 W
WThe 1973 Ice Hockey World Championships were the 40th Ice Hockey World Championships and the 51st European Championships of ice hockey. The tournament took place in the Soviet Union from 31 March to 15 April and the games were played at the Palace of Sports of the Central Lenin Stadium in Moscow.
 W
WThe 20th European Athletics Indoor Championships were held at Houtrust in The Hague, Netherlands, on 18 and 19 February 1989.
 W
WThe 1993 World Games, the fourth World Games, were an international multi-sport event held in The Hague, Netherlands.
 W
WThe 1994 FEI World Equestrian Games were held in The Hague, Netherlands from July 27 to August 7, 1994. They were the second edition of the games which are held every four years and run by the FEI.
 W
WThe Hague Convention Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents, the Apostille Convention, or the Apostille Treaty, is an international treaty drafted by the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It specifies the modalities through which a document issued in one of the signatory countries can be certified for legal purposes in all the other signatory states. A certification under the terms of the convention is called an apostille or Hague apostille. It is an international certification comparable to a notarisation in domestic law, and normally supplements a local notarisation of the document. If the convention applies between two countries, such an apostille is sufficient to certify a document's validity, and removes the need for double-certification, by the originating country and then by the receiving country.
 W
WThe Battle for The Hague was a battle fought on 10 May 1940 during the German invasion of the Netherlands. German Fallschirmjäger units were dropped in and around The Hague in order to capture Dutch airfields and the city itself.
 W
WThe bombing of the Bezuidenhout took place on 3 March 1945, when the Royal Air Force mistakenly bombed the Bezuidenhout neighbourhood in the Dutch city of The Hague. At the time, the neighbourhood was more densely populated than usual with evacuees from The Hague and Wassenaar; tens of thousands were left homeless and had to be quartered in the Eastern and Central Netherlands.
 W
WThe Hague Congress or the Congress of Europe, considered by many as the first federal moment of the European history, was held in The Hague from 7–11 May 1948 with 750 delegates participating from around Europe as well as observers from Canada and the United States of America.
 W
WThe Dutch–Indonesian Round Table Conference was held in The Hague from 23 August to 2 November 1949, between representatives of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Republic of Indonesia and the Federal Consultative Assembly, representing various states the Dutch had created in the Indonesian archipelago.
 W
WThe Eurovision Song Contest 1976 was the 21st edition of the Eurovision Song Contest. It was hosted by NOS and held in The Hague, Netherlands. The arena for the event was the Nederlands Congrescentrum. Teach-In's victory in Stockholm the previous year gave The Netherlands the right to host the contest for the third time. The Contest was won by Brotherhood of Man, who sang "Save Your Kisses for Me" in English, representing the United Kingdom.
 W
WThe Eurovision Song Contest 1980 was the 25th Eurovision Song Contest and was held on 19 April 1980 in The Hague. The presenter was Marlous Fluitsma, although each song was introduced by a presenter from the participating nation. In some cases, this was the same person providing the commentary. The contest was won by Johnny Logan, representing Ireland with a song called "What's Another Year".
 W
WThe 1974 French Embassy attack in The Hague was an attack and siege on the French Embassy in The Hague in the Netherlands starting on Friday 13 September 1974. Three members of the Japanese Red Army (JRA) stormed the embassy, allegedly on the orders of their leader Fusako Shigenobu, demanding the release of their member Yatsuka Furuya. The ambassador and ten other people were taken hostage. The siege and negotiations lasted five days, resulting in the release of Furuya, the embassy hostages and a safe flight out of the Netherlands for the terrorists. During the incident, a café in Paris was bombed which was linked to the embassy crisis.
 W
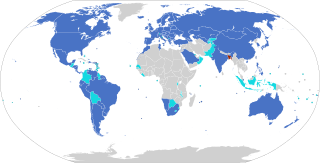
WThe Hague Convention on Protection of Children and Co-operation in Respect of Intercountry Adoption is an international convention dealing with international adoption, child laundering, and child trafficking in an effort to protect those involved from the corruption, abuses, and exploitation which sometimes accompanies international adoption. The Convention has been considered crucial because it provides a formal international and intergovernmental recognition of intercountry adoption to ensure that adoptions under the Convention will generally be recognized and given effect in other party countries.
