 W
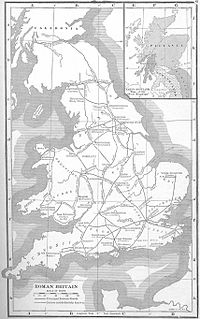
WHillforts in Britain refers to the various hillforts within the island of Great Britain. Although the earliest such constructs fitting this description come from the Neolithic British Isles, with a few also dating to later Bronze Age Britain, British hillforts were primarily constructed during the British Iron Age. Some of these were apparently abandoned in the southern areas that were a part of Roman Britain, although at the same time, those areas of northern Britain that remained free from Roman occupation saw an increase in their construction. Some hillforts were reused in the Early Middle Ages, and in some rarer cases, into the Later Medieval period as well. By the early modern period, these had essentially all been abandoned, with many being excavated by archaeologists in the nineteenth century onward.
 W
WPrehistoric Wales in terms of human settlements covers the period from about 230,000 years ago, the date attributed to the earliest human remains found in what is now Wales, to the year AD 48 when the Roman army began a military campaign against one of the Welsh tribes. Traditionally, historians have believed that successive waves of immigrants brought different cultures into the area, largely replacing the previous inhabitants, with the last wave of immigrants being the Celts. However, studies of population genetics now suggest that this may not be true, and that immigration was on a smaller scale.
 W
WThe Battersea Shield is one of the most significant pieces of ancient Celtic art found in Britain. It is a sheet bronze covering of a wooden shield decorated in La Tène style. The shield is on display in the British Museum, and a replica is housed in the Museum of London.
 W
WThe Britons also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were indigenous Celtic people who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age into the Middle Ages, at which point their culture and language diverged into the modern Welsh, Cornish and Bretons. They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor to the modern Brittonic languages.
 W
WThe Brittonic, Brythonic or British Celtic languages are alleged to form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. The name Brythonic was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word Brython, meaning Ancient Britons as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael.
 W
WButser Ancient Farm is an archaeological open-air museum located near Petersfield in Hampshire, southern England. Butser features experimental reconstructions of prehistoric, Romano-British and Anglo-Saxon buildings. Examples of Neolithic dwellings, Iron Age roundhouses, a Romano-British villa and an early Saxon house are on display. The site is used as both a tourist attraction and a site for the undertaking of experimental archaeology. In this latter capacity, it was designed so that archaeologists could learn more about the agricultural and domestic economy in Britain during the millennium that lasted from circa 400 BCE to 400 CE, in what was the Late British Iron Age and Romano-British periods.
 W
WCeltic field is an old name for traces of early (prehistoric) agricultural field systems found in North-West Europe, i.e. Britain, Ireland, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, France, Sweden, Poland and the Baltic states. The fields themselves are not related to the Celtic culture.
 W
WThe Insular Celts are the speakers of the Insular Celtic languages, which comprise all the living Celtic languages as well as their precursors, which originated in Great Britain and Ireland. The term is mostly used in reference to the peoples of the British Iron Age prior to the Roman conquest, and their contemporaries in Ireland.
 W
WA cross dyke or cross-dyke is a linear earthwork believed to be a prehistoric land boundary that usually measures between 0.2 and 1 kilometre in length. A typical cross dyke consists of one or more ditches running in parallel with one or more raised banks. Univallate cross dykes typically have a flat-bottomed ditch while the ditches of multivallate cross dykes possess a V-shaped cross-section. A defining characteristic of a cross dyke is that it cuts across the width of an upland ridge or the neck of an upland spur. Cross dykes generally occur at altitudes over 150 metres (490 ft) above mean sea level.
 W
WDinas Emrys is a rocky and wooded hillock near Beddgelert in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. Rising some 76 m (250 ft) above the floor of the Glaslyn river valley, it overlooks the southern end of Llyn Dinas in Snowdonia.
 W
WFfridd Faldwyn is an Iron Age Hillfort in northern Powys, in the former county of Montgomeryshire, It is sited on a prominent hill west of Montgomery, close to but higher than Montgomery Castle, overlooking the River Severn. It is one of the largest hill-forts in Wales.
 W
WA fogou or fougou is an underground, dry-stone structure found on Iron Age or Romano-British-defended settlement sites in Cornwall. The original purpose of a fogou is uncertain today. Colloquially called vugs, vows, foggos, giant holts, or fuggy holes in various dialects, fogous have similarities with souterrains or earth-houses of northern Europe and particularly Scotland, including Orkney. Fewer than 15 confirmed fogous have been found.
 W
WGarn Boduan is an Iron Age hillfort and hill near Nefyn, on the Llŷn Peninsula in Wales.
