 W
WThe 190th Fighter Squadron, Blues and Royals friendly fire incident was a friendly fire incident involving two United States Air Force (USAF) Air National Guard 190th Fighter Squadron A-10, and vehicles from the United Kingdom's D Squadron, The Blues and Royals of the Household Cavalry, and took place on 28 March 2003 during the invasion of Iraq by armed forces of the United States and United Kingdom. In the incident, the two USAF A-10s fired on and destroyed two Blues and Royals armored vehicles, killing one British soldier, and wounding five others.
 W
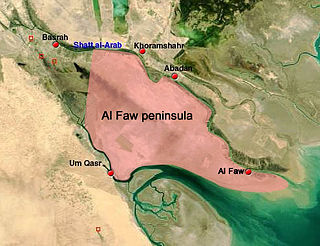
WThe Battle of Al Faw was one of the first battles of the Iraq War. One of the initial objectives of the Coalition campaign in Iraq was to capture the Gas and Oil Platforms ("GOPLATs") in the Al-Faw Peninsula intact before it could be sabotaged or destroyed by the Iraqi military. This would prevent an ecological disaster similar to the 1991 Gulf War and enable a quicker take over of Iraqi oil production.
 W
WOn 22 November 2003, shortly after takeoff from Baghdad, Iraq, an Airbus A300B4-200F cargo plane, registered OO-DLL and owned by European Air Transport, was struck on the left wing by a surface-to-air missile while on a scheduled flight to Muharraq, Bahrain. Severe wing damage resulted in a fire and complete loss of hydraulic flight control systems. Because outboard left wing fuel tank 1A was full at takeoff, there was no fuel-air vapour explosion. Liquid jet fuel dropped away as 1A disintegrated. Inboard fuel tank 1 was pierced and leaking.
 W
WThe Battle of Basra lasted from 21 March to 6 April 2003 and was one of the first battles of the 2003 invasion of Iraq. The British 7 Armoured Brigade fought their way into Iraq's second-largest city, Basra, on 6 April coming under constant attack by the Iraqi Army 51st Division and Fedayeen. While elements of the Parachute Regiment cleared the 'old quarter' of the city that was inaccessible to vehicles. Entering Basra had only been achieved after two weeks of conflict, which included the biggest tank battle of the war by British forces when the Royal Scots Dragoon Guards destroyed 14 Iraqi tanks on the 27 March.
 W
WThe Battle of Majar al-Kabir was the result of a growing distrust between the British military and the local people of the south-eastern region of Iraq over house searches and confiscation of personal weapons that locals felt were crucial for their self-protection. Despite a signed agreement between local people and British forces stating that the British would not enter the town, the 1st Battalion Parachute Regiment started patrolling in the town of Majar al-Kabir on 24 June 2003 the day after the agreement was signed by both sides. The British thought the agreement was to stop the weapons searches that involved going into the houses of local inhabitants.
 W
WThe Canal Hotel bombing was a suicide truck bombing in Baghdad, Iraq, in the afternoon of August 19, 2003. It killed 22 people, including the United Nations' Special Representative in Iraq Sérgio Vieira de Mello, and wounded over 100, including human rights lawyer and political activist Dr. Amin Mekki Medani. The blast targeted the United Nations Assistance Mission in Iraq created just five days earlier. The 19 August bombing resulted in the withdrawal within weeks of most of the 600 UN staff members from Iraq. These events were to have a profound and lasting impact on the UN's security practices globally.
 W
WThe Fallujah killings of April 2003 began when United States Army soldiers from the American 1st Battalion, 325th Infantry Regiment of the 82nd Airborne Division fired into a crowd of Iraqi civilians who were protesting their presence at a school within the city of Fallujah. The soldiers claimed they were receiving fire from the crowd, whereas the civilians said they were shot at first. Human Rights Watch, which inspected the area after the incident, found no physical evidence of shots fired at the building where U.S. forces were based.
 W
WThe 2003–2006 phase of the Iraqi insurgency began following the completion of the invasion of Iraq and the toppling of Saddam Hussein's rule in May 2003. The armed insurgent opposition to the U.S.-led multinational force in Iraq and the post-2003 Iraqi government lasted until early 2006, when it deteriorated into the Sectarian violence, the most violent phase of the Iraq War.
 W
WThe Islamist insurgency in Iraqi Kurdistan was a military conflict in Iraqi Kurdistan between the Islamist militant group Ansar al-Islam and the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG). The conflict began in 2001, but subsequently merged with the larger 2003 invasion of Iraq. After the invasion, Ansar al-Islam continued a low-level terrorist insurgency against the KRG.
 W
WOn 7 August 2003, a bomb exploded outside the Jordanian embassy in Baghdad, Iraq, killing 17 people and injuring dozens more. The bomb, concealed in a minibus, exploded outside the walls of the embassy compound at around 11:00am local time. The force of the explosion sent a car onto a nearby rooftop and killed several people nearby including women and children. Six police officers guarding the embassy were among the dead. Immediately after the blast, the embassy compound was swarmed by a mob of Iraqis who ransacked the building, chanting anti-Jordanian slogans and burning portraits of King Abdullah II. According to Lieutenant-General Ricardo Sanchez, the commander of US forces in Iraq, the attack was the worst in Iraq since the capture of Baghdad that previous March.
