 W
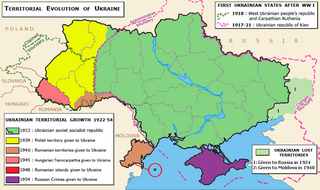
WUkraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and north-east; Belarus to the north; Poland, Slovakia and Hungary to the west; and Romania, Moldova, and the Black Sea to the south. Ukraine also borders Crimea to its south, which Russia annexed from Ukraine in 2014, though Ukraine still continues to claim the territory. Including Crimea, Ukraine has an area of 603,628 km2 (233,062 sq mi), making it the second-largest country by area in Europe after Russia, and the 46th-largest country in the world. Excluding Crimea, Ukraine has a population of about 42 million, making it the eighth-most populous country in Europe, and the 34th-most populous country in the world. Its capital and largest city is Kyiv.
 W
WUkraine emerges as the concept of a nation, and the Ukrainians as a nationality, with the Ukrainian National Revival which is believed started sometime at the end of 18th and the beginning of 19th century. According to Ukrainian historian Yaroslav Hrytsak, the first wave of national revival is traditionally connected with publication of the first part of "Eneyida" by Ivan Kotlyarevsky (1798). In 1846, in Moscow the "Istoriya Rusov ili Maloi Rossii" was published. During the Spring of Nations, in 1848 in Lemberg (Lviv)the Supreme Ruthenian Council was created which declared that Galician Ruthenians are part of the bigger Ukrainian nation. The council adopted the yellow and blue flag.
 W
WDuring World War II, Reichskommissariat Ukraine was the civilian occupation regime (Reichskommissariat) of much of Nazi German-occupied Ukraine. It was governed by the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories headed by Alfred Rosenberg. Between September 1941 and August 1944, the Reichskommissariat was administered by Erich Koch as the Reichskommissar. The administration's tasks included the pacification of the region and the exploitation, for German benefit, of its resources and people. Adolf Hitler issued a Führer Decree defining the administration of the newly occupied Eastern territories on 17 July 1941.
 W
WThe 5th SS Panzer Division "Wiking" was a Panzer division among the thirty-eight Waffen-SS divisions of Nazi Germany. It was recruited from foreign volunteers in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, the Netherlands and Belgium under the command of German officers. During the course of World War II, the division served on the Eastern Front. It surrendered in May 1945 to the American forces in Austria.
 W
WThe General Government, also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region, was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia.
 W
WThe Holocaust in Ukraine took place in the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, the General Government, Crimean General Government and some areas under military control to the East of Reichskommissariat Ukraine and as well in the Transnistria Governorate and Northern Bukovina and Carpathian Ruthenia in World War II. Between 1941 and 1944, more than a million Jews living in the Soviet Union were murdered by Nazi Germany's "Final Solution" extermination policies. Most of them were killed in Ukraine because most pre-WWII Soviet Jews lived in the Pale of Settlement, of which Ukraine was the biggest part.
 W
WThe Janowa Dolina massacre took place on 23 April 1943 in the village of Janowa Dolina, during the occupation of Poland in World War II. Before the Nazi-Soviet invasion of the Polish Second Republic, Janowa Dolina was a model settlement built in the Kostopol County of the Wołyń Voivodeship by workers of the Polish State Basalt Quarry. The town was inhabited by 2,500 people. Its name, which translates as the "Jan's Valley" in Polish, came from the Polish king Jan Kazimierz, who reportedly hunted in the Volhynian forests, and after hunting — rested on the shore of the Horyń (Horyn) River. The town was destroyed during World War II by Ukrainian nationalists who murdered most of its Polish population including women and children.
 W
WThe Korosciatyn massacre took place on the night of February 28/29, 1944, during the province-wide wave of massacres of Poles in Volhynia in World War II. Korosciatyn, which now bears the name of Krynica and is located in western Ukraine, was one of the biggest ethnic Polish villages of the interwar Poland’s within Buczacz County in Tarnopol Voivodeship (pictured). Located along the railway line from Tarnopol to Stanislawów, in 1939 it had some 900 inhabitants, all of them being ethnic Poles. Korosciatyn had an elementary school, a Roman Catholic church and a railway station. It belonged to the Latin Rite Roman Catholic parish of nearby Monasterzyska, which also covered several nearby villages. Among the most famous of the citizens of this parish, are Rev. Stanislaw Padewski, professor Gabriel Turowski as well as two scientists, professor Michal Lesiow of Lublin’s Maria Curie University and doctor Jan Zaleski of Krakow’s Pedagogical College. Altogether, in 1939 the Deaconry of Buczacz had around 45 000 Polish inhabitants.
 W
WDuring the occupation of Ukraine by Nazi Germany, its Jewish community was subject to persecution and deportation to extermination camps. This is the list of Ukrainian Righteous Among the Nations. As of 1 January 2018, 2,619 Ukrainians have been honored with this title by Yad Vashem, the Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority of the state of Israel, for saving Jews during World War II. These people risked their lives or their liberty and position to help Jews during the Holocaust; some suffered death as a result. Below is a partial listing of these individuals:
 W
WThe massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia, were carried out in German-occupied Poland by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, or the UPA, with the support of parts of the local Ukrainian population against the Polish minority in Volhynia, Eastern Galicia, parts of Polesia and Lublin region from 1943 to 1945. The peak of the massacres took place in July and August 1943. Most of the victims were women and children. The UPA's actions resulted in between 50,000 and 100,000 deaths.
 W
WThe NKVD prisoner massacres were a series of mass executions of political prisoners carried out by the NKVD, the People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs of the Soviet Union, across Eastern Europe, primarily Poland, Ukraine, the Baltic states, and Bessarabia. After the start of the German invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941, the NKVD troops were supposed to evacuate political prisoners into the interior of the Soviet Union, but the hasty retreat of the Red Army, the lack of transportation and other supplies and the general disregard for legal procedures often meant that the prisoners were executed.
 W
WThe Polish population transfers in 1944–46 from the eastern half of prewar Poland, refer to the forced migrations of Poles toward the end – and in the aftermath – of World War II. These were the result of Soviet policy that was ratified by the Allies. Similarly the Soviet Union had enforced policy between 1939 and 1941, that targeted and expelled ethnic Poles residing in the Soviet zone of occupation following the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland. The second wave of expulsions resulted from the retaking of Poland by the Red Army during the Soviet counter-offensive. It took over territory for its republic of Ukraine, a shift that was ratified at the end of World War II by the Soviet Union's then Allies of the West.
 W
WThe Przebraże Defence – defensive fights in the village of Przebraże belonging to the Trościaniec cluster, in Lutsk poviat, voivodeship in Volhynia between July 1943 and January 1944. In Przebraże, Polish civilians from Volhynia organized defense against the UPA. The village was never conquered by UPAs.
 W
WReichskommissariat Don-Wolga, literally "Reich Commissariat Don-Volga", was a theoretical civilian occupation regime of Nazi Germany discussed during the early stages of German planning for its occupation of territories in the Soviet Union, one of several other Reichskommissariats. It is also referred to in German memoranda as simply the Dongebiet.
 W
WThe Ukrainian national government of 1941 was a self-proclaimed Ukrainian government established on the Ukrainian territories occupied by Nazi Germany. The government was established by the 30 June 1941 Act of restoration of the Ukrainian state. It was led by the Stepan Bandera's faction of OUN.