 W
WThe Presidency of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, also known as the Arroyo Administration, spanned nine years from January 20, 2001 to June 30, 2010. She served the remainder of her predecessor Joseph Estrada's term after he was deposed, and she was elected to a full second term in 2004 which ended pursuant to the provisions of the 1987 Constitution in 2010.
 W
WIn the Philippines, the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) was the only autonomous region ; as such it is the sole region with a regional government as prescribed by the Constitution of the Philippines. In 2001, Republic Act No. 9054 was passed for the expansion of the ARMM to include the areas which initially rejected inclusion and the provinces which were carved from them. However, only Marawi City and Basilan, with the exception of Isabela City, opted to be integrated in the region.
 W
WThe Batasang Pambansa bombing occurred on the night of November 13, 2007, at the Batasang Pambansa Complex in Quezon City, Philippines. The blast killed Congressman Wahab Akbar and Marcial Taldo, a staff member of Congresswoman Luzviminda Ilagan, and wounded Ilagan, Congressman Pryde Henry Teves, and two others.
 W
WThe Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002, or R.A. No. 9165, is a consolidation of Senate Bill No. 1858 and House Bill No. 4433. It was enacted and passed by the Senate of the Philippines and House of Representatives of the Philippines on May 30, 2002 and May 29, 2002, respectively. It was signed into law by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo on June 7, 2002.
 W
WThe Credit Information Corporation (CIC) is a government-owned and controlled corporation providing credit information system in the Philippines. It was created in 2008 by the Credit Information System Act (CISA) to construct a centralized, comprehensive credit information system for the collection and dissemination of accurate and fair information relevant to, or arising from, credit and credit-related activities of all entities participating in the financial system. This credit information is to be collected from various sources such as banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, financing companies, credit cooperatives, as well as utility companies and other businesses that extend loans. The CIC compiles this credit information to help creditors evaluate the ability of borrowers to pay.
 W
WThe Second EDSA Revolution, also known as EDSA II, was a political protest from January 17–20, 2001 that peacefully overthrew the government of Joseph Estrada, the thirteenth President of the Philippines. Estrada resigned and was succeeded by his Vice President, Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, who was sworn into office by then-Chief Justice Hilario Davide Jr. at around noon on January 20, 2001, several hours before Estrada fled Malacañang Palace. EDSA is an acronym derived from Epifanio de los Santos Avenue, the major thoroughfare connecting five cities in Metro Manila, namely Pasay, Makati, Mandaluyong, Quezon City, and Caloocan, with the revolution's epicenter at the EDSA Shrine church at the northern tip of Ortigas Center, a business district.
 W
WThe May 1 riots, or EDSA III, were protests sparked by the arrest of newly deposed president Joseph Estrada of the Philippines from April 25–May 1, 2001. The protest was held for seven days in a major highway in Metropolitan Manila, the Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA), which eventually culminated in an attempt to storm Malacañang. Taking place four months after the EDSA Revolution of 2001, the protests were considered as a more populist and representative uprising in comparison to the previous demonstrations in the same location in January 2001. The protests and the attack on the presidential palace, however, failed in their objectives. Participants continue to claim that it was a genuine People Power event, a claim disputed by the participants and supporters of EDSA II. President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo has acknowledged the divisive nature of the two terminologies by saying in one statement that she hoped to be the president of "EDSA II and EDSA III".
 W
WThe Inauguration of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo as the fourteenth President of the Philippines occurred on January 20, 2001 under extraordinary circumstances. The inauguration marked the commencement of the first term of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo as President, during the EDSA Revolution of 2001 following the removal of President Joseph Estrada.
 W
WThe Human Security Act of 2007, officially designated as Republic Act No. 9372, was a Philippine law that took effect on July 20, 2007. This law is one of the most primary anti-terrorism law that brings the Philippines in line with its Southeast Asian neighbors battling Islamist militants. It is aimed at tackling militants in the southern Philippines.
