 W
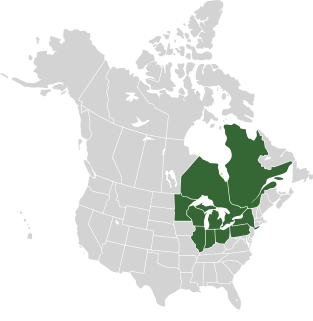
WThe Saint Lawrence Seaway is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North America, as far inland as Duluth, Minnesota, at the western end of Lake Superior. The seaway is named for the Saint Lawrence River, which flows from Lake Ontario to the Atlantic Ocean. Legally, the seaway extends from Montreal, Quebec, to Lake Erie, and includes the Welland Canal.
 W
WThe Beauharnois Canal is located in southwestern Quebec, Canada. The canal is part of the Saint Lawrence Seaway.
 W
WThe Cornwall Canal was built by the British government of Canada to bypass a troublesome rapids hindering navigation on the St. Lawrence at Cornwall, Ontario begun in 1834 it was completed in 1843.
 W
WThe Saint Lawrence Seaway Development Corporation (SLSDC) is the agency of the United States Department of Transportation that operates and maintains the U.S.-owned and operated facilities of the joint United States-Canadian Saint Lawrence Seaway. It operates 2 of the 15 locks of the Seaway between Montreal and Lake Erie.
 W
WThe Great Lakes–Saint Lawrence River Basin Sustainable Water Resources Agreement is a good-faith agreement among the Governors of the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin, and the Premiers of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The agreement details how the States and Provinces will manage the use of the Great Lakes Basin's water supply and builds on the 1985 Great Lakes Charter and its 2001 Annex. It was signed on December 13, 2005.
 W
WThe Lachine Canal is a canal passing through the southwestern part of the Island of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, running 14.5 kilometres from the Old Port of Montreal to Lake Saint-Louis, through the boroughs of Lachine, Lasalle and Sud-Ouest. Before the canal construction there was a lake, Lac St Pierre. The lake and its rivers can be seen on the maps of Montreal of the years 1700, 1744 and on the map titled "The isles of Montreal. As they have been surveyed by the french engineers" (1761).
 W
WLake Erie is the fourth-largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America, and the eleventh-largest globally if measured in terms of surface area. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. At its deepest point Lake Erie is 210 feet deep.
 W
WLake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is surrounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the American state of New York, whose water boundaries meet in the middle of the lake. Ontario, Canada's most populous province, was named for the lake.
 W
WLong Sault was a rapid in the St. Lawrence River west of Cornwall.
 W
WThe Niagara River is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. There are differing theories as to the origin of the river's name. According to Iroquoian scholar Bruce Trigger, Niagara is derived from the name given to a branch of the locally residing native Neutral Confederacy, who are described as being called the Niagagarega people on several late-17th-century French maps of the area. According to George R. Stewart, it comes from the name of an Iroquois town called Ongniaahra, meaning "point of land cut in two".
 W
WThe term Seawaymax refers to vessels which are the maximum size that can fit through the canal locks of the St. Lawrence Seaway, linking the inland Great Lakes of North America with the Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WThe Soulanges Canal is an abandoned shipping canal in Quebec, Canada. It follows the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River between Pointe-des-Cascades and Coteaux-Landing, bypassing the rapids between Lake Saint-Louis and Lake Saint-Francis. In between, it passes through the towns of Les Cèdres and Coteau-du-Lac. It superseded the first Beauharnois Canal which was on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence. It is 23 kilometers (14 mi) long and had a 4.3-meter (14.1 ft) draught. Five locks measuring 85.3 m × 14 m give a total rise of 25 meters (82 ft).
 W
WThe Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines to Port Colborne, it enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and bypass Niagara Falls. The name currently refers to the fourth such canal, three earlier and much smaller canals servicing the same route are also known as the Welland.