 W
WApollo 5, was the first uncrewed flight of the Apollo Lunar Module (LM), which would later carry astronauts to the lunar surface. It lifted off on January 22, 1968, with a Saturn IB rocket on an Earth-orbital flight.
 W
WApollo 6, launched on April 4, 1968, was the second A-type mission of the United States Apollo program, an uncrewed test of the Saturn V launch vehicle. It was also the final uncrewed Apollo test mission.
 W
WApollo 7 was an October 1968 space mission carried out by the United States. It was the first crewed flight in NASA's Apollo program, and saw the resumption of human spaceflight by the agency after the fire that killed the three Apollo 1 astronauts in January 1967. The Apollo 7 crew was commanded by Walter M. Schirra, with command module pilot Donn F. Eisele and lunar module pilot R. Walter Cunningham.
 W
WApollo 8 was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit and the first to reach the Moon, orbit it, and return. Its three-astronaut crew — Frank Borman, James Lovell, and William Anders — were the first humans to fly to the Moon, to witness and photograph an Earthrise, and to escape the gravity of a celestial body.
 W
WThe Byodo-In Temple is a non-denominational Buddhist temple located on the island of Oʻahu in Hawaiʻi in Valley of the Temples Memorial Park. It was dedicated in August 1968 to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the first Japanese immigrants to Hawaiʻi.
 W
WThe Consumer Credit Protection Act (CCPA) is a United States law Pub.L. 90–321, 82 Stat. 146, enacted May 29, 1968, composed of several titles relating to consumer credit, mainly title I, the Truth in Lending Act, title II related to extortionate credit transactions, title III related to restrictions on wage garnishment, and title IV related to the National Commission on Consumer Finance.
 W
WThe Dugway sheep incident, also known as the Skull Valley sheep kill, was a 1968 sheep kill that has been connected to United States Army chemical and biological warfare programs at Dugway Proving Ground in Utah. Six thousand sheep were killed on ranches near the base, and the popular explanation blamed Army testing of chemical weapons for the incident, though alternative explanations have been offered. A report, commissioned by Air Force Press Officer Jesse Stay and first made public in 1998, was called the "first documented admission" from the Army that a nerve agent killed the sheep at Skull Valley.
 W
WIn 1968, the United States FBI, under Director J. Edgar Hoover, continued for a nineteenth year to maintain a public list of the people it regarded as the Ten Most Wanted Fugitives.
 W
WThe Foreign Military Sales Act of 1968, Pub.L. 90–629, 82 Stat. 1320-2, enacted October 22, 1968, was supplemental legislation to the Arms Control and Disarmament Act of 1961 and the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961. The Act discloses the United States commitment and sustainment to a world free from the dangers of armaments and the scourge of war.
 W
WHemisFair '68 was the official 1968 World's Fair held in San Antonio, Texas, from April 6 through October 6, 1968. The theme of the fair was "The Confluence of Civilizations in the Americas", celebrating the many nations which settled the region. The fair was held in 1968 to coincide with the 250th anniversary of the founding of San Antonio in 1718. More than thirty nations and fifteen corporations hosted pavilions at the fair.
 W
W"I've Been to the Mountaintop" is the popular name of the last speech delivered by Martin Luther King Jr.
 W
WThe National Advisory Commission on Civil Disorders, known as the Kerner Commission after its chair, Governor Otto Kerner Jr. of Illinois, was an 11-member Presidential Commission established by President Lyndon B. Johnson in Executive Order 11365 to investigate the causes of the 1967 race riots in the United States and to provide recommendations for the future.
 W
WThe King-assassination riots, also known as the Holy Week Uprising, was a wave of civil disturbance which swept the United States following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. on April 4, 1968. Many believe it to be the greatest wave of social unrest the United States had experienced since the Civil War. Some of the biggest riots took place in Washington, D.C., Baltimore, Chicago, and Kansas City.
 W
WMartin Luther King Jr., an American clergyman and civil rights leader, was fatally shot at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, on April 4, 1968, at 6:01 p.m. CST. He was rushed to St. Joseph's Hospital, where he died at 7:05 p.m. He was a prominent leader of the civil rights movement and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate who was known for his use of nonviolence and civil disobedience.
 W
WIn the "Plato's Stepchildren" season 3 episode 10 of Star Trek: The Original Series, first broadcast November 22, 1968, Uhura and Captain Kirk kiss. The episode is popularly cited as containing the first example of a scripted interracial kiss on United States television, although other previous instances have since come to light.
 W
WMiss America 1969, the 42nd Miss America pageant, was held at the Boardwalk Hall in Atlantic City, New Jersey on September 7, 1968 on NBC Network. Miss Illinois was the winner, Judith Ford performing on a trampoline during the talent competition of the pageant. She later became a physical education teacher at an elementary school.
