 W
WSpain played an important role in the independence of the United States, as part of its conflict with Britain. Spain declared war on Britain as an ally of France, itself an ally of the American colonies. Most notably, Spanish forces attacked British positions in the south and captured West Florida from Britain in the Siege of Pensacola. This secured the southern route for supplies and closed off the possibility of any British offensive through the western frontier of United States via the Mississippi River. Spain also provided money, supplies and munitions to the American forces.
 W
WThe Landing at Barcelona was a failed Allied attempt in May 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession to capture the city of Barcelona from its Spanish pro-Bourbon defenders.
 W
WThe Siege of Barcelona took place between 14 September and 19 October 1705 during the War of the Spanish Succession when a multinational Grand Alliance army led by Lord Peterborough, supporting the Habsburg pretender to the Spanish throne, captured the city of Barcelona from its Spanish Bourbonic defenders, most of whom then joined the Habsburg army.
 W
WThe Bourbon Reforms consisted of political and economical legislation promulgated by the Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon, since 1700, mainly in the 18th century. The beginning of the new Crown's power with clear lines of authority to officials contrasted to the complex system of government that evolved under the Habsburg monarchs. For example, the crown pursued state supremacy over the Catholic Church, pushed economic reforms, and placed power solely into the hands of civil officials.
 W
WThe Carvajal Ministry was a Spanish government which served between 1746 and 1754 during the reign of Ferdinand VI of Spain headed by José de Carvajal.
 W
WThe Casa de Contratación or Casa de la Contratación de las Indias was established by the Crown of Castile, in 1503 in the port of Seville as a crown agency for the Spanish Empire. It functioned until 1790, when it was abolished in a government reorganization. Before the establishment of the Council of the Indies in 1524, the Casa de Contratación had broad powers over overseas matters, especially financial matters concerning trade and legal disputes arising from it. It also was responsible for the licensing of emigrants, training of pilots, creation of maps and charters, probate of estates of Spaniards dying overseas. Its official name was La Casa y Audiencia de Indias.
 W
WThe First Cevallos expedition was a series military actions between September 1762 and April 1763, by Spanish colonial forces led by Don Pedro Antonio de Cevallos, Governor of Buenos Aires, against Portuguese colonial forces in the Banda Oriental area on the aftermath of the failed Spanish and French Invasion of Portugal, as part of the Seven Years' War.
 W
WThe term France–Habsburg rivalry describes the rivalry between France and the House of Habsburg. The Habsburgs headed an expansive and evolving Empire that included, at various times, the Holy Roman Empire, the Spanish Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire from the Diet of Augsburg in the High Middle Ages until the dissolution of the monarchy following the World War I in the Late modern period.
 W
WThe Capture of Gibraltar by Anglo-Dutch forces of the Grand Alliance occurred between 1 and 4 August 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. Since the beginning of the war the Alliance had been looking for a harbour in the Iberian Peninsula to control the Strait of Gibraltar and facilitate naval operations against the French fleet in the western Mediterranean Sea. An attempt to seize Cádiz had ended in failure in September 1702, but following the Alliance fleet's successful raid in Vigo Bay in October that year, the combined fleets of the 'Maritime Powers', the Netherlands and England, had emerged as the dominant naval force in the region. This strength helped persuade King Peter II of Portugal to sever his alliance with France and Bourbon-controlled Spain, and ally himself with the Grand Alliance in 1703 as the Alliance fleets could campaign in the Mediterranean using access to the port of Lisbon and conduct operations in support of the Austrian Habsburg candidate to the Spanish throne, the Archduke Charles, known to his supporters as Charles III of Spain.
 W
WThe Great Gypsy Round-up, also known as the general imprisonment of the gypsies, was a raid authorized and organized by the Spanish Monarchy that led to the arrest of all gypsies (Romani) in the region, and their imprisonment in labor camps. The raid was approved by the King Ferdinand VI of Spain, and organized by the Marquis of Ensenada, and set in motion simultaneously across Spain on July 30, 1749.
 W
WSpain entered a new era with the death of Charles II, the last Spanish Hapsburg monarch, who died childless in 1700. The War of the Spanish Succession was fought between proponents of a Bourbon prince, Philip of Anjou, and an Austrian Hapsburg claimant. With the Bourbon victory, Philip V's rule began in 1715. Spain entered a period of reform and renewal, as well as continued decline. Ideas of the Age of Enlightenment entered Spain and Spanish America during the eighteenth century. The invasion of the Iberian Peninsula by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807–1808 upended political arrangements of the Spanish Empire and the Portuguese Empire. The eighteenth century in Spanish historiography is often referred to as Bourbon Spain, but the Spanish Bourbons continued to reign from 1814–1868, from 1874–1931 and from 1975–present.