 W
WThe Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict is the first international treaty that focuses exclusively on the protection of cultural property in armed conflict. It was signed at The Hague, Netherlands, on 14 May 1954 and entered into force on 7 August 1956. As of September 2018, it has been ratified by 133 states.
 W
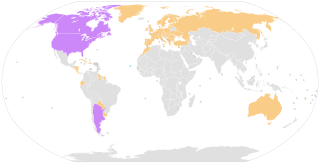
WThe Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction or Hague Abduction Convention is a multilateral treaty developed by the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH) that provides an expeditious method to return a child internationally abducted by a parent from one member country to another.
 W
WThe Hague Convention on parental responsibility and protection of children, or Hague Convention 1996, officially Convention of 19 October 1996 on Jurisdiction, Applicable Law, Recognition, Enforcement and Co-operation in respect of Parental Responsibility and Measures for the Protection of Children or Hague Convention 1996 is a convention of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It covers civil measures of protection concerning children, ranging from orders concerning parental responsibility and contact to public measures of protection or care, and from matters of representation to the protection of children's property. It is therefore much broader in scope than two earlier conventions of the HCCH on the subject.
 W
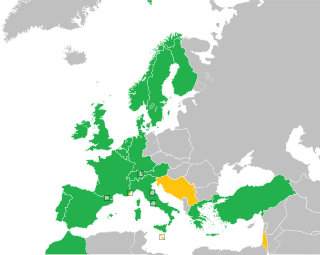
WThe Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place due to the start of World War I.
 W
WThe Convention on the Taking of Evidence Abroad in Civil or Commercial Matters—more commonly referred to as the Hague Evidence Convention—is a multilateral treaty which was drafted under the auspices of the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCPIL). The treaty was negotiated in 1967 and 1968 and signed in The Hague on 18 March 1970. It entered into force in 1972. It allows transmission of letters of request from one signatory state to another signatory state without recourse to consular and diplomatic channels. Inside the US, obtaining evidence under the Evidence Convention can be compared to comity.
 W
WThe Convention on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters, more commonly called the Hague Service Convention, is a multilateral treaty which was adopted in The Hague, The Netherlands, on 15 November 1965 by member states of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It came into existence to give litigants a reliable and efficient means of serving the documents on parties living, operating or based in another country. The provisions of the convention apply to service of process in civil and commercial matters but not criminal matters. Also, Article 1 states that the Convention shall not apply if the address of the person to be served with the document is not known.
 W
WThe Hague Convention on the Law Applicable to Trusts and on their Recognition, or Hague Trust Convention is a multilateral treaty developed by the Hague Conference on Private International Law on the Law Applicable to Trusts. It concluded on 1 July 1985, entered into force 1 January 1992, and is as of September 2017 ratified by 14 countries. The Convention uses a harmonised definition of a trust, which is the subject of the convention, and sets Conflict rules for resolving problems in the choice of the applicable law. The key provisions of the Convention are:each party recognises the existence and validity of trusts. However, the Convention only relates to trusts with a written trust instrument. It would not apply trusts which arise without a written trust instrument. the Convention sets out the characteristics of trusts under the convention the Convention sets out clear rules for determining the governing law of trusts with a cross border element.
 W
WThe International Opium Convention, signed at The Hague on January 23, 1912 during the First International Opium Conference, was the first international drug control treaty. It was registered in League of Nations Treaty Series on January 23, 1922. The United States convened a 13-nation conference of the International Opium Commission in 1909 in Shanghai, China, in response to increasing criticism of the opium trade. The treaty was signed by Germany, the United States, China, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Persia, Portugal, Russia, and Siam. The Convention provided, "The contracting Powers shall use their best endeavours to control, or to cause to be controlled, all persons manufacturing, importing, selling, distributing, and exporting morphine, cocaine, and their respective salts, as well as the buildings in which these persons carry such an industry or trade."
 W
WThe Pension de Vogel homeless hostel fire took place at the Scheepmakersstraat 22 in The Hague in the Netherlands on 16 September 1992. After an occupant set a fire 11 people died and 15 people were injured.
 W
WSir Richard Adam Sykes, was the British Ambassador to the Netherlands, who was assassinated by the IRA in The Hague in 1979.