 W
WThe Battle of Karbala took place during the 2003 invasion of Iraq as U.S. troops fought to take control of the city from Iraqi forces. The city had been bypassed during the advance on Baghdad, leaving American units to clear it in two days of street fighting against Iraqi irregular forces.
 W
WOperation Northern Watch (ONW), the successor to Operation Provide Comfort, was a Combined Task Force (CTF) charged with enforcing its own no-fly zone above the 36th parallel in Iraq. Its mission began on 1 January 1997.
 W
WOperation Southern Watch was an air-centric military operation conducted by the United States Department of Defense from Summer 1992 to Spring 2003.
 W
WOperation Telic was the codename under which all of the United Kingdom's military operations in Iraq were conducted between the start of the Invasion of Iraq on 19 March 2003 and the withdrawal of the last remaining British forces on 22 May 2011. The bulk of the mission ended on 30 April 2009 but around 150 troops, mainly from the Royal Navy, remained in Iraq until 22 May 2011 as part of the Iraqi Training and Advisory Mission. 46,000 troops were deployed at the onset of the invasion and the total cost of war stood at £9.24 billion in 2010.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1472, adopted unanimously on 28 March 2003, after recalling all previous resolutions on Iraq, including resolutions 661 (1991), 986 (1995), 1409 (2002) and 1454 (2002) concerning the provision of humanitarian aid to the Iraqi people, the Council approved adjustments to the Oil-for-Food Programme giving the Secretary-General more authority to administer the programme for the following 45 days. The programme had been suspended when the Secretary-General ordered all United Nations staff out of Iraq days before the U.S.-led invasion.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1476, adopted unanimously on 24 April 2003, after recalling all previous resolutions on Iraq, including resolutions 661 (1991), 986 (1995), 1409 (2002), 1454 (2002) and 1472 (2003) concerning the provision of humanitarian aid to the Iraqi people, the Council extended the Oil-for-Food Programme until 3 June 2003.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1483, adopted on 22 May 2003, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation between Iraq and Kuwait, the Council lifted trade sanctions against Iraq and terminated the Oil-for-Food Programme.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1500, adopted on 14 August 2003, after reaffirming previous resolutions on Iraq, particularly Resolution 1483 (2003), the Council established the United Nations Assistance Mission in Iraq (UNAMI) and welcomed the creation of the Iraqi Governing Council.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1511 was adopted unanimously on 16 October 2003, after reaffirming previous resolutions on Iraq, particularly 1483 (2003), 1500 (2003), and Resolution 1373 (2001) on terrorism. The Council urged countries to contribute towards a multinational force to maintain security and called for power to be returned to the Iraqi people as soon as possible.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 1518, adopted unanimously on 24 November 2003, after reaffirming previous resolutions on Iraq, particularly 1483 (2003), the council established a committee to investigate financial assets removed from the country by persons connected to Saddam Hussein.
 W
WThe war on terror, also known as the Global War on Terrorism and U.S. War on Terror, is an international military campaign launched by the United States government after the September 11 attacks. The targets of the campaign are primarily Sunni Islamic fundamentalist armed groups located throughout the Muslim world, with the most prominent groups being Al-Qaeda, the Islamic State, the Taliban, Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan, and the various franchise groups of the former two organizations. The naming of the campaign uses a metaphor of war to refer to a variety of actions that do not constitute a specific war as traditionally defined. U.S. president George W. Bush first used the term "war on terrorism" on 16 September 2001, and then "war on terror" a few days later in a formal speech to Congress. In the latter speech, George Bush stated, "Our enemy is a radical network of terrorists and every government that supports them." The term was originally used with a particular focus on countries associated with al-Qaeda. The term was immediately criticised by such people as Richard B. Myers, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and more nuanced terms subsequently came to be used by the Bush administration to publicly define the international campaign led by the U.S. While it was never used as a formal designation of U.S. operations in internal government documentation, a Global War on Terrorism Service Medal was issued.
 W
WWMD conjecture in the aftermath of the 2003 invasion of Iraq concerns the immediate reactions and consequences to the failure by the United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission (UNMOVIC) and the U.S.-led Iraq Survey Group (ISG) to find the alleged stockpiles of weapons of mass destruction during and after 2003 invasion of Iraq. The United States effectively terminated the search effort for unconventional weaponry in January 2005, and the Iraq Intelligence Commission concluded that the judgements of the U.S. intelligence community about the continued existence of weapons of mass destruction and an associated military program were wrong. The official findings by the CIA in October 2004 were that Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein "did not possess stockpiles of illicit weapons at the time of the U.S. invasion in March 2003 and had not begun any program to produce them."