 W
WMesopotamian religion refers to the religious beliefs and practices of the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia, particularly Sumer, Akkad, Assyria and Babylonia between circa 3500 BC and 400 AD, after which they largely gave way to Syriac Christianity. The religious development of Mesopotamia and Mesopotamian culture in general was not particularly influenced by the movements of the various peoples into and throughout the area, particularly the south. Rather, Mesopotamian religion was a consistent and coherent tradition which adapted to the internal needs of its adherents over millennia of development.
 W
WBabylonian religion is the religious practice of Babylonia. Babylonian mythology was greatly influenced by their Sumerian counterparts and was written on clay tablets inscribed with the cuneiform script derived from Sumerian cuneiform. The myths were usually either written in Sumerian or Akkadian. Some Babylonian texts were translations into Akkadian from the Sumerian language of earlier texts, although the names of some deities were changed.
 W
WUsed by Sumerians and other Mesopotamian cultures beginning in the third millennium BC, clay nails, also referred to as dedication or foundation pegs, cones, or nails, were cone-shaped nails made of clay, inscribed with cuneiform, baked, and stuck into the mudbrick walls to serve as evidence that the temple or building was the divine property of the god to whom it was dedicated. Versions were also made of metal, including castings with figurative designs, such as the Hurrian foundation pegs.
 W
WThe E-ninnu 𒂍𒐐 was the E (temple) to Ningirsu in Lagash. It was constructed by King Gudea of Lagash in the mid 22nd century BC. The Gudea cylinders, perhaps the longest surviving text written in the Sumerian language, give an mythical account of the building of the temple, along with a description of the rituals and symbols associated with E-ninnu. In Uruk, the temple is also claimed to be built by Ur-Nammu.
 W
WE-sara (Cuneiform: E2 SAR.A 𒂍𒊬𒀀 "House of the Universe"), was the temple dedicated to Inanna in Uruk by Ur-Nammu.
 W
WE-anna was an ancient Sumerian temple in Uruk. Considered "the residence of Inanna" and Anu, it is mentioned several times in the Epic of Gilgamesh, and elsewhere. The evolution of the gods to whom the temple was dedicated is the subject of scholarly study.
 W
WEhursag is a Sumerian term meaning "house of the mountains".
 W
WEnamtila is a Sumerian term meaning "house of life" or possibly "house of creation". It was a sanctuary dedicated to Enlil, likely to have been located within the Ekur at Nippur during the Akkadian Empire. It also referred to various other temples including those to later versions of Enlil; Marduk and Bel as well as one to Ea. It was likely another name for Ehursag, a temple dedicated to Shulgi in Ur. A hymn to Nanna suggests the link "To Ehursag, the house of the king, to the Enamtila of prince Shulgi we go!" Another reference in the Inanna - Dunmuzi text translated by Samuel Noah Kramer references the king's palace by this name and possibly makes references to the "sacred marriage": "In the Enamtila, the house of the king, his wife dwelt with him in joy, in the Enamtila, the house of the king, Inanna dwelt with him in joy. Inanna, rejoicing in his house ...". A fire is reported to have broken out next to the Enamtila in a Babylonian astronomical diary dated to the third century BC. The Enamtila is also referred to as a palace of Ibbi-Sin at Ur in the Lament for Sumer and Ur, "Its king sat immobilised in his own palace. Ibbi-Suen was sitting in anguish in his own palace. In E-namtila, his place of delight, he wept bitterly. The flood dashing a hoe on the ground was levelling everything."
 W
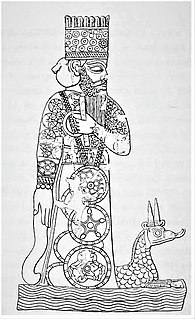
WThe Statue of Marduk, also known as the Statue of Bêl, was the physical representation of the god Marduk, the patron deity of the ancient city of Babylon, traditionally housed in the city's main temple, the Esagila. There were seven statues of Marduk in Babylon, but 'the' Statue of Marduk generally refers to the god's main statue, placed prominently in the Esagila and used in the city's rituals. This statue was nicknamed the Asullḫi and was made of a type of wood called mēsu and covered with gold and silver.
 W
WSumerian religion was the religion practiced and adhered to by the people of Sumer, the first literate civilization of ancient Mesopotamia. The Sumerians regarded their divinities as responsible for all matters pertaining to the natural and social orders.
 W
WÉ is the Sumerian word or symbol for house or temple.