 W
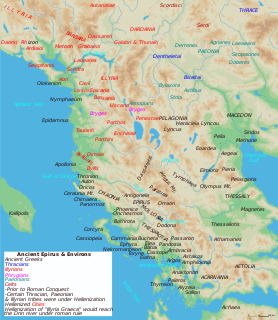
WThis is a list of ancient cities in Illyria, towns, villages, and fortresses by Illyrians, Veneti, Liburni, Romans, Celts, Thracians, Dacians or Greeks located in or near Illyrian lands. A number of cities in Illyria and later Illyricum were built on the sites or close to the sites of pre-existing Illyrian settlements, though that was not always the case. Some settlements may have a double entry, e.g., Greek Pola and Roman Pietas Julia, and some toponyms are reconstructed.
 W
WThe following is a list of ancient Illyrian peoples and tribes.
 W
WThis is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria. The name Illyrians seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks, causing the name Illyrians to be applied to all people of similar language and customs. The locations of Illyrian tribes/peoples prior to the Roman conquest are approximate, as sometimes many wholly different locations are given by ancient writers and modern authors.
 W
WThe Ardiaei were an Illyrian people residing on territory of present-day Albania, Kosovo, Montenegro, and Bosnia and Herzegovina between Adriatic coast on the south, Konjic on the north, along the Neretva river and its right bank on the west, extending to Lake Shkodra to the southeast. From the 3rd century BC to 168 BC the capital cities of the Ardiaean State were Rhizon and Scodra.
 W
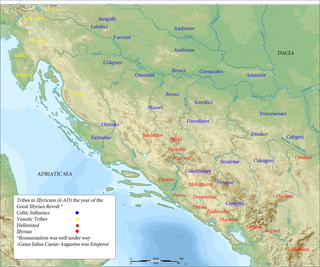
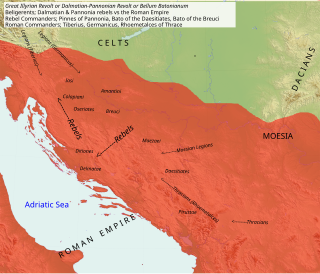
WBato the Daesitiate was a chieftain of the Daesitiates, an Illyrian tribe which fought against the Roman Empire between 6 and 9 AD in a conflict known as Bellum Batonianum.
 W
WBato the Breucian or Bato of the Breuci was the chieftain of the Breuci, an Illyrian tribe that fought against the Roman Empire in a war known as Bellum Batonianum. Bato joined his rebel forces with those led by Bato of the Daesitiates. After facing defeat, he surrendered to Tiberius in 8 CE on the bank of the Bosna river. Ultimately, Bato of the Breuci was captured by Bato of Daesitiates and was put to death after a decision was made by an assembly of the Daesitiates.
 W
WThe Bellum Batonianum was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Romans. The rebellion began among native peoples who had been recruited as auxiliary troops for the Roman army. They were led by Bato the Daesitiate, a chieftain of the Daesitiatae in the central part of present-day Bosnia, and were later joined by the Breuci, a tribe in Pannonia led by Bato the Breucian. Many other tribes in Illyria also joined the revolt.
 W
WDaesitiates were an Illyrian tribe that lived in the territory of today's central Bosnia, during the time of the Roman Republic. Along with the Maezaei, the Daesitiates were part of the western group of Pannonians in Roman Dalmatia. They were prominent from the end of the 4th century BC up until the beginning of the 3rd century CE. Evidence of their daily activities can be found in literary sources, as well as in the rich material finds from Central Bosnian cultural group that is commonly associated with tribe of Daesitiates.
 W
WThe Delmatae were a group of Illyrian tribes which lived in Dalmatia - which takes its name from them - and present-day western Bosnia and Herzegovina in classical antiquity.
 W
WDaorson was the capital of a Hellenised Illyrian tribe called the Daorsi. The Daorsi lived in the valley of the Neretva River between 300 BC and 50 BC. The ruins of Daorson can be found at Ošanjići, near Stolac, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
 W
WDesilo is an underwater archaeological site in southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, located near the Neretva river and the Croatian border. The site was first discovered in the late 20th century, but Desilo's history can be traced as far back as ancient times. Investigations by a University of Mostar archaeological team in 2007 uncovered many sunken boats at the bottom of the small lake in Desilo valley. The archaeologists believe these boats to be Illyrian ships, dating back to the first and second centuries B.C. Further excavations in 2008 by University of Oslo archaeologists found evidence suggesting that Desilo was an Illyrian trading post. These archaeological findings are significant because they are the first known discovery of Illyrian ships. Additionally, Desilo functioning as a trading centre suggests there were peaceful interactions between the Illyrians and the Romans.
 W
WHedum Kastelum was an ancient city located in central Bosnia, in the modern-day town of Breza, Bosnia and Herzegovina. The name Hedum Kastelum means "Inhabited Castle", or in Bosnian, Naseljena Tvrđava. The city was also the capital of the Illyrian tribe Daesitiates. Today, only the Basilica and some grave tombs remain.
 W
WThe Iapydes were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the Colapis (Kupa) and Oeneus (Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans.