 W
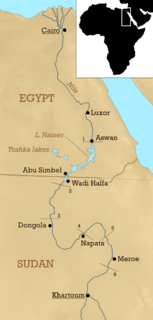
WNubia is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, or more strictly, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC. Nubia was home to several empires, most prominently the kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in eighth-century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its 25th Dynasty.
 W
WAbu Simbel is a village in the Egyptian part of Nubia, about 240 km (150 mi) southwest of Aswan and near the border with Sudan. As of 2012, it has about 2600 inhabitants. It is best known as the site of the Abu Simbel temples, which were built by King Ramses II.
 W
WAlodia, also known as Alwa, was a medieval Nubian kingdom in what is now central and southern Sudan. Its capital was the city of Soba, located near modern-day Khartoum at the confluence of the Blue and White Nile rivers.
 W
WThe Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is the world's largest embankment dam built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan Low Dam initially completed in 1902 downstream. Based on the success of the Low Dam, then at its maximum utilization, construction of the High Dam became a key objective of the government following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952; with its ability to better control flooding, provide increased water storage for irrigation and generate hydroelectricity the dam was seen as pivotal to Egypt's planned industrialization. Like the earlier implementation, the High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy and culture of Egypt.
 W
WBatn-El-Hajar or Belly of Stones is a reach of approximately 160 km in length stretching from the Dal Cataract of the Nile downriver to the now under Lake Nubia submerged Second Cataract in present-day Sudan.
 W
WThe Cataracts of the Nile are shallow lengths of the Nile River, between Khartoum and Aswan, where the surface of the water is broken by many small boulders and stones jutting out of the river bed, as well as many rocky islets. In some places, these stretches are punctuated by whitewater, while at others the water flow is smoother, but still shallow.
 W
WDar al-Manasir is the region of the Fourth Cataract, the most impassable of all rapids of the Nile. It is the homeland of the Arab tribe of the Manasir and from them gets its name. Still today the water rapids cannot be crossed by any large boats making the region accessible only via a sandy and rocky desert track.
 W
WDebeira is an archaeological site in Sudan situated on the eastern bank of the Nile some 20 kilometres north of Wadi Halfa.
 W
WThe Dongola Reach is a reach of approximately 160 km in length stretching from the Fourth downriver to the Third Cataracts of the Nile in Upper Nubia, Sudan. Named after the Sudanese town of Dongola which dominates this part of the river, the reach was the heart of ancient Nubia.
 W
WFaras Cathedral was a cathedral in the Lower Nubian city of Faras. Nobadian rulers controlling the Nile Valley from the first to the third cataracts converted to Christianity around 548 AD influenced by missionaries sent from Constantinople by the Empress Theodora. The first cathedral was erected in the 7th century, when the city was still known as Pachoras, and likely stood at the exact site where Polish archaeologists taking part in the Nubia Campaign discovered the subsequent 8th century cathedral. The site was excavated by Polish archaeologists under Kazimierz Michalowski between 1960 and 1964.
 W
WHamadab is an ancient city of ruins located in Sudan. It appears to have been abandoned 4th century AD. The name is borrowed from the nearby village of al Dumat Hamadab, as the ancient name of the city is initially unknown. The ruins lie about 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) south of Meroë. They consist of two hills, 200 by 250 metres in width and length, one being 500 metres (1,600 ft) in height, and the other being half of that. The two hills are separated from each other within the Nile. In 1914, a temple was excavated northeast of the settlement; it included pillars dedicated to Queen Amanirenas and her son, Akinidad. While Amun is suspected, it is unknown which god was worshiped in the temple. Other excavations have occurred since 2001. They revealed mud brick built houses surrounded by a wall.
 W
WJebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal is a very small mountain located some 400 km north of Khartoum, in Karima town in Northern State in Sudan, on a large bend of the Nile River, in the region called Nubia. The mountain is 98 m tall, has a flat top, and apparently was used as a landmark by the traders in the important route between central Africa, Arabia, and Egypt, as the point where it was easier to cross the great river. In 2003, the mountain, together with the historical city of Napata, were named World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. The Jebel Barkal area houses the Jebel Barkal Museum. The Jebel Barkal pyramids are one example of Nubian pyramids.
 W
WKawa is a site in Sudan, located between the Third and Fourth Cataracts of the Nile on the east bank of the river, across from Dongola. In ancient times it was the site of several temples to the Egyptian god Amun, built by the Egyptian rulers Amenhotep III and Tutankhamun, and by Taharqa and other Kushite kings.
 W
WThe Kerma culture or Kerma kingdom was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BCE to 1500 BCE in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia", and later extended its reach northward into Lower Nubia and the border of Egypt. The polity seems to have been one of a number of Nile Valley states during the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. In the Kingdom of Kerma's latest phase, lasting from about 1700–1500 BCE, it absorbed the Sudanese kingdom of Sai and became a sizable, populous empire rivaling Egypt. Around 1500 BCE, it was absorbed into the New Kingdom of Egypt, but rebellions continued for centuries. By the eleventh century BCE, the more-Egyptianized Kingdom of Kush emerged, possibly from Kerma, and regained the region's independence from Egypt.