 W
WThe Miss America protest was a demonstration held at the Miss America 1969 contest on September 7, 1968, attended by about 200 feminists and civil rights advocates. The feminist protest was organized by New York Radical Women and included putting symbolic feminine products into a "Freedom Trash Can" on the Atlantic City boardwalk, including bras, hairspray, makeup, girdles, corsets, false eyelashes, mops, and other items. The protesters also unfurled a large banner emblazoned with "Women's Liberation" inside the contest hall, drawing worldwide media attention to the Women's Liberation Movement.
 W
WThe National Trails System was created by the National Trails System Act, codified at 16 U.S.C. § 1241 et seq.
 W
WDuring their medal ceremony in the Olympic Stadium in Mexico City on October 16, 1968, two African-American athletes, Tommie Smith and John Carlos, each raised a black-gloved fist during the playing of the US national anthem, "The Star-Spangled Banner". While on the podium, Smith and Carlos, who had won gold and bronze medals respectively in the 200-meter running event of the 1968 Summer Olympics, turned to face the US flag and then kept their hands raised until the anthem had finished. In addition, Smith, Carlos, and Australian silver medalist Peter Norman all wore human-rights badges on their jackets.
 W
WThe United States's Bowline nuclear test series was a group of 47 nuclear tests conducted in 1968–1969. These tests followed the Operation Crosstie series and preceded the Operation Mandrel series.
 W
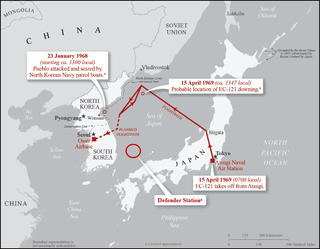
WOn 23 January 1968 North Korean patrol boats supported by two Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 fighters captured the USS Pueblo northeast of the North Korean island of Ung-do. The seizure of the Pueblo led to President Lyndon Johnson ordering a show of force with a massive deployment of U.S. air and navy assets to Korea. The airlift and deployment of 200+ aircraft was code named Operation Combat Fox while the deployment of six aircraft carriers plus support vessels was code named Operation Formation Star. The operations were supported by the partial mobilization of reservists for the first time since the Cuban Missile Crisis. CIA A-12 Oxcart reconnaissance overflights over North Korea were used to monitor a feared retaliatory mobilization of North Korean forces and when these flights revealed no mobilization or large scale deployments by North Korean forces, Operation Combat Fox forces were stood down.
 W
WOperation Formation Star was the code name for the emergency re-deployment of U.S. Seventh Fleet warships to the Sea of Japan off the eastern coast of North Korea following that country's seizure of the USS Pueblo (AGER-2) in international waters on 23 January 1968.
 W
WUSS Pueblo (AGER-2) is a Banner-class environmental research ship, attached to Navy intelligence as a spy ship, which was attacked and captured by North Korean forces on 23 January 1968, in what is known today as the "Pueblo incident" or alternatively, as the "Pueblo crisis".
 W
WUSS Scorpion (SSN-589) was a Skipjack-class nuclear powered submarine that served in the United States Navy and the sixth vessel of the U.S. Navy to carry that name.
 W
WPHASE II of the Tet Offensive of 1968 was launched by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and Viet Cong (VC) against targets throughout South Vietnam, including Saigon from 29 April to 30 May 1968. The May Offensive was considered much bloodier than the initial phase of the Tet Offensive. US casualties across South Vietnam were 2,169 killed for the entire month of May making it the deadliest month of the entire Vietnam War for U.S. forces, while South Vietnamese losses were 2,054 killed. PAVN/VC losses exceeded 24,000 killed and over 2,000 captured. The May Offensive was a costly defeat for the PAVN/VC.
 W
WOn 21 January 1968, an aircraft accident ; Danish: Thuleulykken) involving a United States Air Force (USAF) B-52 bomber occurred near Thule Air Base in the Danish territory of Greenland. The aircraft was carrying four B28FI thermonuclear bombs on a Cold War "Chrome Dome" alert mission over Baffin Bay when a cabin fire forced the crew to abandon the aircraft before they could carry out an emergency landing at Thule Air Base. Six crew members ejected safely, but one who did not have an ejection seat was killed while trying to bail out. The bomber crashed onto sea ice in North Star Bay, Greenland, causing the conventional explosives aboard to detonate and the nuclear payload to rupture and disperse, resulting in radioactive contamination of the area.
 W
WThe Truth in Lending Act (TILA) of 1968 is a United States federal law designed to promote the informed use of consumer credit, by requiring disclosures about its terms and cost to standardize the manner in which costs associated with borrowing are calculated and disclosed.