 W
WThe Austro–Serbian Convention of 1881 was a secret bilateral treaty signed in Belgrade on 28 June 1881 by Gabriel Freiherr Herbert-Rathkeal on behalf of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and by Čedomilj Mijatović on behalf of the Principality of Serbia. The convention effectively turned Serbia into a vassal state of Austria-Hungary and meant her accession by proxy to the subsequent Triple Alliance (1882).
 W
WHadži-Prodan's rebellion was a Serbian rebellion against the Ottoman Empire, which took place from 27 September to 30 December 1814. It occurred between the First (1804–13) and Second (1815–17) uprisings of the Serbian Revolution.
 W
WThe Kumanovo uprising was an uprising organized by an assembly of chiefs of the districts of Kumanovo, Kriva Palanka, and Kratovo in the Vilayet of Kosovo in 1878. The movement sought to liberate the region from the hands of the Ottoman Empire and unify it with the Principality of Serbia, which was at war with the Ottomans at the time. Following the Serbian Army's liberation of Niš on 31 December 1877, the rebellion began on 20 January 1878 with guerrilla operations during the army's liberation of Vranje. The rebels received secret aid from the Serbian government. The uprising lasted four months until its suppression by the Ottomans on 20 May, during which the Ottomans retaliated with atrocities on the local population.
 W
WThe Macedonian Society or Secret Macedonian Society was secret organization established in 1885 by Macedonian Slavs in Sofia, Bulgaria, to promote a kind of Macedonian identity, distinguished especially from the ethnic identity of the Bulgarians, the establishment of the Archbishopric of Ohrid separate from the Bulgarian Exarchate and the promotion of the Macedonian language. Its leaders were Naum Evrov, Kosta Grupčev, Vasilij Karajovev and Temko Popov.
 W
WMagyarization, after "Magyar"—the autonym of Hungarians—was an assimilation or acculturation process by which non-Hungarian nationals came to adopt the Hungarian culture and language, either voluntarily or due to social pressure, often in the form of a coercive policy.
 W
WThe Marche slave in B-flat minor, Op. 31, is an orchestral tone poem by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky published in 1876. It was written to celebrate Russia's intervention in the Serbo-Turkish War.
 W
WThe House of Obrenović was a Serbian dynasty that ruled Serbia from 1815 to 1842, and again from 1858 to 1903. They came to power through the leadership of their progenitor Miloš Obrenović I in the Serbian Uprising of 1815–1817 against the Ottoman Empire, which led to the formation of the Principality of Serbia in 1817. The Obrenović dynasty were traditionally allied with Austria-Hungary and opposed the Russian-supported Karađorđević dynasty.
 W
WPrečani was a Serbian blanket term used at the end of the 19th- and early 20th century for ethnic Serb communities located preko ("across") the Danube, Sava and Drina rivers, beyond the northern and western borders of 19th-century Serbia, that is, in Austria-Hungary-held Vojvodina, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia. It was thus used to distinguish Serbs of Serbia ("Serbians") from those in the historical Habsburg Monarchy; it was not applied to the Serbs of Montenegro or those in the Sanjak of Novi Pazar and elsewhere in the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WThe Serbian Revolution was a national uprising and constitutional change in Serbia that took place between 1804 and 1835, during which this territory evolved from an Ottoman province into a rebel territory, a constitutional monarchy, and modern Serbia. The first part of the period, from 1804 to 1817, was marked by a violent struggle for independence from the Ottoman Empire with two armed uprisings taking place, ending with a ceasefire. The later period (1817–1835) witnessed a peaceful consolidation of political power of the increasingly autonomous Serbia, culminating in the recognition of the right to hereditary rule by Serbian princes in 1830 and 1833 and the territorial expansion of the young monarchy. The adoption of the first written Constitution in 1835 abolished feudalism and serfdom, and made the country suzerain. The term Serbian Revolution was coined by a German academic historiographer, Leopold von Ranke, in his book Die Serbische Revolution, published in 1829. These events marked the foundation of modern Serbia.
 W
WThe Second Serbian Uprising was the second phase of the Serbian Revolution against the Ottoman Empire, which erupted shortly after the re-annexation of the country to the Ottoman Empire in 1813. The occupation was enforced following the defeat of the First Serbian Uprising (1804–1813), during which Serbia existed as a de facto independent state for over a decade. The second revolution ultimately resulted in Serbian semi-independence from the Ottoman Empire. The Principality of Serbia was established, governed by its own parliament, constitution and royal dynasty. De jure independence, however, was attained in 1878, following the decisions of the Congress of Berlin.
 W
WThe Principality of Serbia was a semi-independent state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was negotiated first through an unwritten agreement between Miloš Obrenović, leader of the Second Serbian Uprising, and Ottoman official Marashli Pasha. It was followed by the series of legal documents published by the Porte in 1828, 1829 and finally, 1830 — the Hatt-i Sharif. Its de facto independence ensued in 1867, following the expulsion of all Ottoman troops from the country; its independence was recognized internationally in 1878 by the Treaty of Berlin. In 1882 the country was elevated to the status of kingdom.
