 W
WThis is a timeline of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368).
 W
WThe Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division and a ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongol Borjigin clan, lasting from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese historiography, this dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty.
 W
WThe Ming dynasty continued to improve on gunpowder weapons from the Yuan and Song dynasties. During the early Ming period larger and more cannons were used in warfare. In the early 16th century Turkish and Portuguese breech-loading swivel guns and matchlock firearms were incorporated into the Ming arsenal. In the 17th century Dutch culverin were incorporated as well and became known as hongyipao. At the very end of the Ming dynasty, around 1642, Chinese combined European cannon designs with indigenous casting methods to create composite metal cannons that exemplified the best attributes of both iron and bronze cannons. While firearms never completely displaced the bow and arrow, by the end of the 16th century more firearms than bows were being ordered for production by the government, and no crossbows were mentioned at all.
 W
WThe military of the Ming dynasty was the military apparatus of China from 1368 to 1644. It was founded in 1368 during the Red Turban Rebellion by the Ming founder Zhu Yuanzhang. The military was initially organised along largely hereditary lines and soldiers were meant to serve in self-sufficient agricultural communities. They were grouped into guards (wei) and battalions (suo), otherwise known as the wei-suo system. This hereditary guard battalion system went into decline around 1450 and was discarded in favor of mercenaries a century later.
 W
WThe Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by Han Chinese. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng, numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662.
 W
WThis is a timeline of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) from the rise of the Hongwu Emperor to the rise and establishment of the Qing dynasty.
 W
WYunnan under Ming rule saw the continuation of the tusi system instituted during the Yuan dynasty, increasing centralization, and Han migration into Yunnan.
 W
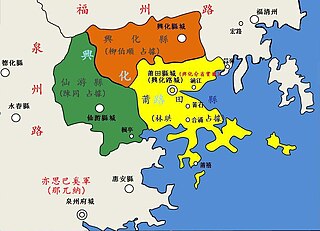
WThe Ispah rebellion was a series of civil wars in the middle of 14th century in Fujian during the Yuan dynasty. The term Ispah might derive from the Persian word "سپاه" (sepâh), meaning "army" or "Sepoy". Thus, the rebellion is also known as the Persian Sepoy rebellion in Chinese documents.
 W
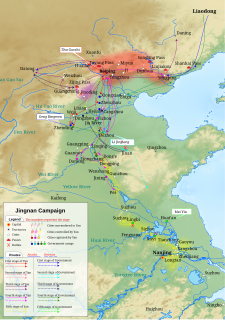
WThe Jingnan campaign, or Jingnan rebellion, was a three-year civil war from 1399–1402 in the early years of the Ming dynasty of China. It occurred between two descendants of the Ming dynasty's founder Zhu Yuanzhang: his grandson Zhu Yunwen by his first son, and Zhu Yuanzhang's fifth son Zhu Di, the Prince of Yan. Though Zhu Yunwen had been the chosen crown prince of Zhu Yuanzhang and been made emperor upon the death of his grandfather in 1398, friction began immediately after Yuanzhang's death. Zhu Yunwen began arresting Zhu Yuanzhang's other sons immediately, seeking to decrease their threat. But within a year open military conflict began, and the war continued until the forces of the Prince of Yan captured the imperial capital Nanjing. The fall of Nanjing was followed by the demise of Zhu Yunwen, aka the Jianwen Emperor, and Zhu Di was thus crowned the Ming Dynasty's third emperor, the Yongle Emperor.
 W
WThe Miao rebellions were a series of rebellions of the indigenous tribes of southern China against the Ming Dynasty. The Ming defeated the rebels with overwhelming force. Later, under the Qing Dynasty, another series of Miao rebellions broke out.
 W
WThe military of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) were the armed forces of the Yuan dynasty, a fragment of the Mongol Empire created by Kublai Khan in China. The forces of the Yuan were based on the troops that were loyal to Kublai after the Division of the Mongol Empire in 1260. At first this Tamma, a frontier army drawn from all Mongol tribes for conquest of China, had no central organisation but was rather a loose collection of local warlords and Mongol princely armies. However the army was gradually reformed by Kublai Khan into a more systematic force.
 W
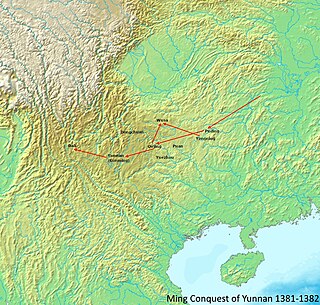
WThe Ming conquest of Yunnan was the final phase in the Ming dynasty expulsion of Mongol-led Yuan dynasty rule from China proper in the 1380s.
 W
WOdoric of Pordenone, OFM (1286–1331), also known as Odorico Mattiussi/Mattiuzzi, Odoricus of Friuli or Orderic of Pordenone, was an Italian late-medieval Franciscan friar and missionary explorer. His account of his visit to China was an important source for the account of John Mandeville. Many of the incredible reports in Mandeville have proven to be garbled versions of Odoric's eyewitness descriptions.
 W
WThe Red Turban Rebellions were uprisings against the Yuan dynasty between 1351 and 1368, eventually leading to the overthrow of Mongol rule in China.
 W
WThe Shenjiying was one of three elite military divisions stationed around Beijing during the Ming dynasty. Its name has been variously rendered as Firearms Division, Artillery Camp, Shen-chi Camp,Firearm Brigade, and Divine Engine Division.
 W
WThe Tomb of Chang Yuchun is the tomb of Chang Yuchun (1330–1369), a military general in late Yuan and early Ming dynasties. The tomb dates from 1369, and is located on Purple Mountain in Nanjing. There are stone horses, stone tigers, stone sheep and stone warriors in front of the tomb. It has been categorized as a "Major National Historical and Cultural Site in Jiangsu" by the State Council of China.
 W
WThe 1344 Yellow River flood was a major natural disaster during the Yuan dynasty of Imperial China. The impact was devastating both for the peasants of the area as well as the leaders of the empire. The Yuan dynasty was waning, and the emperor forced enormous teams to build new embankments for the river. The terrible conditions helped fuel rebellions that led to the founding of the Ming dynasty.