 W
WThe Battle of Authion was a military engagement that took place towards the end of World War II, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945. Units of the French Army were sent to the French Alps to clear an important route from central France to Italy. A critical choke point was the 2,080 metre high Authion massif, held by determined but weakened German and Italian forces.
 W
WBetween the time of the German victory in the Battle of France and the liberation of the country, the Allied Forces bombed many locations in France. In all 1,570 French cities and towns were bombed by the Allies between June 1940 and May 1945. The total number of civilians killed was 68,778 men, women and children.
 W
WThe Bombing of Normandy during the Normandy invasion was meant to destroy the German communication lines in the Norman cities and towns. However, very few Germans occupied these municipalities. German troops were mostly located outside these areas. On 9 July 1944, Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery demanded a massive air assault against Caen in hopes of clearing the way for an attack the following morning. Four hundred and fifty heavy aircraft participated, dropping 2,500 tons of bombs. The pilots however negated most of the effect by releasing their loads well back from the forward line to avoid hitting their own troops. As a result, the city incurred heavy damage but German defenses went largely unscathed.
 W
WBefore and during World War II, the various Breton nationalist movements were generally right-wing, and sometimes fascist. The extent to which this led to collaboration with the Nazi occupiers of France during the war, together with their motivations, is a matter of historical controversy.
 W
WThe Compiègne Wagon was the train carriage in which both the Armistice of 11 November 1918 and Armistice of 22 June 1940 were signed.
 W
WDeath In The City Of Light: The Serial Killer Of Nazi-Occupied Paris is a nonfiction true crime book by David King first published in 2011. The book covers the serial killing spree in Paris that took place while that city was occupied by the Nazis during World War II, the trial of the chief suspect - Dr. Marcel Petiot, and the circus that ensued.
 W
WWorld War II for Écouché culminated with several days of street fighting by Free French forces under General Philippe Leclerc. This engagement was part of the encirclement of the remaining German army in the final engagement of the Battle of Normandy. This final carnage of the German army was later called the Falaise Pocket, the Argentan-Falaise Pocket or Couloir de la Mort as the local French named it.
 W
WA Franco-British Union is a concept for a union between the two independent sovereign states of the United Kingdom and France. Such a union was proposed during certain crises of the 20th century; it has some historical precedents.
 W
WThe French Committee of National Liberation was a provisional government of Free France formed by the French generals Henri Giraud and Charles de Gaulle to provide united leadership, organize and coordinate the campaign to liberate France from Nazi Germany during World War II. The committee was formed on 3 June 1943 and after a period of joint leadership, on 9 November it came under the chairmanship of de Gaulle. The committee directly challenged the legitimacy of the Vichy regime and unified all the French forces that fought against the Nazis and collaborators. The committee functioned as a provisional government for Algeria and the liberated parts of the colonial empire. Later it evolved into the Provisional Government of the French Republic, under the premiership of Charles de Gaulle.
 W
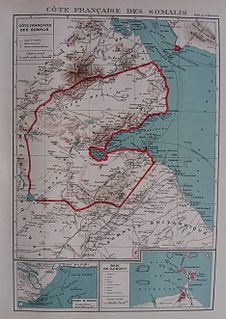
WFrench Somaliland, with its capital at Djibouti, was the scene of only minor skirmishing during World War II, principally between June and July 1940. After the fall of France the colony was briefly in limbo until a governor loyal to the Vichy government was installed on 25 July. It was the last French possession in Africa to remain loyal to Vichy, surrendering to Free French forces only on 26 December 1942. Pierre Nouailhetas governed the territory through most of the Vichy period. After aerial bombardment by the British, he instituted a reign of terror against Europeans and locals. Nouailhetas was eventually recalled and forced to retire. From September 1940, the colony was under an Allied blockade, and many of its inhabitants fled to neighbouring British Somaliland. After the territory's liberation, there were many governors and recovery from the deprivation of 1940–42 was only beginning when the war ended in 1945.
 W
WParis started mobilizing for war in September 1939, when Nazi Germany attacked Poland, but the war seemed far away until May 10, 1940, when the Germans attacked France and quickly defeated the French army. The French government departed Paris on June 10, and the Germans occupied the city on June 14. During the Occupation, the French Government moved to Vichy, and Paris was governed by the German military and by French officials approved by the Germans. For Parisians, the Occupation was a series of frustrations, shortages and humiliations. A curfew was in effect from nine in the evening until five in the morning; at night, the city went dark. Rationing of food, tobacco, coal and clothing was imposed from September 1940. Every year the supplies grew more scarce and the prices higher. A million Parisians left the city for the provinces, where there was more food and fewer Germans. The French press and radio contained only German propaganda.
 W
WLe Juif et la France was an anti-Semitic propaganda exhibition that took place in Paris from 5 September 1941 to 15 January 1942 during the German occupation of France in the Second World War. A film version of the exhibition came out in French cinemas in October 1941.
 W
WThe Provisional Government of the French Republic (PGFR; French: Gouvernement provisoire de la République française was an interim government of Free France between 1944 and 1946 following the liberation of continental France after Operations Overlord and Dragoon, and lasted until the establishment of the French Fourth Republic. Its establishment marked the official restoration and re-establishment of a provisional French Republic, assuring continuity with the defunct French Third Republic.
 W
WStrange Defeat is a book written in the summer of 1940 by French historian Marc Bloch. The book was published in 1946; in the meanwhile, Bloch had been tortured and executed by the Gestapo in June 1944 for his participation in the French resistance. An English translation was published by W. W. Norton in 1968.
 W
WThe tragedy of the Guerry's wells designates the massacre of 36 Jews during the summer 1944 in Savigny-en-Septaine in France. It is located at 47°02′07″N 02°31′26″E.
 W
WThe Union générale des israélites de France was an antisemitic body created by Xavier Vallat under the Vichy regime after the Fall of France in World War II. UGIF was created by decree on 29 November 1941 following a German request, for the express purpose of enabling the discovery and classification of Jews in France and isolating them both morally and materially from the rest of the French population. The mission of the UGIF was to represent Jews before the public authorities, particularly in matters of assistance, welfare and social reintegration. All Jews who were living in France were required to join the UGIF, because the other Jewish associations had been dissolved and their assets had been donated to the UGIF. The administrators of this body mostly belonged to the French-Jewish bourgeoisie, administrators who were appointed by the Commissariat-General for Jewish Affairs (CGQJ), the structure which had been initiated by the Vichy government at the instigation of the Nazis to reinforce antisemitic persecution. In order to finance its activities, the UGIF drew on a solidarity fund whose income was generated from the confiscation of Jewish property, from contributions from its members and funds from the CGQJ.
 W
WVichy France is the common name of the French State headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Evacuated from Paris to the resort town of Vichy in the unoccupied "Free Zone" in the southern part of Metropolitan France, it remained responsible for the civil administration of France as well as its colonies.
 W
WVichy France is the common name of the French State headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Evacuated from Paris to the resort town of Vichy in the unoccupied "Free Zone" in the southern part of Metropolitan France, it remained responsible for the civil administration of France as well as its colonies.
 W
WIn World War II, French West Africa was not a major scene of major fighting. Only one large-scale action took place there: the Battle of Dakar. The region remained under the control of Vichy France after the fall of France and until the Allied invasion of North Africa. French Gabon, the only colony of French Equatorial Africa not to join Free France after the armistice, fell to invading Free French Forces from the neighbouring colonies after the Battle of Gabon, further isolating West Africa.