 W
WThe Ahom kingdom was a late medieval kingdom in the Brahmaputra Valley in Assam. It is well known for maintaining its sovereignty for nearly 600 years and successfully resisting Mughal expansion in Northeast India. Established by Sukaphaa, a Tai prince from Mong Mao, it began as a mong in the upper reaches of the Brahmaputra based on wet rice agriculture. It expanded suddenly under Suhungmung in the 16th century and became multi-ethnic in character, casting a profound effect on the political and social life of the entire Brahmaputra valley. The kingdom became weaker with the rise of the Moamoria rebellion, and subsequently fell to repeated Burmese invasions of Assam. With the defeat of the Burmese after the First Anglo-Burmese War and the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826, control of the kingdom passed into East India Company hands.
 W
WAnanta Vasudeva Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Krishna, an avatar of Lord Vishnu located in Bhubaneswar, the state capital of Odisha, India. The temple was constructed in the thirteenth century, and the complete murtis of Krishna, Balarama and Subhadra are worshipped there. Balarama stands under a seven hooded serpent, Subhadra holds Jewels pot and lotus in her two hands keeping her left foot over another jewel pot, while Krishna holds a mace, chakra, lotus and a conch. The temple dates back to the period of Chandrika Devi, the daughter of Anangabhima III, during the reign of the king Bhanudeva. A commemorative inscription that marked the foundation of the temple can be found in the British Museum's collection.
 W
WThe Arya Chakravarti dynasty were kings of the Jaffna Kingdom in Sri Lanka. The earliest Sri Lankan sources, between 1277 and 1283, mention a military leader of this name as a minister in the services of the Pandyan Empire; he raided the western Sri Lankan coast and took the politically significant relic of the Buddha’s tooth from the Sinhalese capital city of Yapahuwa. Political and military leaders of the same family name left a number of inscriptions in the modern-day Tamil Nadu state, with dates ranging from 1272 to 1305, during the late Pandyan Empire. According to contemporary native literature, such as Cekaracecekaramalai, the family also claimed lineage from the Tamil Brahmins of the prominent Hindu pilgrimage temple of Rameswaram in the modern Ramanathapuram District of India. They ruled the Jaffna kingdom from the 13th until the 17th century, when the last of the dynasty, Cankili II, was ousted by the Portuguese.
 W
WThe Tomb of Ghiyas ud din Balban is located in Mehrauli, New Delhi, India. Built in circa 1287 CE in rubble masonry, the tomb is a building of historical importance in the development of Indo-Islamic architecture, as it was here that first Islamic arch made its appearance in India, and according to many, the first Islamic dome as well, which however hasn't survived, making Alai Darwaza built in 1311 CE, in the nearby Qutb complex, the earliest surviving dome in India. Ghiyas ud din Balban (1200–1287) was a Turkic ruler of the Delhi Sultanate during the rule of Mamluk dynasty of Delhi from 1266 to 1287. He was one of the most prominent rulers of the Slave Dynasty. The tomb of Balban was discovered in the mid-20th century.
 W
WCharaideo or Che-Rai-Doi is a town in Charaideo district, Assam, India and was also the first capital of the Ahom kingdom established by the first Ahom king Chao Lung Siu-Ka-Pha in 1253. Even though the capital moved to other places over the course of the 600 years of rule, Charaideo remained the symbol of Ahom power. It is now known for its collection of maidams, tumuli or burial mounds of the Ahom kings and Ahom royalty.