 W
WSerbia is the nation state of the Serbs, who are Serbia's dominant ethnic group. Serbs are also dominant in Republika Srpska, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. In the 19th century, the Serbian national identity was manifested, with awareness of history and tradition, medieval heritage, cultural unity, despite Serbs living under different empires. Three elements, together with the legacy of the Nemanjić dynasty, were crucial in forging identity and preservation during foreign domination: the Serbian Orthodox Church, Kosovo Myth, and the Serbian language. The identification with medieval heritage through venerating Serbian saints, together with Serbian epic poetry, had helped develop a national consciousness separate from other Orthodox peoples in the Balkans. The heroic epic cycles inspired the Serbs to revive their heroic past and freedom. In the stories, the hajduks were heroes: they had played the role of the Serbian elite during Ottoman rule, they had defended the Serbs against Ottoman oppression, and prepared for the national liberation and contributed to it in the Serbian Revolution. The symbolical Kosovo Myth became the mythomoteur, signifying martyrdom and defence of Serb honour and Christendom against Turks (Muslims). When the Principality of Serbia gained independence from the Ottoman Empire, Orthodoxy became crucial in defining the national identity, instead of language which was shared by other South Slavs.
 W
WSerbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, under the influence of Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Serbian statesman Ilija Garašanin. Serbian nationalism was an important factor during the Balkan Wars which contributed to the decline of the Ottoman Empire, during and after World War I when it contributed to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and again during the breakup of Yugoslavia and the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s.
 W
WThe Serbian Vojvodina was a short-lived self-proclaimed Serb autonomous province within the Austrian Empire during the Revolutions of 1848, which existed until 1849 when it was transformed into the new (official) Austrian province named Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar.
 W
WThe Modern Serbo-Byzantine architectural style, Neo-Byzantine architectural style or Serbian national architectural style is the style in Serbian architecture which lasted from the second half of the 19th century to the first half of the 20th century. This style originated in the tradition of medieval Serbian-Byzantine school and was part of international Neo-Byzantine style.
 W
WThe Society of Saint Sava or Saint Sava Society was a Serbian non-governmental association with the aim of maintaining and protecting the Serb people in the Ottoman Empire, in Old Serbia and Macedonia, and in Austro-Hungarian Bosnia and Herzegovina, founded in 1886 in Belgrade, the capital of the Kingdom of Serbia. It was active, with a brief pause during the First World War, until the Invasion of Yugoslavia (1941).
 W
WSrpski rječnik is a dictionary written by Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, first published in 1818. It is the first known dictionary of the vernacular Serbian language.
 W
WThe Battle of Šumatovac or Battle of Aleksinac happened in 1876, in central Serbia, near the town of Aleksinac. The outnumbered Serbian army, led by colonel Kosta Protić, won a tactical victory in this defensive battle against the Ottoman forces. In a major tactical blunder the Ottomans spent a whole day frontally attacking a well-entrenched pentagonal redoubt defended by two Serbian battalions armed with muzzle-loading rifles and 6 cannons supported by about 40 additional artillery pieces positioned on the overlooking hills. The Ottomans finally retreated towards the end of the day having lost 500 killed and 1,500 wounded and captured. The Serbian army did not press the advantage with a counterattack, however so it ended up as just a tactical success.
 W
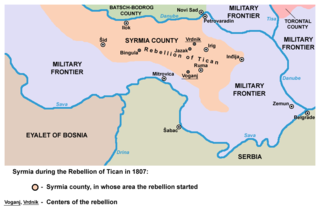
WThe Tican's rebellion was a rebellion of the Syrmian peasants against feudal relations in society. The rebellion started in April 1807 on the estate of Ruma of earl Karlo Pejačević and estate of Ilok of earl Odescalchi. The reason for the rebellion was large increase of feudal tributes and dissatisfaction because of land regulation.
 W
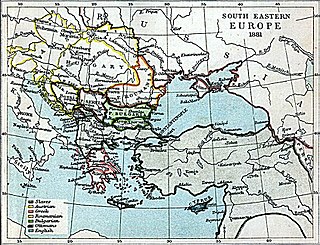
WThe Treaty of Berlin was signed on 13 July 1878. In the aftermath of the Russian victory against the Ottoman Empire in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, the major powers restructured the map of the Balkan region. They reversed some of the extreme gains claimed by Russia in the preliminary Treaty of San Stefano, but the Ottomans lost their major holdings in Europe. It was one of three major peace agreements in the period after the 1815 Congress of Vienna. It was the final act of the Congress of Berlin and included Great Britain and Ireland, Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Italy, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. Germany's Otto von Bismarck was the chairman and dominant personality.