 W
WHasholme logboat is a late Iron Age boat discovered at Hasholme, an area of civil parish of Holme-on-Spalding-Moor in the East Riding of the English county of Yorkshire. It is now on display in the Hull and East Riding Museum, in Hull.
 W
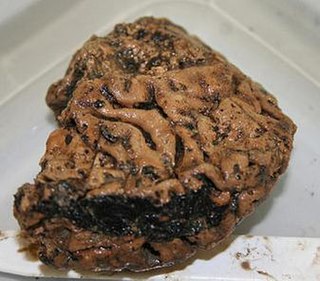
WThe Heslington Brain is a 2,600-year-old human brain found inside a skull buried in a pit in Heslington, Yorkshire, in England, by York Archaeological Trust in 2008. It is the oldest preserved brain ever found in Eurasia, and is believed to be the best-preserved ancient brain in the world. The skull was discovered during an archaeological dig commissioned by the University of York on the site of its new campus on the outskirts of the city of York. The area was found to have been the site of well-developed permanent habitation between 2,000–3,000 years before the present day.
 W
WLindow Man, also known as Lindow II and as Pete Marsh, is the preserved bog body of a man discovered in a peat bog at Lindow Moss near Wilmslow in Cheshire, North West England. The remains were found on 1 August 1984 by commercial peat cutters. Lindow Man is not the only bog body to have been found in the moss; Lindow Woman was discovered the year before, and other body parts have also been recovered. The find was described as "one of the most significant archaeological discoveries of the 1980s" and caused a media sensation. It helped invigorate study of British bog bodies, which had previously been neglected.
 W
WLlyn Fawr is a lake occupying a glacial cirque in the northern escarpment of the South Wales Coalfield uplands overlooking the heads of the Vale of Neath and the Cynon Valley, South Wales. It is known as the site of an important hoard of weapons and tools from the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age. It lies within Craig-y-Llyn an area that is designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest.
 W
WThe Meyrick Helmet is an Iron Age bronze peaked helmet, with La Tène style decoration, that is held at the British Museum in London. It is one of only four Iron Age helmets to have been discovered in Britain, the other three being the more famous Waterloo Helmet, the Canterbury Helmet and the North Bersted Warrior helmet. Unlike the Waterloo Helmet, which bears two cone-shaped horns, the Meyrick Helmet is hornless and appears to be based on a Roman model. Vincent Megaw, emeritus professor of archaeology at the University of Leicester, has conjectured that the helmet may have belonged to a British auxiliary fighting in the Roman army during the campaigns against the Brigantes in AD 71–74.
 W
WThe Newark Torc is a complete Iron Age gold alloy torc found by a metal detectorist on the outskirts of Newark-on-Trent, Nottinghamshire, England, in February 2005.
 W
WPen y Gaer is the location of a Bronze Age and Iron Age hillfort near the village of Llanbedr-y-Cennin in the Conwy valley, Wales.
 W
WPytheas of Massalia was a Greek geographer and explorer from the Greek colony of Massalia. He made a voyage of exploration to northwestern Europe in about 325 BC, but his account of it, known widely in Antiquity, has not survived and is now known only through the writings of others.
 W
WThe Roman conquest of Britain was a gradual process, beginning in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius and being largely completed by 87 when the Stanegate was established as the northern frontier.
 W
WRoundton Hill is a rounded, steep sided, 1,210 feet (370 m) hill, volcanic in origin, in the easternmost part of old Montgomeryshire, Wales, which juts into the English border near Church Stoke. It is managed as a nature reserve by the Montgomeryshire Wildlife Trust, who acquired it in 1985.
 W
WThe Mynde is a historic site and property located in Caerleon on the northern outskirts of the city of Newport. The town is the historic site of the Isca Augusta Roman Fortress.
 W
WThe Wandsworth Shield is a circular bronze Iron Age shield boss or mount decorated in La Tène style which was found in the River Thames at Wandsworth in London sometime before 1849. Another incomplete bronze shield mount, sometimes called the Wandsworth Mask Shield was found at the same time. Both shield mounts are now held at the British Museum. The bold repoussé decoration on the Wandsworth Shield, comprising two birds with outstretched wings and long trailing tail feathers, has led Barry Cunliffe, Emeritus Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, to consider the shield to be "among the masterpieces of British Celtic art".
 W
WThe Waterloo Helmet is a pre-Roman Celtic bronze ceremonial horned helmet with repoussé decoration in the La Tène style, dating to circa 150–50 BC, that was found in 1868 in the River Thames by Waterloo Bridge in London, England. It is now on display at the British Museum in London.