 W
WDaulatabad Fort, also known as Devagiri or Deogiri, is a historical fortified citadel located in Daulatabad village near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. It was the capital of the Yadava dynasty, for a brief time the capital of the Delhi Sultanate (1327–1334), and later a secondary capital of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate (1499–1636). Around the sixth century CE, Devagiri emerged as an important uplands town near present-day Aurangabad, along caravan routes going towards western and southern India. The historical triangular fortress in the city was initially built around 1187 by the first Yadava king, Bhillama V. In 1308, the city was annexed by Sultan Alauddin Khalji of the Delhi Sultanate, which ruled over most of the Indian subcontinent. In 1327, Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq of the Delhi Sultanate renamed the city as "Daulatabad" and shifted his imperial capital to the city from Delhi, ordering a mass migration of Delhi's population to Daulatabad. However, Muhammad bin Tughluq reversed his decision in 1334 and the capital of the Delhi Sultanate was shifted back from Daulatabad to Delhi. In 1499, Daulatabad became a part of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate, who used it as their secondary capital. In 1610, near Daulatabad Fort, the new city of Aurangabad, then named Khadki, was established to serve as the capital of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate by the Ethiopian military leader Malik Ambar, who was brought to India as a slave but rose to become a popular Prime Minister of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate. Most of the present-day fortification at Daulatabad Fort was constructed under the Ahmadnagar Sultanate.
 W
WThe Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526). Five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk/Slave dynasty (1206–1290), the Khilji dynasty (1290–1320), the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1414), the Sayyid dynasty (1414–1451), and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526). It covered parts of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and some parts of southern Nepal.
 W
WThe Dilwara Temples or Delvada Temples are a group of svetambara Jain temples located about 2 1⁄2 kilometres from the Mount Abu settlement, Rajasthan's only hill station. The earliest were built by Vimal Shah and supposedly designed or at least financed by Vastupala, Jain minister of Dholka. They date between the 11th and 16th centuries, forming some of the most famous monuments in the style of Māru-Gurjara architecture, famous for their use of a very pure white marble and intricate marble carvings. They are a pilgrimage place for Jains, and a significant general tourist attraction. Although Jains built many temples at other places in Rajasthan, the Dilwara temples are believed to be the most impressive.
 W
WGomsi is an ancient archaeological site located between Rani Village and Sika Tode in East Siang District, Arunachal Pradesh, India. It is associated with the 13th-century Chutiya Kingdom, which was located at the field of Rani Village, about 15 km from the town of Pasighat.
 W
WThe Jama Masjid or Great Mosque is a major mosque built in historic center of Budaun, Uttar Pradesh.
 W
WJodhpur State also historically known as the Kingdom of Marwar, was a kingdom in the Marwar region from 1226 to 1818 and a princely state under British rule from 1818 to 1947. Its capital was the city of Jodhpur since 1450.
 W
WThe Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Turko-Afghan dynasty which ruled on the Delhi sultanate, covering large parts of the Indian subcontinent for nearly three decades between 1290 and 1320. Founded by Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji as the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate of India, it came to power through a revolution that marked the transfer of power from the monopoly of Turkish nobles to a heterogeneous Indo-Mussalman nobility. Its rule is known for conquests into present day South India and successfully fending off the repeated Mongol invasions of India.
 W
WKondaveedu Fort is a historically significant ancient hill fortress located in Kondaveedu, a village in the Chilakaluripet constituency of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The site is located 16 miles west of the city of Guntur. Apart from this main fort, there are two other forts nearby. Efforts are in progress to classify Kondaveedu Fort as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
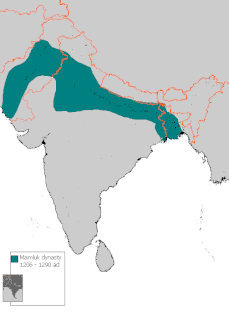
WThe Mamluk Dynasty was directed into Northern India by Qutb ud-Din Aibak, a Turkic Mamluk general from Central Asia. The Mamluk Dynasty ruled from 1206 to 1290; it was the first of five unrelated dynasties to rule as the Delhi Sultanate till 1526. Aibak's tenure as a Ghurid dynasty administrator lasted from 1192 to 1206, a period during which he led invasions into the Gangetic heartland of India and established control over some of the new areas.
 W
WSultan Ghari was the first Islamic Mausoleum (tomb) built in 1231 AD for Prince Nasiru'd-Din Mahmud, eldest son of Iltumish, in the "funerary landscape of Delhi" in the Nangal Dewat Forest, Near Nangal Dewat Vasant Kunj).