 W
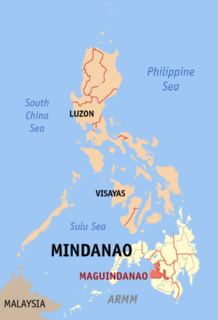
WThe Maguindanao massacre, also known as the Ampatuan massacre, named after the town where mass graves of victims were found, occurred on the morning of November 23, 2009, in the town of Ampatuan in Maguindanao province, on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. The 58 victims were on their way to file a certificate of candidacy for Esmael Mangudadatu, vice mayor of Buluan, when they were kidnapped and later killed. Mangudadatu was challenging Datu Unsay mayor Andal Ampatuan Jr., son of the incumbent Maguindanao governor Andal Ampatuan Sr. and member of one of Mindanao's leading Muslim political clans, in the forthcoming Maguindanao gubernatorial election, part of the national elections in 2010. The people killed included Mangudadatu's wife, his two sisters, journalists, lawyers, aides, and motorists who were witnesses or were mistakenly identified as part of the convoy.
 W
WThe Manila Peninsula siege occurred on November 29, 2007, at The Peninsula Manila hotel in Makati, Philippines. Senator Antonio Trillanes IV, Brigadier General Danilo Lim, and 25 other Magdalo (mutineers) officers walked out of their trial and marched through the streets of Makati. The mutineers called for the ousting of President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo, and seized the Rizal function room on the second floor of the Manila Peninsula Hotel along Ayala Avenue. Former Vice-President Teofisto Guingona, Jr. as well as some of the soldiers from the Armed Forces of the Philippines joined the march to the hotel.
 W
WThe 2009 National Artist of the Philippines controversy refers to the controversial proclamation as National Artists of the Philippines of four individuals via the Presidential prerogative of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, when the four had not been nominated by the selection committee, composed of representatives from National Commission for Culture and the Arts (NCCA) and the Cultural Center of the Philippines (CCP).
 W
WThe National Cultural Heritage Act is a law, or Republic Act, of the Republic of the Philippines. It created the Philippine Registry of Cultural Property and took other steps to preserve historic buildings that are over 50 years old. It was signed into law on March 25, 2009.
 W
WThe Oakwood mutiny occurred in the Philippines on July 27, 2003. A group of 321 armed soldiers who called themselves "Bagong Katipuneros" led by Army Capt. Gerardo Gambala and Lt. Sg. Antonio Trillanes IV of the Philippine Navy took over the Oakwood Premier Ayala Center serviced apartment tower in Makati to show the Filipino people the alleged corruption of the Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo administration. They also stated that they saw signs suggesting that the President was going to declare martial law.
 W
WPantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program, also known as 4Ps and formerly bangon Pamilyang Pilipino, is a conditional cash transfer program of the Philippine government under the Department of Social Welfare and Development. It aims to eradicate extreme poverty in the Philippines by investing in health and education particularly in ages 0–14. It is patterned on programs in other developing countries like Brazil and Mexico (Oportunidades). The 4Ps program now operates in 17 regions, 79 provinces and 1,484 municipalities and 143 key cities covering 4,090,667 household beneficiaries as of 25 June 2014.
 W
WThis is a list of foreign presidential trips made by Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, the 14th President of the Philippines from 2001 to 2010. During her ten-year presidency, Arroyo has visited a total of 44 countries. With a total of 127 foreign trips, Arroyo has made the most foreign trips by a Philippine president in office.
 W
WThe Inauguration of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo as the fourteenth President of the Philippines took place on Wednesday, June 30, 2004 at the Cebu Provincial Capitol in Cebu City. The inauguration marked the commencement of the second term of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo as President and the only six-year term of Noli de Castro as Vice President. The oath of office was administered by Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines Hilario Davide, Jr. Before that, Arroyo delivered her inaugural speech at the Quirino Grandstand in Manila.
 W
WThe trial of Philippine president Joseph Estrada took place between 2001 and 2007 at the Sandiganbayan. Estrada, popularly called Erap, was ousted from office in 2001 during a popular uprising in Metro Manila after an aborted impeachment trial in which he was charged with plunder and perjury. Soon after his ouster, the same charges were filed against him at the Sandiganbayan.