 W
WThe kissar, Tanbour or Gytarah barbaryeh, the ancient Nubian lyre, still in use in Egypt, Sudan and Abyssinia. It consists of a body having instead of the traditional tortoise-shell back, a shallow, round bowl of wood, covered with a soundboard of sheepskin, in which are three small round sound-holes. The arms, set through the soundboard at points distant about the third of the diameter from the circumference, have the familiar fan shape. Five gut strings, knotted round the bar and raised from the soundboard by means of a bridge tailpiece similar to that in use on the modern guitar, are plucked by means of a plectrum by the right hand for the melody, while the left hand sometimes twangs some of the strings as a soft drone accompaniment.
 W
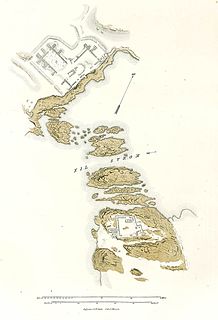
WKumma or Semna East is an archaeological site in Sudan. Established in the mid-12th Dynasty of Egypt, it served as a fortress of ancient Egypt in Nubia. Along with Semna, Kumma was built by the Pharaoh Sesostris III. The forts protected the border between ancient Egypt and the southern areas.
 W
WMakuria was a Nubian kingdom located in what is today Northern Sudan and Southern Egypt. Makuria originally covered the area along the Nile River from the Third Cataract to somewhere south of Abu Hamad as well as parts of northern Kordofan. Its capital was Dongola, and the kingdom is sometimes known by the name of its capital.
 W
WMeinarti was an island with a Nubian village in northern Sudan. Situated in the Nile, Meinarti was just north of the 2nd Cataract, a few kilometers upstream of the Sudanese border town of Wadi Halfa. On the island was an artificial mount 175m long and 12.5m high, consisting of stratified archaeological remains. When excavated it proved to contain 18 recognizable levels, the result of six separate and distinct phases of occupation. Each phase was followed by a period of abandonment and then a complete rebuilding. Structural remains at all phases were entirely of mud brick. Meinarti was excavated by William Yewdale Adams from 1962 to 1964, prior to perishing in the 1960s with the rising of Lake Nubia due to the Aswan Dam.
 W
WThe Monastery in Ghazali is a medieval Christian monastery in the Bayuda Desert in northern Sudan. Probably founded by the Makurian king Merkurios in the late 7th century, it functioned until the 13th century.
 W
WThe Nubian Desert is in the eastern region of the Sahara Desert, spanning approximately 400,000 km2 of northeastern Sudan and northern Eritrea, between the Nile and the Red Sea. The arid region is rugged and rocky and contains some dunes, it also contains many wadis that die out before reaching the Nile. The average annual rainfall in the Nubian Desert is less than 5 inches (130 mm).
 W
WThe Sabu-Jaddi rock art site in Sudan is a unique cluster of more than 1600 rock drawings from different historical periods expanding for more than 6000 years through different eras of Nubian civilization. The site is located 600 km north of Khartoum between the villages of Sabu and Jaddi. The well-preserved drawings include wild and domestic animals, humans and boats.
 W
WSoba is an archaeological site and former town in what is now central Sudan. Three kingdoms existed in medieval Nubia: Nobadia with the capital in Faras, Makuria with the capital in Dongola, and Alodia (Alwa) with the capital in Soba. The latter used to be the capital of the medieval Nubian kingdom of Alodia from the sixth century until around 1500. E. A. Wallis Budge identified it with a group of ruins on the Blue Nile 19 kilometres (12 mi) from Khartoum, where there are remains of a Meroitic temple that had been converted into a Christian church.
 W
WThe Temple of Amun is an archaeological site at Jebel Barkal in Northern State, Sudan. It is situated about 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of Khartoum near Karima. The temple stands near a large bend of the Nile River, in the region that was called Nubia in ancient times. The Temple of Amun, one of the largest temples at Jebel Barkal, is considered sacred to the local population. Not only was the Amun temple a main centre of what at one time was considered to be an almost universal religion, but, along with the other archaeological sites at Jebel Barkal, it was representative of the revival of Egyptian religious values. Up to the middle of the 19th century, the temple was subjected to vandalism, destruction, and indiscriminate plundering, before it came under state protection.
 W
WThe Temple of Mut, also named Temple B300, is a temple at Jebel Barkal in Northern State, Sudan. It is situated about 400 km north of Khartoum near Karima and stands near a large bend of the Nile River, in the region that was called Nubia in ancient times. The partially rock-cut temple was built on the west side base of the Jebel Barkal pinnacle, from which angle it assumed the shape of an Uraeus wearing the White Crown of Upper Egypt. Dedicated to the goddess Mut, the wife of Amun, the Temple of Mut was erected by pharaoh Taharqa in the 680s BCE, at a time when he ruled Upper and Lower Egypt.
 W
WThe Triakontaschoinos, Latinized as Triacontaschoenus, was a geographical and administrative term used in the Greco-Roman world for the part of Lower Nubia between the First and Second Cataracts of the Nile, which formed a buffer zone between Egypt and later Rome on the one hand and Meroe on the other hand. The northern part of this area, stretching from the First Cataract south to Maharraqa was known as the Dodekaschoinos or Dodecaschoenus. In the Ptolemaic and Roman periods the Dodekaschoinos was often annexed to Egypt or controlled from it, and the rest of the Triakontaschoinos sometimes was as well.
 W
WThe X-Group Culture was an ancient civilization that existed from ca. 300 CE to ca. 600 CE. It was centered in Nubia stretching from the Dodekaschoinos in the north to Delgo in the south. George A. Reisner, who first discovered their civilization, used the term X-Group Culture for lack of a more exact historical definition.