 W
WThe Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between the Spanish Empire, the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the fledgling United States of America triggered by a series of events that took place during the summer of 1789 at the Spanish outpost Santa Cruz de Nuca, in Nootka Sound, present-day British Columbia, Canada. The commander of the outpost, Jose Esteban Martínez, seized some British commercial ships which had come for the maritime fur trade and to build a permanent post at Nootka Sound. Public outcry in England led to the mobilization of the British and Spanish navies and the possibility of war. Both sides called upon allies, and although Spain's key ally France also mobilized their navy, they soon announced they would not go to war. Without French help Spain had little hope against the allied forces of the British and the Dutch, resulting in Spain seeking a diplomatic solution and making concessions.
 W
WThe Pacte de Famille is one of three separate, but similar alliances between the Bourbon kings of France and Spain. As part of the settlement of the War of the Spanish Succession that brought the House of Bourbon of France to the throne of Spain. Spain and France made a series of agreements that did not unite the two thrones, but did cooperate on defined bases.
 W
WPinckney's Treaty, also known as the Treaty of San Lorenzo or the Treaty of Madrid, was signed on October 27, 1795 by the United States and Spain.
 W
WManuel de Roda y Arrieta,, was Ambassador in Rome under King Ferdinand VI of Spain and then nominated by King Charles III of Spain, half-brother of Ferdinand VI and formerly King of Naples and Sicily till the death of his half-brother Ferdinand, Ministry of "Grace and Justice", which he held for 17 years.
 W
WThe Siege of Roses began on 28 November 1794 and lasted until 4 February 1795 when the Spanish garrison abandoned the port and the forces of the First French Republic took control. Dominique Catherine de Pérignon commanded the French army and Domingo Salvator Izquierdo led the Spanish defenders. The siege took place during the War of the Pyrenees which was part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The war ended in July 1795 and Roses was soon restored to Spain. Roses is a coastal city in northeastern Spain, located 43 kilometres (27 mi) northeast of Girona, Catalonia.
 W
WSpanish Baroque Painting refers to the style of painting which developed in Spain throughout the 17th century and the first half of the 18th century. The style appeared in early 17th century paintings, and arose in response to Mannerist distortions and idealisation of beauty in excess, appearing in early 17th century paintings. Its main objective was, above all, to allow the viewer to easily understand the scenes depicted in the works through the use of realism, while also meeting the Catholic Church's demands for 'decorum' during the Counter-Reformation.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of Oran and Mers el-Kebir took place from 15 June to 2 July 1732, between the Kingdom of Spain against the Ottoman protectorate of Algiers. The great Spanish expedition led by Don José Carrillo de Albornoz, Duke of Montemar and Don Francisco Javier Cornejo defeated the Ottoman-Muslim troops under the command of the Bey Hassan, and conquered the fortress-cities of Oran and Mers el-Kebir, ruled and administered by the Ottoman Empire from 1708, during the War of the Spanish Succession, when both cities, ruled by Spain, fell into the hands of the Ottoman Dey of Algiers.
 W
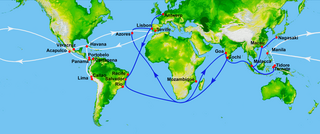
WThe Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet Spanish: Flota de Indias, was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction.
 W
WThe Spanish-Portuguese War between 1735-1737 was fought over the Banda Oriental, roughly present-day Uruguay.
 W
WThe suppression of the Jesuits was a politically instigated removal of all members of the Society of Jesus from most of the countries of Western Europe and their colonies, beginning in 1759, and ultimately approved by The Holy See in 1773. In 1814, Pope Pius VII restored the Society to its previous provinces and Jesuits began resuming their work in those countries.
 W
WThe Treaty of Hanover was a treaty of defensive alliance signed on 3 September 1725 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Electorate of Hanover, the Kingdom of France, and the Kingdom of Prussia. The alliance was formed to combat the power of the Austro-Spanish alliance founded at the Peace of Vienna months earlier in May 1725.
 W
WThe War of Jenkins' Ear was a conflict between Britain and Spain lasting from 1739 to 1748, mainly in New Granada and among the West Indies of the Caribbean Sea, with major operations largely ended by 1742. Its name, coined by British historian Thomas Carlyle in 1858, refers to Robert Jenkins, a captain of a British merchant ship, who suffered having his ear severed when Spanish sailors boarded his ship at a time of peace. There is no evidence that supports the stories that the severed ear was exhibited before the British Parliament.