 W
WThe Bedford Flag is the oldest known flag in the United States. It is associated with the Minutemen of Bedford, Massachusetts and the Battles of Lexington and Concord of 1775.
 W
WThe Bennington flag is a version of the American flag associated with the American Revolution Battle of Bennington, from which it derives its name. Its distinguishing feature is the inclusion of a large '76' in the canton, a reference to the year 1776 when the Declaration of Independence was signed.
 W
WThe Betsy Ross flag is an early design of the flag of the United States, named for early American upholsterer and flag maker Betsy Ross. The pattern of the Betsy Ross flag is 13 alternating red-and-white stripes with stars in a field of blue in the upper left corner canton. Its distinguishing feature is thirteen 5-pointed stars arranged in a circle representing the 13 colonies that fought for their independence during the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe Brandywine flag was a banner carried by Captain Robert Wilson's company of the 7th Pennsylvania Regiment. The company flag received the name after it was used in the Battle of Brandywine, September 11, 1777. The flag is red, with a red and white American flag image in the canton.
 W
WThe George Rogers Clark Flag is a red and green striped banner in the model of American Flags commonly associated with George Rogers Clark, although Colonel Clark did not campaign under these colors. The "Clark" flag was made in Vincennes, Indiana, and likely flew over Fort Sackville even before Clark arrived.
 W
WThe Cowpens flag, or 3rd Maryland flag, is an early version of the United States flag that meets the congressional requirements of the Flag Resolution of 1777. Like the Betsy Ross flag, the white stars are arranged in a circle on a blue field; but the circle consists of just 12 stars, with the 13th star in the center.
 W
WThe Culpeper Minutemen was a militia group formed in 1775 in the district around Culpeper, Virginia. Like minutemen in other British colonies, the men drilled in military tactics and trained to respond to emergencies "at a minute's notice".
 W
WThe Easton flag is a banner used to represent Easton, Pennsylvania.
 W
WThe flag of Taunton, Massachusetts, also known as the Taunton Flag and the Liberty and Union Flag, is the city flag of Taunton, Massachusetts, United States. The flag was first adopted in 1774 and has since been adopted as the flag of Taunton. It consists of a red ensign with the flag of Great Britain in canton defaced with the words "Liberty and Union" across the lower portion.
 W
WThe Gadsden flag is a historical American flag with a yellow field depicting a timber rattlesnake coiled and ready to strike. Beneath the rattlesnake resting on grass are the words: "Dont Tread on Me" [sic].
 W
WThe George Rex Flag was a protest flag used in the Province of New York at the start of the American Revolutionary War. The flag was adopted following the passage of the Quebec Act 1774 whereby French Roman Catholics were granted emancipation and Roman Catholicism adopted as the state church of Quebec. Though it is not known exactly what the design of the flag was, the commonly accepted version consisted of either an altered Red Ensign or Blue Ensign with the words "George III Rex and the Defender of the Liberties of America. No Popery".
 W
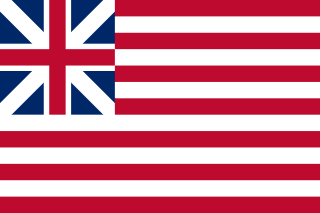
WThe "Grand Union Flag" is considered to be the first national flag of the United States of America.
 W
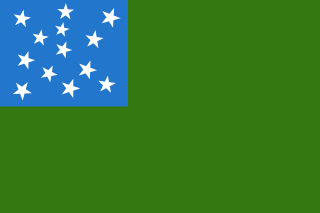
WThe Green Mountain Boys flag, also known as the Stark flag, is a reconstruction of a regimental flag commonly stated to have been used by the Green Mountain Boys. A remnant of a Green Mountain Boys flag, originally belonging to John Stark, is owned by the Bennington Museum. It still exists as one of the few regimental flags from the American Revolution. Although Stark was at the Battle of Bennington and likely flew this flag, the battle has become more commonly associated with the Bennington flag, which is believed to be a 19th-century banner.
 W
WThe Guilford Courthouse Flag is the name given to a North Carolina militia banner which was reported to have flown at the Battle of Guilford Courthouse. The flag is recognizable by the reverse colors normally seen on American flags: red and blue stripes in the field with eight-pointed blue stars on an elongated white canton.
 W
WFrancis Hopkinson was an author and composer. He designed Continental paper money, the first United States coin, and two early versions of the American flag, one for the United States and one for the United States Navy. He was also one of the signers of the Declaration of Independence in July 1776, as a delegate from New Jersey. He served in various roles in the early United States government including as a member of the Second Continental Congress and as a member of the Navy Board. He later became the first federal judge of the Eastern District Court of Pennsylvania on September 30, 1789.
 W
WThe Moultrie Flag, also known as the Liberty Flag, was a key flag flown in the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe First Navy Jack was the naval jack of the United States from 1975 to 1976 and again from 2002 to 2019. It was authorized by the U.S. Navy and was flown from the jackstaff of commissioned vessels of the U.S. Navy while moored pierside or at anchor. It is now only used as a naval jack by the oldest active warship in the U.S. Navy. The design is traditionally regarded as that of the first U.S. naval jack flown in the earliest years of the United States' existence, though this is disputed by the historical record.
 W
WNew England has no official flag, but there have been many historical and modern banners used to represent the New England Colonies or the six states of New England. There are some variations, but common designs include a plain colored field with a pine tree in the canton. The eastern white pine is the most common symbol of New England and often represents that tree's former importance in shipbuilding and New England's maritime culture.
 W
WThe Tree Flag was one of the flags used during the American Revolution. The flag, featuring a pine tree with the motto "An Appeal to God" or, more usually, "An Appeal to Heaven", was used originally by a squadron of six cruisers commissioned under George Washington's authority as commander in chief of the Continental Army in October 1775. It was also used by Massachusetts state navy vessels in addition to privateers sailing from Massachusetts.
 W
WElizabeth Griscom Ross, née Griscom, also known by her second and third married names, Ashburn and Claypoole, was an American upholsterer who was credited by her relatives in 1870 with making the first American flag, accordingly known as the Betsy Ross flag. Though most historians dismiss the story, Ross family tradition holds that General George Washington, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army and two members of a congressional committee—Robert Morris and George Ross—visited Mrs. Ross in 1776. Mrs. Ross convinced George Washington to change the shape of the stars in a sketch of a flag he showed her from six-pointed to five-pointed by demonstrating that it was easier and speedier to cut the latter. However, there is no archival evidence or other recorded verbal tradition to substantiate this story of the first American flag. It appears that the story first surfaced in the writings of her grandson in the 1870s, with no mention or documentation in earlier decades.
 W
WSerapis is a name given to an unconventional, early United States ensign flown from the captured British frigate Serapis.