 W
WAcerra is a town and comune of Campania, southern Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Naples, about 15 kilometres northeast of the capital in Naples. It is part of the Agro Acerrano plain.
 W
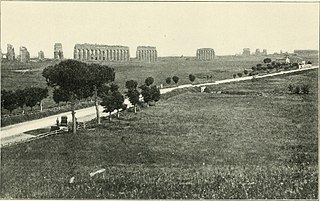
WAeclanum was an ancient town of Samnium, southern Italy, about 25 km east-southeast of Beneventum, on the Via Appia. It lies in Passo di Mirabella, near the modern Mirabella Eclano.
 W
WThe Atellan Farce, also known as the Oscan Games, were masked improvised farces. The games were very popular in Ancient Rome, and usually put on after longer pantomime plays. The origin of the Atellan Farce is uncertain but the farces are similar to other forms of ancient theatre, such as the South Italian Phlyakes, the plays of Plautus and Terrence, and Roman mime. Most historians believe the name is derived from Atella, an Oscan town in Campania. The farces were written in Oscan and imported to Rome in 391 BC. In later Roman versions, only the ridiculous characters read their lines in Oscan, while the others read in Latin.
 W
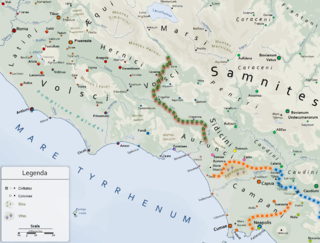
WThe Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC.
 W
WThe Monti Aurunci is a mountain range of southern Lazio, in central Italy. It is part of the Antiappennini, a group running from the Apennines chain to the Tyrrhenian Sea, where it forms the promontory of Gaeta. It is bounded to the north-west by the Ausoni Mountains, to the north by the Liri river, to the east by the Ausente, to the south-east by the Garigliano and to the south by the Tyrrhenian sea. The line between the Aurunci and the Ausoni has not been clearly established but the Aurunci are considered by convention to be east of a line through Fondi, Lenola, Pico, S. Giovanni and Incarico. Altitudes vary from hills to the 1,533 m of Monte Petrella. Main peaks include the Redentore (1,252 m) and Monte Sant'Angelo (1,402 m). They include a regional park, the Parco Naturale dei Monti Aurunci, created in 1997.
 W
W"Ausones", the original Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the particular tribe which Livy called the Aurunci, but later it was applied to all Italians, and Ausonia became a poetic term, in Greek and Latin, for Italy itself.
 W
WThe Monti Ausoni is a mountain range in southern Lazio, in central Italy. It is part of the Antiappennini, a group running from the Apennines chain to the Tyrrhenian Sea. They are bounded to the north by the Monti Lepini and to the south by the Monti Aurunci. They take the name from the ancient tribe of the Ausoni. The Monti Ausoni consist mainly of friable limestone. Altitudes vary from hills to the 1,152 m of Cima del Nibbio and the 1,141 m of Monte Calvo. Near Pastena are the Grotte di Pastena (caves).
 W
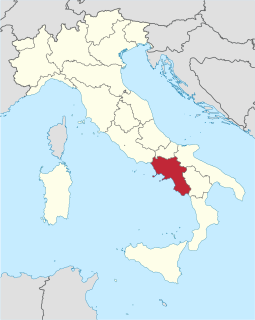
WCampania is an administrative region of Italy. Located on the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, with the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west, it includes the small Phlegraean Islands and Capri for administration as part of the region. As of 2018, the region has a population of around 5,820,000 people, making it the third-most-populous region in the country; its total area of 13,590 km2 (5,247 sq mi) makes it the most densely populated region in Italy. Campania is the most productive region in southern Italy by GDP, with Naples' urban area being the 7th-most populous in the European Union. The region is home to 10 of the 55 UNESCO sites in Italy, like Pompeii and Herculaneum, the Royal Palace of Caserta, the Amalfi Coast and the Historic Centre of Naples. Moreover, Mount Vesuvius is part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
 W
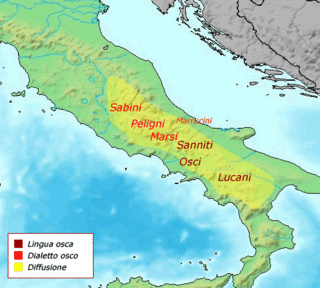
WThe Campanians were an ancient Italic tribe, part of the Osci nation, speaking an Oscan language.
 W
WGiugliano in Campania [dʒuʎˈʎaːno iŋ kamˈpaːnja], also known simply as Giugliano, is a city and comune in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, Italy. As of 2017, it had some 124,000 inhabitants, making it the most populated Italian city that is not a provincial capital.
 W
WLatium adiectum or Latium Novum is an ancient Roman geographical term used at least as early as the 1st century AD, when mention of it occurs in Pliny in conjunction with Latium antiquum, the original territory of the Latini tribe. Says Pliny of the latter:"Its inhabitants have often changed: at various times it has been occupied by various peoples — the Aborigines, the Pelasgi, the Arcades, the Siculi, the Aurunci, the Rutuli ..."
 W
WLicola is an area in the province of Naples which takes its name from Lago dei Follicoli, a lake which formerly occupied most of the area. The current population of Licola ranges between 4,000 and 5,000. Licola is a strip of land facing the sea, and is roughly three kilometers by ten kilometers in size. It begins at the foot of Mount Cuma and ends in Marina di Varcaturo.
 W
WThe Lucanians were an Italic tribe living in Lucania, in what is now southern Italy, who spoke an Oscan language, a member of the Italic languages. Today, the inhabitants of the Basilicata region are still called Lucani, and so their dialect.
 W
WNola is a town and a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, southern Italy. It lies on the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines. It is traditionally credited as the diocese that introduced bells to Christian worship.
 W
WOscan is an extinct Indo-European language of southern Italy. The language is also the namesake of the language group to which it belonged. As a member of the Italic languages, Oscan is therefore a sister language to Latin and Umbrian.
 W
WPompeii was an ancient city located in what is now the comune of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area, was buried under 4 to 6 m of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.