or rediscovered, in 1899. It is now one of China's oldest and largest archeological sites, and has been selected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Yinxu is located in northernmost Henan province near the modern city of Anyang, and near the Hebei and Shanxi province borders. Public access to the site is permitted.
 W
WZhongdu was the capital of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in medieval China. It was located in the southwestern part of Beijing's Xicheng District. It had a population of nearly one million by the late 12th century, and was the last and largest pre-modern city built on that location.