 W
WDarius III, originally named Artashata and called Codomannus by the Greeks, was the last king of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia, from 336 BC to 330 BC. Artashata adopted Darius as a dynastic name.
 W
WThe Alexander Mosaic is a Roman floor mosaic originally from the House of the Faun in Pompeii that dates from circa 100 BC. It is typically dated in the second half of the century between 120 and 100 B.C. It depicts a battle between the armies of Alexander the Great and Darius III of Persia and measures 2.72 by 5.13 metres. This work of art is a combination of different artistic traditions such as Italic, Hellenistic, and Roman. The mosaic is considered “Roman” based on the broader context of its time and location in relation to the later Roman Republic. The original is preserved in the Naples National Archaeological Museum. The mosaic is believed to be a copy of an early 3rd-century BC Hellenistic painting.
 W
WThe wars of Alexander the Great were fought by King Alexander III of Macedon, first against the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Darius III, and then against local chieftains and warlords as far east as Punjab, India. By the time of his death, he had conquered most of the world known to the ancient Greeks. However, he failed to conquer all of South Asia. Although being successful as a military commander, he failed to provide any stable alternative to the Achaemenid Empire—his untimely death threw the vast territories he conquered into civil war.
 W
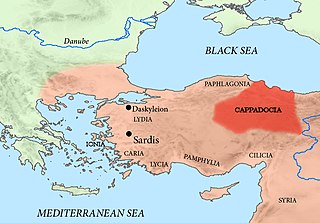
WAriarathes I was the last Achaemenid Persian governor (satrap) of the province (satrapy) of Northern Cappadocia, serving from the 340s BC to 331 BC. He led defensive efforts against the Macedonian invasion, commanded by Alexander the Great, and later fought at the Battle of Gaugamela under Darius III, the last King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire. After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, Ariarathes continued his resistance against the Macedonians, ruling concomitantly as an Achaemenid remnant and a precursor to the Kingdom of Cappadocia. He is regarded as the founder of the Iranian Ariarathid dynasty.
 W
WAtropates was a Persian nobleman who served Darius III, then Alexander the Great, and eventually founded an independent kingdom and dynasty that was named after him. Diodorus (18.4) refers to him as 'Atrapes', while Quintus Curtius (8.3.17) erroneously names him 'Arsaces'.
 W
WThe Battle of Alexander at Issus is a 1529 oil painting by the German artist Albrecht Altdorfer, a pioneer of landscape art and a founding member of the Danube school. The painting portrays the 333 BC Battle of Issus, in which Alexander the Great secured a decisive victory over Darius III of Persia and gained crucial leverage in his campaign against the Persian Empire. The painting is widely regarded as Altdorfer's masterpiece, and is one of the most famous examples of the type of Renaissance landscape painting known as the world landscape, which here reaches an unprecedented grandeur.
 W
WDrypetis or Drypteis, was a princess of the Achaemenid dynasty in Persia.
 W
WThe Family of Darius before Alexander is a 1565–1570 oil on canvas painting by Paolo Veronese. It depicts Alexander the Great with the family of Darius III, the Persian king he had defeated in battle. Although Veronese had previously painted a version of the subject, since destroyed, the theme had rarely been depicted by other artists before him. The painting has been in the collection of the National Gallery in London since 1857.
 W
WMazaeus, Mazday or Mazaios was a Persian noble and satrap of Cilicia and later satrap of Babylon for the Achaemenid Empire, a satrapy which he retained under Alexander the Great.
 W
WMithrobuzanes was a Persian governor (satrap) of Cappadocia in the 4th century BC, during the reign of Darius III. He was probably a son of Ariarathes. As a Persian military commander he was killed at the Battle of Granicus fighting Alexander the Great.
 W
WSisygambis was the mother of Darius III of Persia, whose reign was ended during the wars of Alexander the Great. After she was captured by Alexander at the Battle of Issus, she became devoted to him, and Alexander referred to her as "mother".
 W
WSpithridates was a Persian satrap of Lydia and Ionia under the high king Darius III Codomannus. He was one of the Persian commanders at the Battle of the Granicus, in 334 BC. In this engagement, while he was aiming a blow from behind at Alexander the Great, his arm was cut off by Cleitus the Black and he subsequently died.
 W
WStateira I was a queen of Persia as the wife of Darius III of Persia of the Achaemenid dynasty.
 W
WStateira II, possibly also known as Barsine, was the daughter of Stateira I and Darius III of Persia. After her father's defeat at the Battle of Issus, Stateira and her sisters became captives of Alexander of Macedon. They were treated well, and she became Alexander's second wife at the Susa weddings in 324 BC. At the same ceremony Alexander also married her cousin, Parysatis, daughter of Darius' predecessor. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, Stateira was killed by Roxana, his first wife.
 W
WThe wars of Alexander the Great were fought by King Alexander III of Macedon, first against the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Darius III, and then against local chieftains and warlords as far east as Punjab, India. By the time of his death, he had conquered most of the world known to the ancient Greeks. However, he failed to conquer all of South Asia. Although being successful as a military commander, he failed to provide any stable alternative to the Achaemenid Empire—his untimely death threw the vast territories he conquered into civil war.